Colonial Regions
advertisement

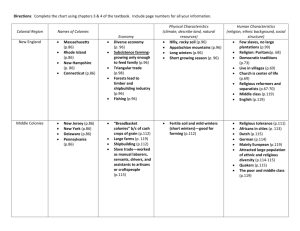
Today’s Agenda • Discuss “One-Pager” Region Project-due Thursday • Colonial Regions Review- Freeform Mapping • Colonial Regions Quiz • Fill in P.L.A.C.E.S. for colonial regions in ISN. • Colonial Placement Program Activity British Colonization 1607-1733 Between 1607 and 1733, the British founded thirteen colonies on North America’s east coast and successfully ruled them for 169 years. Other nationalities helped settled the colonies, but the population, language, laws and culture remained predominantly British. Reasons for Colonization (motives for settlement) Types of Colonies Private enterprise financed all thirteen British colonies, but all were required to govern by English law. Three kinds of colonies received charters from the king. On the next clean page of your ISN, install the Thirteen Colonies Foldable. Use this chart to place them in chronological order. Shade the tabs by colonial region and create a key for your notes. Directions • You will take notes on the development of each colonial region in your foldable utilizing PLACE + S. Physical Environment- how would you explain the overall physical environment? Location- Where is it? Agriculture- What types of plants grow there? Soil type? Natural resources? Climate- What the normal weather? Economy- How do people make money? Society- What’s the culture? New England Colonies rocky soil, forests, harbors, sandy coasts Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Hampshire, Rhode Island potatoes, corn, pumpkin, fish, beans, sustenance farming (small) long bitter winters, short mild summers Fishing, lumbering, shipbuilding, slave trading, rum Puritans, Pilgrims, towns and villages, Mayflower Compact, Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, Middle Colonies rocky soil in some areas, fertile soil, navigable rivers, harbors New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware wheat, rye, oats, beef, pork, corn Moderate: cold winters, hot summers “Breadbasket” exporting grains, iron, trade religious and ethnic diversity, rural (farms) urban- large cities, trade centers, merchants, craftsmen Southern Colonies fertile soil, broad lowlands, many rivers, tidewater area Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia rice, beef, pork, corn, indigo, tobacco, plantations Short, mild winters, long, hot summers cash crops, plantation system, slavery House of Burgesses; Catholics, Anglicans, Baptists; wealthy planters, small farmers, debtors, indentured servants, slaves; rural (farms) Virginia P-coastal lowlands and wooded mountains L- south of Maryland and north of North Carolina; * Jamestown, *Williamsburg A- tobacco, cotton, corn, vegetables, grain, fruit; beef, pork, rich fertile soil C- mild winters and hot summers (long growing season = $) E- cash crops, Iron industry S- religious diversity, House of Burgesses (elected governing assembly) Plantation New Hampshire P- low coast, hills, mountains, and plateau. Heavily forested, rivers L- north and west of Massachusetts A- potatoes, poor rocky soil C- long, cold winters and mild short summers E- fish, timber, furs, shipbuilding, and livestock S- towns and villages; Puritan Plateau- raised area with level top: an area of high ground with a fairly level surface New York P- mountains, lowlands; L- North of Pennsylvania, West of New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire; *NYC, *Albany A- wheat, corn, beef, pork, lumber, fertile soil C- mild climate with warm summers and mild winters E- cash crops, shipbuilding, trade S- religious diversity Massachusetts P- jagged coast and hills, mountains thick with trees, rivers L- north of Connecticut, and Rhode Island, east of New York and New Hampshire, *Boston A- corn, poor rocky soil C- mild short summers and long cold winters E- manufacturing and exporting rum, and shipbuilding, fishing, furs S- Mayflower Compact (self-governing), Puritan, Salem Witchcraft Trials, Jagged coasts Maryland P- coastal plains, piedmont plateau, and the Blue Ridge Mountains, separated by the Chesapeake Bay L- north of Virginia, west of Delaware, south of Pennsylvania, *Baltimore A- corn, wheat, rice, beef, pork,indigo C- hot and humid summers, cold winters E- cash crops, livestock S- religious toleration Rhode Island P- flat rolling hills and lowlands, mountains thick with trees, rivers L- east of Connecticut, south of Massachusetts A- poor rocky soil C- mild short summers, long cold winters E- fishing, whaling, lumber, manufacturing, shipbuilding, rum and syrup-making S- Religious Toleration; villages/towns Connecticut P- narrow lowlands, hilly eastern upland, mountains thick with trees, rivers L- east of New York, South of Massachusetts, west of Rhode Island A- corn, pumpkins, rye, squash, and beans; beef, pork, poor rocky soil C- mild short winters, long cold summers E- shipbuilding, rum S- Religious tolerance; Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Fundamental Orders of Connecticut • First written constitution • Created democratic government with voting rights based on property ownership NOT religious beliefs Delaware P- flat lowland, swampland L- east of Maryland, South of Pennsylvania, west of New Jersey A- timber, furs, coal and iron ore, wheat, flax, hemp C- mild climate with warm summers and mild winters E- cash crops, iron ore, lumber, textiles, furs, and shipbuilding S- religious toleration North Carolina P- coastal plains, plateau and mountain ranges L- north of South Carolina and south of Virginia, *Raleigh A- good agricultural land, fish, forests, C- warm climate year round farming E- cash crops S- religious diversity; slavery South Carolina P- coastal plains, plateau and mountain ranges L- south of North Carolina, and North of Georgia; *Charleston A- good agricultural land C- hot and humid summers E- cash crops; slave trade S- religious diversity, slavery New Jersey P- mountains, lowlands L- East of Pennsylvania and Delaware, south and west of New York; *Princeton, *Trenton A- good farmland, timber, furs, and coal, iron ore C- warm summers and mild winters E- cash crops, livestock S- religious diversity Pennsylvania P- mountains, coastal plain, plateaus, lowlands, L- south of New York, west of New Jersey, north of Maryland and Delaware; *Philadelphia A- good farmland; timber, furs, coal, and iron ore C- warm summers and mild winters E- cash crops, iron ore products S- religious diversity; Quakers Georgia P- hilly coastal plains with plenty of forests L- south of South Carolina and north of Spanish Florida; *Atlanta, *Savannah A- fish, forests, and good farmland C- warm climate, year round farming E- cash crops S- religious diversity HOW CAN WE SUMMARIZE WHAT WE LEARNED ABOUT THE COLONIES? A “one-pager” is a one page summary of what you have learned. The format is flexible and up to you, however, the whole page must be filled in. It must include a combination of pictures and words and it must be in color. INSTRUCTIONS •Split your paper into three sections. Leave a center section for your title. Create a Title. Make it catchy! Label each section. 1.New England Colonies 2.Middle Colonies 3.Southern Colonies •Write a summary about each region. 1.At least 5 sentences. 2.Include geography, climate, natural resources, and economic activity. •Create an essential question about each region AND answer it. •Example: How did the geography of the Southern Colonies affect the economic activity of the region? ANSWER: The rich soil and long growing season made cash crop farming very profitable in the Southern colonies. •BONUS POINTS: Create “Level 2” questions. These questions will force you to think critically about what you have learned when you answer them. •State one main idea about the colonies and put that in the center of your one-pager under the title. REMINDERS •Include at least 2 pictures per section to support your summaries. •The pictures can be drawn, printed, or cut from magazines. •FILL IN ALL OF THE WHITE SPACE ON THE PAGE. Use lots of color and be creative!