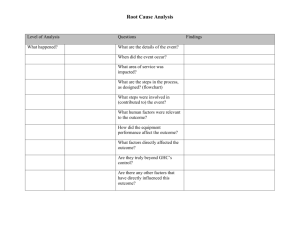
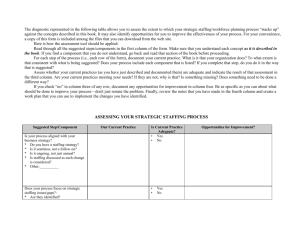
Staffing Strategy
advertisement

MGTO 324 Recruitment and Selections Staffing model, strategy, & planning Kin Fai Ellick Wong Ph.D. Department of Management of Organizations Hong Kong University of Science & Technology Prologue • The idea of staffing has been very salient in Chinese history and culture – “Recruitment” was a highly valued activity in our History • East Han Dynasty (東漢), – Recruitment = assessing moral standard but not others – Filial piety x integrity (察舉孝廉) • Wei Dynasty in the three-kingdom period (魏) – Recruitment = assessing relevant knowledge and skills, regardless of moral – Relevant knowledge » 唯才是舉,吾得而用之 <<三國志,魏書,武帝操>> » Those with relevant skills and knowledge will be selected Outline Class 2: Staffing model, strategy, & planning Part I: Staffing Model Part II: Staffing Strategy Part III: Human Resource Planning Outline Class 2: Staffing model, strategy, & planning Part I: Staffing Model Part II: Staffing Strategy Part III: Human Resource Planning Part I: Staffing Model • Defining “staffing” – “the process of acquiring, deploying, and retaining, a workforce of sufficient quantity and quality to create positive impacts on the organization’s effectiveness” • Acquiring: external staffing, new blood • Deploying: internal staffing (promotion, transfer) • Retention: turnover, compensation, etc. Part I: Staffing Model • Can “good” staffing lead to better organizational effectiveness? – Yes, strongly supported by research findings • Youndt et al., (1996, Academy of Management Journal) – Selectivity +ve organizational performance • Greer et al. (2001, Journal of Business Research) – Countercyclical hiring +ve organizational performance 2 years later • Russell (2001, Journal of Applied Psychology) – Using the effective selection system used by a Fortune 500 organization resulted in more profits. Part I: Staffing Model • The Basic Model – Staffing = counting • Considering quantity but not quality • The simplest model • Exhibit 1.1 Exhibit 1.1 Staffing Quantity Projected Staffing Requirements Overstaffed Compare Fully Staffed Understaffed Projected Staffing Availabilities Part I: Staffing Model • The person/job match model – Staffing = counting + the person-job match • Job characteristics x individual characteristics – Designers: create new items » Creative, imaginative – Social workers: help people with problems » Empathetic, not selfish – Researchers: discover new knowledge » Hardworking, curious to knowledge Exhibit 1.2 Person/Job Match Job Requirements Rewards Match Person KSAOs Motivation HR Outcomes Impact Attraction Performance Retention Attendance Satisfaction Other Part I: Staffing Model • The person/organization match model – Staffing = counting + the person-job match • Job characteristics x individual characteristics x organizational contexts – Organization values, culture, career development • East Han Dynasty Exhibit 1.3 Person/Organization Match Organization Values New Job Duties Job Requirements Rewards Multiple Jobs Future Jobs Match Person KSAOs Motivation HR Outcomes Impact Attraction Performance Retention Attendance Satisfaction Other Part I: Staffing Model • Relationship between applicants and job – Depending on the economy • At times, organization may be the dominant player • At other times, the applicant may be the aggressor – Depending on demand / supply • For jobs that the supply is more than the demand – Organization becomes dominant » E.g., The demand of IT jobs dropped significantly in and after 2001 • For jobs that the demand is less than the supply – Applicants become dominant » E.g., hiring good professors in business school Exhibit 1.4 Staffing System Components Organization (job) Applicant (person) Recruitment (identification and attraction) Selection (assessment and evaluation) Employment (decision making and final match) Part I: Staffing Model • Staffing Organizations Model – Strategic Human Resource Management • Organizational Strategy HR (Staffing) strategy • Staffing becomes part of the overall organization strategy • Core staffing activities are carefully “calibrated” to match the organization strategy Exhibit 1.5 Staffing Organizations Model Organization Missions Goals and Objectives Organization Strategy HR and Staffing Strategy Staffing Policies and Programs Support Activities Core Staffing Activities Legal compliance Planning Job analysis Recruitment: external, internal Selection: measurement, external, internal Employment: decision making, final match Staffing System and Retention Management Outline Class 2: Staffing model, strategy, & planning Part I: Staffing Model Part II: Staffing Strategy Part III: Human Resource Planning Part II: Staffing Strategy Staffing Strategy Staffing Levels: Staffing Quality: Getting sufficient no. of staff Getting qualified staff Part II: Staffing Strategy Staffing Strategy Staffing Levels: Staffing Quality: Getting sufficient no. of staff Getting qualified staff Part II: Staffing Strategy • Staffing Levels (think about HKUST) – – – – – – – – – Acquire or develop talent Lag or lead system External or internal hiring Core or flexible workforce Hire or retain National or Global Attract or relocate Overstaff or understaff Hire or acquire Part II: Staffing Strategy Staffing Strategy Staffing Levels: Staffing Quality: Getting sufficient no. of staff Getting qualified staff Part II: Staffing Strategy • Staffing Quality (again, think about HKUST) – Person/job or person/organization match – Specific or General KSAOs • Knowledge, Skills, Abilities, and Other characteristics – Exceptional or Acceptable Workforce Quality – Active or passive diversity Outline Class 2: Staffing model, strategy, & planning Part I: Staffing Model Part II: Staffing Strategy Part III: Human Resource Planning Part III: Human Resource Planning • Defining “Human Resource Planning” – A process and set of activities undertaken to forecast an organization’s labor demand and internal labor supply (availabilities) – Key steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. determine future human resource demands determine future human resource availabilities conduct external & internal environment scanning determine gaps between demands and availabilities develop action plans to close the projected gaps Exhibit 3.13 Operational Format and Example for Human Resource Planning (HRP) Organizational Unit: Sales and Customer Service Forecast for Workforce— One Year Job Category and Level Current Workforce Requirements Availabilities Reconciliation and Gaps A1 (Sales) 100 110 71 -39 (shortage) A2 (Sales manager) 20 15 22 +7 (surplus) B1 (Customer service representative) 200 250 140 -110 (shortage) B2 (Customer service manager) 15 25 22 -3 (shortage) 335 400 255 -145 (shortage) Action Planning Staffing activities Recruitment Selection Employment Other HR activities Compensation Training and development Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 1: forecasting the demands – Use of statistical techniques • Project the past to the future – Ratio analysis » $1000 sales per each salesmen; I need 20 salesmen for $20,000 sales – Multiple regression analysis » The concepts are relatively complex » Some techniques will be introduced in Workshop 6 Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 2: forecasting HR (within organization) availabilities – Use of statistical techniques • It is a simple probability calculation • Four job positions – Sale team: A1 (Sale manager); A2 (Account manager) – Support team: B1 (Executive officer); B2 (Clerk) • List all possible movements – – – – Job stability (remain in A1, A2, B1, and B2) Promotion (A2 A1; B2 B1) Demotion (A1 A2; B1 B2) Exit (leaving the organization) • This information enables us to know the availability of each position – Markov Analysis (Workshop 2) Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 2: forecasting HR (within organization) availabilities – Use of statistical techniques • It is a simple probability calculation • Four jobs – Sale team: A1 (Sale manager); A2 (Account manager) – Support team: B1 (Executive officer); B2 (Clerk) • List all possible movements – – – – Job stability (remain in A1, A2, B1, and B2) Promotion (A2 A1; B2 B1) Demotion (A1 A2; B1 B2) Exit (leaving the organization) Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 3: Environment Scanning – External scanning • Process of tracking trends and developments in the outside world – More and more females decide not to have children, which implies that the projected supply of female workforce in the future years may have been underestimated – HK government significantly increases no. of undergraduate students – The government plans to recognize the diploma and degree offered by some mainland universities – Internal scanning • Understanding the organization’s internal environment – Nagging personnel problems » High turnover rates, difficult in getting new qualified employees » Any conflict between the values and attitudes of manages and the current business plan? Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 4: Determining the gaps – Surplus • The availabilities will be more than the demands – Slowing down promotion – Early retirement – Shortages • The demands will be more than the availabilities – Increasing transfer – External staffing Exhibit 3.13 Operational Format and Example for Human Resource Planning (HRP) Organizational Unit: Sales and Customer Service Forecast for Workforce— One Year Job Category and Level Current Workforce Requirements Availabilities Reconciliation and Gaps A1 (Sales) 100 110 71 -39 (shortage) A2 (Sales manager) 20 15 22 +7 (surplus) B1 (Customer service representative) 200 250 140 -110 (shortage) B2 (Customer service manager) 15 25 22 -3 (shortage) 335 400 255 -145 (shortage) Action Planning Staffing activities Recruitment Selection Employment Other HR activities Compensation Training and development Part III: Human Resource Planning Step 1: Forecasting HR demands Step 2: Forecasting HR availabilities Step 3: Environment scanning Step 4: Determining gaps Step 5: Action plans Part III: Human Resource Planning • Step 5: Action plans – Set objectives • Set clear additions or subtractions of head count on each of the possible movements (e.g., new hires, promotions, transfers, demotions, and exits) – Generating alternatives • How to solve the shortage of 39 account managers? – Long-term vs. short-term solutions – Alternative 1: +20 new hires, +20 promotions, +20 transfers, 0 demotions, and -21 exits – Alternative 2: +40 new hires, + 0 promotions, +0 transfers, 0 demotions, and -1 exits – Alternative 3: hiring more part-time account managers, encouraging overtime working, outsourcing, etc.