KUMC 55 Popliteal Fossa and Leg Student
advertisement

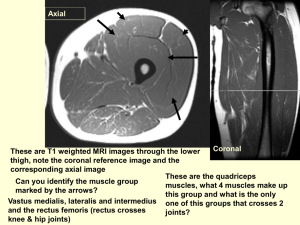
POPLITEAL FOSSA Popliteal Fossa Bony landmarks: Popliteal surface of femur (floor). Boundaries: Superior: Semimembranosus and semitendinosus. Inferior: Medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius. Popliteal Fossa Contents: Fat. Several popliteal lymph nodes. Popliteal bursa. Superficial to deep: Tibial nerve. Popliteal vein. Popliteal artery. Common peroneal (fibular) nerve. Small saphenous vein. Popliteal Fossa Contents: Popliteal artery: Continuation of femoral artery. Begins at adductor hiatus. Ends at lower border of popliteus muscle. Divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Popliteal Fossa Contents: Popliteal vein: Formed from venae comitantes of anterior and posterior tibial arteries. Receives lesser saphenous vein. Becomes femoral vein at adductor hiatus. Popliteal Fossa Contents: Tibial nerve: Part of sciatic nerve. Supplies posterior thigh and leg. Common peroneal nerve: Part of sciatic nerve. Branches into superficial and deep peroneal (fibular) nerves: Supplies lateral and anterior leg. Popliteal Fossa Sural nerve: Arises via: Communicating branch from tibial nerve. Communicating branch from common peroneal (fibular) nerve. Popliteal Fossa Genicular anastomosis: Descending genicular: from femoral. Descending branch of lateral femoral circumflex. Genicular branches of popliteal artery: Medial superior/inferior genicular. Lateral superior/inferior genicular. Middle genicular. Popliteal Fossa Genicular anastomosis: Branches of anterior tibial: Circumflex fibular. Anterior tibial recurrent. Branches of posterior tibial: Posterior tibial recurrent. LEG Bones of the Leg Tibia: Most common long bone to be fractured. Relatively poor blood supply. Anteromedial surface is “bare.” Available for bone grafts. Soleal (oblique) line on posterior surface. Fibula: Lateral malleolus important in ankle stability. Site for muscle attachment. Crural Fascia Continuous with fascia latae. Attachment to anterior and medial borders of tibia: Continuous with periosteum. Leaves bare area. Fascia forms retinacula in foot: Superior (extensor) retinaculum: Proximal to malleoli. Binds tendons in anterior crural compartment. Crural Fascia Fascia forms retinacula in foot: Inferior (extensor) retinaculum: “Y”-shaped. Flexor retinaculum: Binds tendons of the deep posterior compartment. Superior/inferior peroneal retinacula: Bind tendons of lateral crural compartment. Superficial Posterior Compartment Cutaneous nerves: Lateral sural cutaneous nerve: From common peroneal. Medial sural cutaneous: From tibia. Sural nerve runs with lesser saphenous vein. Superficial Posterior Compartment Muscles: Gastrocnemius: Crosses both knee and ankle joint. Two heads form inferior boundaries of the popliteal fossa. Lateral head may have a sesamoid bone: Fabella. Plan: plantaris MG: med. Gastroc. LG: lat. Gastroc. Sol: soleus TC: tendo calcaneus Superficial Posterior Compartment Muscles: Plantaris: May be absent. Tendon may be used for hand surgery. Superficial Posterior Compartment Muscles: Soleus: Broad multipennate muscle. Unijoint muscle. Triceps surae: = soleus + two heads of gastrocnemius. Common insertion: Calcaneus via Achilles tendon (tendo calcaneus) Plan: plantaris Sol: soleus Superficial Posterior Compartment Nerve supply: Tibial nerve: Supplies all muscles in posterior compartment. Divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves inferior and posterior to medial malleolus. Gives off medial sural cutaneous nerve. Joins with communicating branch of common peroneal (fibular) nerve to form: Sural nerve: Cutaneous. Superficial Posterior Compartment Blood supply: Posterior tibial artery: Largest branch of popliteal artery. Divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries deep to origin of abductor hallucis muscle. Peroneal artery: Most important branch of posterior tibial artery. Supplies lateral compartment and popliteus muscles. Supplies other muscles in posterior compartment. Deep Posterior Compartment Muscles: Popliteus: Lies in floor of popliteal fossa. Flexes and rotates knee. Flexor digitorum longus: Tendon passes posterior to medial malleolus and to tendon of tibialis posterior. Plantarflexes foot at ankle joint. Deep Posterior Compartment Muscles: Flexor hallucis longus: Tendon occupies groove on posterior surface of talus: Continuous with groove on plantar surface of sustentaculum tali. Tendon passes posterior to medial malleolus. Tendon passes between two sesamoid bones. Push-off muscle for walking, jumping, running. Deep Posterior Compartment Muscles: Tibialis posterior: Functions in plantarflexion and foot inversion. Helps to maintain medial longitudinal arch. Pop: popliteus TP: tibialis post. PL: peroneus longus FD: flex. dig. long. PB: peroneus brevis FHL: flex. hall. long. Deep Posterior Compartment Nerve supply: Tibialis nerve: Blood supply: Posterior tibial artery. Anterior Compartment Muscles: Tibialis anterior: Lateral to crest of tibia. Foot dorsiflexion and inversion. L4-L5. Paralysis results in foot drop. Anterior Compartment Muscles: Extensor digitorum longus: Four tendons of insertion: Each tendon inserts on an extensor expansion . Similar to arrangement in hand. Extends toes at MTP and dorsiflexion. Anterior Compartment Muscles: Peroneus (fibularis) tertius: Part of extensor digitorum longus. Sometimes missing. Functions in foot dorsiflexion and eversion. Extensor hallucis longus. TA: tibialis anterior EDL: extensor digitorum longus EHL: extensor hallucis longus PT: peroneus tertius IM: interosseous membrane ED: extensor digitorum longus EHL: extensor hallucis longus PT: peroneus tertius Anterior Compartment Function: Toe extension. Ankle dorsiflexion. Anterior Compartment Innervation: Deep peroneal (fibular) nerve. L4-5 to tibialis anterior. L5-S1 for remaining muscles. Runs deep to extensor digitorum longus. Accompanies anterior tibial artery between extensor hallucis longus and tibialis anterior muscles. Anterior Compartment Blood supply: Anterior tibial artery: Smaller of terminal branches of popliteal artery. Begins at inferior border of popliteus muscle. Becomes dorsalis pedis artery at ankle joint. Lateral Compartment Muscles: Peroneus (fibularis) longus: More superficial of the two. Easily palpated. Its tendon uses lateral malleolus as a pulley. Tendon crosses sole of foot and inserts on first metatarsus and cuneiform. Helps to maintain transverse and longitudinal arches of the foot. Lateral Compartment Muscles: Peroneus (fibularis) brevis: Deep to peroneus longus. Inserts on lateral tuberosity. Function: Plantar flexion. Foot eversion. Lateral Compartment Nerve supply: Superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve: Deep to peroneus longus. Inserts on lateral tuberosity. Blood supply: No major arteries in lateral compartment. Muscular branches arise from the peroneal artery: Branch of posterior tibial. Lateral Compartment Spinal cord levels: L5, S1-2