Regions for the colonies
advertisement

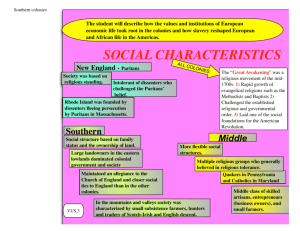
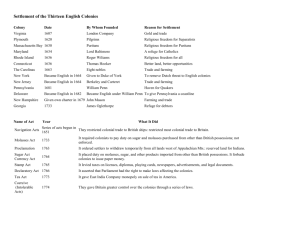
Original 13 Colonies Regional Colonies • New England Colonies o o o o Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New Hampshire • Middle Colonies o o o o Delaware New York New Jersey Pennsylvania • Southern Colonies o o o o o Maryland Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia New England Colonies Geography • Bitterly cold winters and mild summers. • Land was flat close to the coastline but became hilly and mountainous farther inland. • Soil was rocky, making farming difficult. • Very short growing season • Cold winters reduced the spread of disease Religion • Puritans, reformers seeking to “purify” Christianity • Puritans followed strict rules and were intolerant of other religions • New England Way of Life • Singing and celebrating holidays were among things prohibited in Puritan New England Puritans Even Ban CHRISTMAS! Economy • Dependent on the ocean. • Fishing, trapping and fur trading, shipbuilding, and logging • Subsistence Farming • Triangular Trade Triangular Trade Government • Seeds of Democracy • Mayflower Compact – majority rule • Fundamental Orders of Connecticut – first Constitution • Virginia House of Burgesses- first Representative Assembly Middle Colonies Geography • Warm summers and cold winters • Coastal plains along the coastline, piedmont (rolling hills) in the middle, and mountains farther inland • Good coastal harbors for shipping • Climate and land were ideal for agriculture Economy • Longer growing season • “Breadbasket colonies” • Grain = Cash Crop Religion • No single religion seemed to dominate the entire region. • Religious tolerance attracted immigrants Quakers, Catholics, Jews, Lutherans and Presbyterians Southern Colonies Geography • Warm climate with hot summers and mild winters. • Coastal plains in the east to piedmont farther inland. The westernmost regions were mountainous. • Soil was perfect for farming long growing season • Hot summers = diseases (malaria & yellow fever) Economy • Almost entirely based on farming. • Rice, indigo, tobacco, sugarcane, and cotton were cash crops. • Crops were grown on large plantations where slaves and indentured servants worked the land. • Charleston, South Carolina became one of the centers of the American slave trade in the 1700′s. Religion • Anglican (Baptist or Presbyterian) • Maryland founded it as a refuge for English Catholics. • Religion did not have the same impact on communities • Plantations that were often distant and spread out from one another. Columbian Exchange Columbian Exchange • Movement of plants, animals, & diseases between the Americas and Europe • Negatives: • Diseases brought by Europeans decimate Native Americans • Positives: • Introduction of new crops and foods to both hemispheres o Grapes, onions, wheat, cattle, pigs & horses thrive in Americas o Potatoes and corn brought back to Europe – basis for new diets Slavery Begins • As plantation system grows there is an increased need for labor • Indentured servants • Slavery begins • Little need for slaves in New England colonies due to short growing season • Planter class grows in Southern colonies as cash crops such as indigo grow Life in Slavery Directed by an overseer Spent 15 + hours working Lived in small one room cabins Slaves do retain customs, traditions and beliefs from their homeland • African kinship customs become basis for African American family unit • • • •