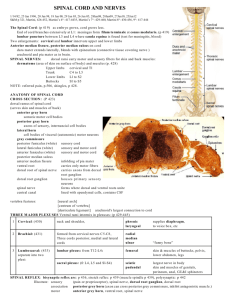
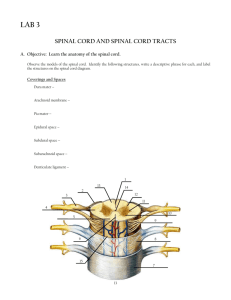
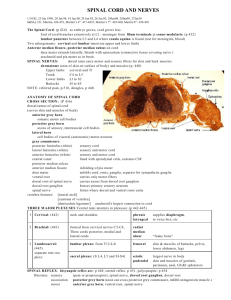
D F J A H G J E C B the gray matter is in the center of the cord and
advertisement

D F J A H G J E C B the gray matter is in the center of the cord and forms horns, the white matter surrounds the perimeter and forms columns the meninges of the spinal cord cover and protect it. the layers are in the same order as the coverings of the brain: dura mater (outer), arachnoid (middle), and pia mater (inner) see table 13-2 on page 432 of text. 1. stimulus, 2. activation of sensory neuron, 3. information processing in CNS, 4. activation of motor neuron, 5. response be effector. posterior median sulcus central canal posterior root of spinal n. posterior root ganglion anterior root of spinal n. gray matter anterior white column anterior median fissure anterior gray horn lateral gray horn posterior gray horn lateral white column posterior white column obturator nerve innervates the adductor muscles of the hip; this nerve is part of the lumbar plexus attaching to the spinal cord at segments L2-L4. anterior gray horn contains somatic motor nuclei; posterior gray horn contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; lateral gray horn contains visceral motor nuc. it could happen, if the nerve were mixed containing axons of motor neurons and dendrites of sensory neurons; problems with the nerve could affect both. the patellar reflex is an example of a stretch reflex; beginning with the knee bent, the physician taps the knee which stretches the muscle group further and triggers contraction of the group to counteract the stretch.