Diversity Unit 1 review Which of the following statements about
advertisement

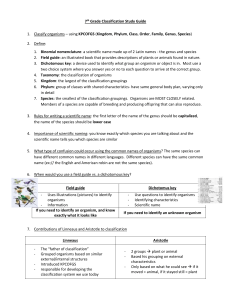
Diversity Unit 1 review 1. Which of the following statements about prokaryotes is false? a. They possess circular DNA that is not bound by a membrane b. Many species of bacteria are anaerobic c. They perform both mitosis and meiosis d. They do not possess membrane-bound organelles 2. Which two organisms are most closely related? a. Organisms in the same Genus but different Species b. Organisms in the same Phylum and different Class c. Organisms in the same Family and different Genus d. Organisms in the same Kingdom and different Phylum e. Organisms in the same Class and different Order 3. What is the importance of genetic diversity? a. Increased resistance to disease b. Increased chance of survival as climate changes c. Increased ability to compete with invasive species d. All of the above 4. What is a species? a. The fifth highest rank in the hierarchical classification scheme that identifies organisms b. A group of individuals of the same species in a specific area at a specific time c. A group of organisms that can interbreed in nature and produce fertile offspring d. An organism that cannot makes its own food and gets its nutrients and energy from consuming other organisms 5. What is the term used to describe “an organism that captures energy from sunlight to produce its own energy-yielding food? a. Autotroph b. Heterotroph c. Consumer d. Decomposer 6. Which organism is known to cause red tide? a. Diatom b. Dinoflagellate c. Slime mould d. Paramecia e. Phytoplankton 7. Where would you find a halophilic Archaeabacteria? a. Sea water with high salt concentrations b. Deep water sea vents with hot temperatures c. Craters of volcanoes d. Sediment of landfills e. Inside you 8. The phylogentic species concept is based on which evidence? a. Body shape and size of organisms b. Evolutionary history of organisms c. Ability of organisms to interbreed d. Structural function of organisms e. Existing population of a species 9. The greatest similarity in structure occurs between members belonging to: a. Kingdom b. Species c. Phylum d. Class 10. Organisms capable of mating and producing fertile offspring belong to the same: a. Phylum b. Genus c. Class d. Species 11. Which of the following represents the correct order of classification from largest grouping to the smallest grouping? a. Species genus phylum class b. Phylum class genus species c. Genus species phylum class d. Phylum genus class species 12. Which group includes the other four? a. Genus b. Species c. Kingdom d. Phylum 13. Eukaryotic organisms: a. Lack a nuclear membrane b. Have a nuclear membrane c. Lack chromosomes d. Lack DNA 14. Archaea and Bacteria are similar because: a. They are multicellular b. They are prokaryotic cells c. They contain membrane-bound organelles d. They are eukaryotic cells 15. A virus that invades a bacterium and remains inactive through several years has underdone which cycle? a. Lytic cycle b. Temperate cycle c. Lysogenic cycle d. Bacteria cycle 16. What is wrong with the way the species name, Acer Canadians, has been written? a. It should not be italicized b. It should not be underline c. Acer should not be capitalized d. Canadians should not be capitalized e. Neither word should be capitalized 17. Of the organisms listed below, which is the closest relative of the snowy owl (Bubo scandiacus)? a. barn owl (Tyto alba) b. great horned owl (Bubo virginianus) c. saw-whet owl (Aegolius acadicus) d. eastern screech owl (Megascops asio) e. burrowing owl (Athene cunicularia) 18. Which statement about binomial nomenclature is false? a. An organism’s scientific name is made up of two words. b. The first word of an organism’s scientific name is its genus, and the second word is its species. c. The scientific name is italicized if typed. d. The scientific name is underlined if handwritten. e. Both the genus and species names are capitalized. Fill in the Blanks 19. ____________________________, Kingdom, ____________________________, Class, Order, ____________________________, Genus ____________________________, 20. Which two groups are used for an organism’s scientific name? 21. Which of the following pairs is most closely related? Acer rubrum & Acer saccharum OR Acer rubrum & Chenopodium rubrum 22. These plants contain flowers __________________________ 23. These plants have cones __________________________ Short Answer 24. List the taxa of classification from the largest grouping to the smallest 25. Give one reason why viruses are living and one why they are not 26. Draw the lytic and lysogenic cycle and explain it. ** know briefly the stages 27. Name 4 differences between prokaryotic and eurkaryotic cells. 28. Explain the difference between heterotrophs/autotrophs, and sexual reproduction/asexual reproduction. 29. Why must a virus enter a host cell in order to reproduce itself? 30. What are the different ways a virus can reproduce using a host cell? 31. Define the term extremophile and given an example. 32. Name 4 differences between monocots and dicots. 33. Who is Carl Linnaeus? 34. Label the following diagram 35. Describe 3 ways that bacteria are helpful 36. Name one example of a harmful bacteria. 37. Draw a virus and label it 57. Use the dichotomous key to find the names of each pasta. Numbered List: 1) a. If your pasta is tube shaped go to……………………..………………………..Step 2 b. If your pasta is irregularly shaped, go to…………………..………………….Step 3 2) a. If your pasta is straight, it is….........................................Penneus pastaus b. If your pasta is curved, it is…………………………………….Macaronus noodleus 3) a. If your pasta is round, it is…………………………………………Wheelus pastaus b. If your pasta has jagged ends, it is…………………………….Bowtieus noodleus 58. Create a dichotomous key using the following things: blue jeans, red t-shirt, purple hat, gold necklace, pink dress ** answers are on next page Diversity Unit 1 review 38. Which of the following statements about prokaryotes is false? a. They possess circular DNA that is not bound by a membrane b. Many species of bacteria are anaerobic c. They perform both mitosis and meiosis d. They do not possess membrane-bound organelles 39. Which two organisms are most closely related? f. Organisms in the same Genus but different Species g. Organisms in the same Phylum and different Class h. Organisms in the same Family and different Genus i. Organisms in the same Kingdom and different Phylum j. Organisms in the same Class and different Order 40. What is the importance of genetic diversity? e. Increased resistance to disease f. Increased chance of survival as climate changes g. Increased ability to compete with invasive species h. All of the above 41. What is a species? e. The fifth highest rank in the hierarchical classification scheme that identifies organisms f. A group of individuals of the same species in a specific area at a specific time g. A group of organisms that can interbreed in nature and produce fertile offspring h. An organism that cannot makes its own food and gets its nutrients and energy from consuming other organisms 42. What is the term used to describe “an organism that captures energy from sunlight to produce its own energy-yielding food? e. Autotroph f. Heterotroph g. Consumer h. Decomposer 43. Which organism is known to cause red tide? f. Diatom g. Dinoflagellate h. Slime mould i. Paramecia j. Phytoplankton 44. Where would you find a halophilic Archaeabacteria? f. Sea water with high salt concentrations g. Deep water sea vents with hot temperatures h. Craters of volcanoes i. Sediment of landfills j. Inside you 45. The phylogentic species concept is based on which evidence? f. Body shape and size of organisms g. Evolutionary history of organisms h. Ability of organisms to interbreed i. Structural function of organisms j. Existing population of a species 46. The greatest similarity in structure occurs between members belonging to: a. Kingdom b. Species c. Phylum d. Class 47. Organisms capable of mating and producing fertile offspring belong to the same: a. Phylum b. Genus c. Class d. Species 48. Which of the following represents the correct order of classification from largest grouping to the smallest grouping? a. Species genus phylum class b. Phylum class genus species c. Genus species phylum class d. Phylum genus class species 49. Which group includes the other four? a. Genus b. Species c. Kingdom d. Phylum 50. Eukaryotic organisms: a. Lack a nuclear membrane b. Have a nuclear membrane c. Lack chromosomes d. Lack DNA 51. Archaea and Bacteria are similar because: a. They are multicellular b. They are prokaryotic cells c. They contain membrane-bound organelles d. They are eukaryotic cells 52. A virus that invades a bacterium and remains inactive through several years has underdone which cycle? a. Lytic cycle b. Temperate cycle c. Lysogenic cycle d. Bacteria cycle 53. What is wrong with the way the species name, Acer Canadians, has been written? a. It should not be italicized b. It should not be underline c. Acer should not be capitalized d. Canadians should not be capitalized e. Neither word should be capitalized 54. Of the organisms listed below, which is the closest relative of the snowy owl (Bubo scandiacus)? a. barn owl (Tyto alba) b. great horned owl (Bubo virginianus) c. saw-whet owl (Aegolius acadicus) d. eastern screech owl (Megascops asio) e. burrowing owl (Athene cunicularia) 55. Which statement about binomial nomenclature is false? a. An organism’s scientific name is made up of two words. b. The first word of an organism’s scientific name is its genus, and the second word is its species. c. The scientific name is italicized if typed. d. The scientific name is underlined if handwritten. e. Both the genus and species names are capitalized. Fill in the Blanks 56. DOMAIN, Kingdom, PHYLUM Class, Order, FAMILY Genus SPECIES 57. Which two groups are used for an organism’s scientific name? GENUS, SPECIES 58. Which of the following pairs is most closely related? Acer rubrum & Acer saccharum OR Acer rubrum & Chenopodium rubrum 59. These plants contain flowers ANGIOSPERMS 60. These plants have cones GYMNOSPERMS Short Answer 61. List the taxa of classification from the largest grouping to the smallest a. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species 62. Give one reason why viruses are living and one why they are not a. They can reproduce, but they cannot live outside of a host 63. Draw the lytic and lysogenic cycle and explain it Lytic cycle: A virus attaches to the host cell. The virus injects DNA into the host cell. Cell creates new viral DNA and proteins. The host cell assembles virus. Cell lyses, releasing viruses. Lysogenic cycle: A virus attaches to the host cell. The virus injects DNA into the host cell. Viral DNA inserts itself into host DNA. Cell divides. Stays dormant. Provirus leaves host cell’s DNA. Cell creates new viral DNA and proteins. The host cell assembles virus. Cell lyses, releasing viruses. 64. Name 4 differences between prokaryotic and eurkaryotic cells. Characteristic Prokaryotes: Bacteria, Archaea Eukaryotes: Protists, plants, Fungi, Animals Size 1-10 µm 100-1000 µm Genetic material Circular DNA, not bound by a membrane Genome made up of a single chromosome DNA in nucleus bounded by membrane Genome made u of several chromosomes Cell Division Not by mitosis and meiosis By mitosis and meiosis Reproduction Asexual reproduction common Sexual reproduction common Number of cells Unicellular Most forms are multicellular Organelles Mitochondria and other membrane bound organelles absent Mitochondria and other membrane bound organelles present Metabolism Many are anaerobic (do not require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration) Most are aerobic (require oxygen to carry out cellular respiration) 65. Explain the difference between heterotrophs/autotrophs, and sexual reproduction/asexual reproduction. a. Heterotrophs: cannot make their own food and rely on eating other organisms to gain energy b. Autotrophs: produce their own food, using light c. Sexual reproduction: offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only d. Asexual reproduction: genetic material from two parents combine to form offspring with a unique combination of genes 66. Why must a virus enter a host cell in order to reproduce itself? It cannot survive on its own 67. What are the different ways a virus can reproduce using a host cell? Going through the lytic or lysogenic cycle 68. Define the term extremophile and given an example. An archaea that lives in extreme conditions. A halophile lives in water with a high salt concentration 69. Name 4 differences between monocots and dicots. 70. Who is Carl Linnaeus? Father of taxonomy. Attempted to name every species with a two-part name. 71. Label the following diagram 72. Describe 3 ways that bacteria are helpful. Help ferment cheese, protect against infection, break down organic materials for plants, makes vitamins, breaks down food 73. Name one example of a harmful bacteria. Streptococcus, salmonella 74. Draw a virus and label it Capsid DNA or RNA Tail fibers 57. Use the dichotomous key to find the names of each pasta. Numbered List: 1) a. If your pasta is tube shaped go to……………………..………………………..Step 2 b. If your pasta is irregularly shaped, go to…………………..………………….Step 3 2) a. If your pasta is straight, it is….........................................Penneus pastaus b. If your pasta is curved, it is…………………………………….Macaronus noodleus 3) a. If your pasta is round, it is…………………………………………Wheelus pastaus b. If your pasta has jagged ends, it is…………………………….Bowtieus noodleus Pasta 1 = Penneus pastaus Pasta 2 = Bowtieus noodleus Pasta 3= Macaronus noodleus Pasta 4 = Wheelus pastaus 58. Create a dichotomous key using the following things: blue jeans, red t-shirt, purple hat, gold necklace, pink dress (an example) 1) A. If it is an accessory go to ………………………………………………………. Step 2 B. If it is a piece of clothing go to …………………………………………………. Step 3 2) A. If you wear it around your neck…..……………………………………. goldus necklaceus B. If you wear it on your head…..……………………………………. purplus hateus 3) A. If it goes over your head …………………………………………………. Step 4 B. If it goes over your legs …………………………………………………. Blueus jeanus 4) A. If another piece of clothing is required to wear on the bottom …………………… redeus t-shirtus B. If it is a complete outfit ………………………………………………………… pinkus dresseus