Data Flow Diagrams
advertisement

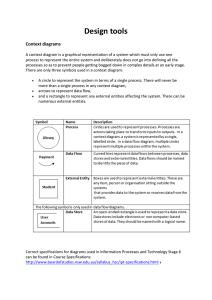
Data Flow Diagrams • Often a good way of summarising sources and destinations of data and the processing that takes place • Shows how data is transformed into information as it moves through a system and what data needs to be stored • Can be used at both the Analysis (existing system) and Design (proposed system) stages of a project Context diagram • Analyst should start with this before drawing a full DFD • Focuses on the inputs and outputs • Only uses the source/destination and data flow symbols • A blank circle is drawn where the rest of the DFD should appear • Identifies the system’s users and their interactions with the system Diagram Levels • Diagrams are in layers or levels with each providing a greater degree of detail • Context diagrams show the whole context and are also called Level 0 • Level 1 shows a process to handle each incoming data flow and a process to generate each output data flow • Level 2 is part of the system with more detail of processing Example Context Diagram Club secretary MembershipNo DatePaid amount System Printed members letters ErrorMessage1 Club secretary Club secretary Data Flow Diagrams Data source or data destination e.g. user documentation or OMR or ID Description Data Store - where data is held within the system e.g. stock file ID Bottom Process e.g. validate code Location Data Flow e.g. customer ID DFD for an electricity meter Meter reading Bill Validate entry Calculate bill Customer details Customer file Updated details Customer file A library loans system identifies each book in its stock by a unique BookID. This is encoded in a bar code and attached to the book. When a borrower returns a book it is scanned and any fine that is due is calculated by extracting from the library database the date that the book was due back. Copy and complete the given DFD that describes this part of the library system. Book Bar code Borrower 2 1 1 Example Mr Jollifant owns a children’s party entertainment business and employs a number of clowns, conjurers etc on a part-time basis. All bookings are kept in a large ledger type book. Mrs Jollifant produces a word processed list of bookings for the next month for each entertainer. At the end of the year she goes through the books, and produces a table similar to the one shown below. Jollifant Jolly Parties Summary of Events 1998 Entertainer No. of Events Total Hours Total Pay Cleo the Clown Magic Marcus Jumping Jimmy 5 2 24 13 6 65 319.50 117.83 1926.21 Inputs/Process/Storage Output Input/output • booking details from client (input) • monthly schedules produced (output) • annual statistical summary (output) Storage • bookings ledger •Processes • calculate available bookings and store in ledger • produce monthly schedules • calculate statistics DFD Client tai ls of mo nth ly Make Booking Details of new booking Clown L1 Bookings' Ledger s ing ok bo of ils ta De Location Location De ID Booking details Produce monthly schedule le du he Sc bo ok ing s ID ID Produce end of year statistics Location s tic s i at St Mr Jollifant