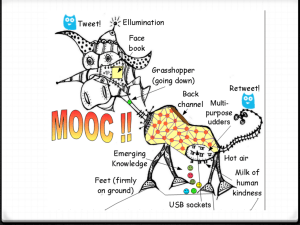
MOOCs - Netmode
advertisement

Πολυμεσικό Υλικό στο Internet: Συγχρονισμός, Επεξεργασία και Διακίνηση Multimedia content delivery in the Internet: Multimedia platforms & video service providers, MOOCs – Coursera & edX cases 10/12/2015 Β. Μάγκλαρης <maglaris@netmode.ntua.gr> Μ. Γραμματικού <mary@netmode.ntua.gr> Δ. Καλογεράς <dkalo@noc.ntua.gr> www.netmode.ntua.gr Outline • • • • • • • Massive Open On-Line Courses – MOOCs Brief History of MOOCs Types of MOOCs Major players in MOOCs MOOCs players in Europe Platforms for creating Courses Coursera & edX Cases Massive Open On-Line Courses (MOOCs) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Massive_open_online_course • MOOC is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the web • Not only traditional course materials such as videos, readings, and problem sets, MOOCs provide interactive user forums that help build a community for students, professors, and teaching assistants • MOOCs are a recent development in distance education which began to emerge in 2012 Why offer a MOOC http://www.slideshare.net/beboac/ichl-moo-cs History of MOOCs (I) • A MOOC is an open education movement and is found online • It influences connectivism where learning is successful and networks are created in different fields • 2002: MIT OpenCourseWare project formed • 2004: The term Connectivism was developed by George Siemens (University of Texas at Arlington) and Stephen Downes (Canada's National Research Council) • 2008: The first MOOC was presented at the University of Manitoba, Canada and it consisted of 2200 learners • 2008: Khan Academy starts up (actually at 2006) • 2010: Dave Cormier (University of Prince Edward Island) made video about MOOCs and uploaded onto YouTube • 2012: Harvard’s first MOOC has 370,000 students, New York Times calls 2012 the year of the MOOC • 2013: cMOOCs and xMOOCs too numerous to count Stephen Downes’ MOOC Model http://www.slideshare.net/beboac/ichl-moo-cs • Four elements for a successful MOOC: – Autonomy – students decide how much to participate – Diversity – students come from all backgrounds, different countries, different experiences – Openness – MOOCs should be free or with low cost – Interactivity – Chats, video meetings… • In his new book: Learning is the creation and removal of connections between the entities, or the adjustment of the strengths of those connections. A learning theory is, literally, a theory describing how these connections are created or adjusted The different types of MOOCs (I) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Massive_open_online_course#Connectivist_design • There are different types of MOOCs: – The cMOOC (connectivist MOOC): • the first MOOC ever offered was a cMOOC • The term describes a MOOC where people learn through social networks e.g. blogs with a focus on knowledge creation instead of acquisition • cMOOCs are used by the individual, academics and non profit organizations • the cMOOC is based on a connectivist learning theory • the cMOOC is an informal learning environment The different types of MOOCs (II) • The xMOOC: – xMOOCs are used by the Universities – xMOOCs use a behaviourist approach – the xMOOC is a more formal learning environment, it focus purely on knowledge acquisition – EdX can be characterized as xMOOC – MIT announced MITx at the end of 2011, MITx is morphed into EdX with the addition of Harvard and UC Berkley (EdX 2012) Synchronous Massive Online Course sMOOCs http://www.slideshare.net/beboac/ichl-moo-cs • This term was coined at University of Texas in August 2013 • A course that features live, synchronous broadcasts to students • Coursera MOOCs could be characterized as a standard MOOCs or an sMOOC Platforms for creating Courses (Modular object-oriented dynamic learning environment - Moodle) (I) https://moodle.org/ http://webvm.netmode.ntua.gr/courses • Moodle is a free online learning management system, or LMS • Written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License • Moodle runs without modification on Unix, Linux, FreeBSD, Windows, Mac OS X and any other systems that support PHP and a database, including webhost providers • Moodle allows for extending and tailoring learning environments using community sourced plugins Platforms for creating Courses (Open edX) (II) http://code.edx.org/ • Open edX is a not-for-profit enterprise • Founded 2012 • Open edX – is implemented mostly in Python for the server, and Javascript for the browser – the code is being made available under an AGPL license – the main repository is edx-platform which includes both the LMS and the authoring tool, Studio • Open edX is already receiving code contributions from around the world (e.g. Stanford University, Google, MIT, The University of Queensland, Tsinghua University, UC Berkeley, and Harvard University) edX Platform Stack • Almost all of the server-side code in Open edX is in Python, with Django as the web application framework, using Mako templates (written in Python) • The browser-side code is written primarily in JavaScript. Some of the code is written in CoffeeScript, and edX is working to replace that code with JavaScript. Parts of the client-side code use the Backbone.js framework (available under the MIT software license), and edX is moving more of the codebase to use that framework • Open EdX uses Sass and the Bourbon framework for CSS code • • • Platforms for creating Courses (III) CourseSites by Blackboard is an exceptionally robust platform – it has all of the features that Moodle has – including extensive teaching tools – reporting features and SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) compliance – it is also cloud-based – you can set up a course in minutes and never have to worry about maintenance or upgrades Udemy is a platform or marketplace for online learning and is specialized in the private MOOC – think of it as the YouTube of MOOCs – instructors can build and host their own courses on the platform and then offer them to users for free or for a fee Versal is a new platform, create interactive e-learning courses for your LMS – intuitive user interface and a robust drag-and-drop functionality – a user can sign up for free and then build a course that includes mathematical expressions, image drill-downs and many more widgets, all without any coding knowledge Platforms for creating Courses (IV) http://bit.ly/1ginXMb Major Players in the MOOC Universe http://chronicle.com/article/The-Major-Players-in-the-MOOC/138817/ Major Players in the MOOC Universe http://chronicle.com/article/The-Major-Players-in-the-MOOC/138817/ • Coursera: This for-profit MOOC founded by Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller (Chief Scientist at Baidu Research in Silicon Valley) has teamed up with 62 colleges (and counting) for its classes. It attracted $22-million in venture capital in its first year • Khan Academy: Salman Khan (American teacher) made waves when he quit his job as a hedge-fund analyst to record short video lectures on everything from embryonic stem cells to—you guessed it—hedge funds and venture capital • Udacity: This for-profit MOOC, started by the Stanford professor Sebastian Thrun, works with individual professors to offer courses. By March 2013, Udacity had raised more than $21-million in venture capital. Udacity provides with Nanodegrees to learners • EdX: Harvard and MIT put up the original $60-million to start this non-profit MOOC Overview of potential revenue sources for three MOOC providers edX •Certification Coursera •Certification •Secure assessments •Employee recruitment •Applicant screening •Human tutoring or assignment marking •Enterprises pay to run their own training courses •Sponsorships •Tuition fees UDACITY •Certification •Employers paying to recruit talented students •Students résumés and job match services •Sponsored high-tech skills courses "Charging for content would be a tragedy," said Andrew Ng. But "premium" services such as certification or placement would be charged a fee Visual Representation of a MOOC http://www.slideshare.net/krisbeukes/moocs-introduction MOOCs Players in Europe http://www.openuped.eu/, https://iversity.org http://openeducationeuropa.eu/ • OpenupEd is an open, it was launched in April 2013 by European Association of Distance Teaching Universities (EADTU), non-profit partnership offering MOOCs that contribute to open up education • iversity.org is a platform for Massive Open Online Courses that contribute to open education • Open Education Europa is a portal based on an initiative of the European Commission to offer access to all existing European Open Educational Resources OpenupEd • 12 European countries have joined forces to launch the first pan-European MOOCs initiative, with the support of the European Commission • 149 courses in different European languages • The OpenupEd framework features: – – – – – – – – Learner-centred Openness to learners Digital openness Independent learning Media-supported interaction Recognition options Quality focus Spectrum of diversity iversity • 6 European partners • In 3 European languages: – English, German, Russian • Certificates with a fee • Courses subjects include: – – – – – – medicine computer science economics physics law design and philosophy Open Education Europa • Open Education Europa is a dynamic platform built with the latest opensource technology, offering tools for communicating, sharing and discussing The portal is structured in 3 main sections: – The FIND section showcases MOOCs, courses, and Open Educational Resources by leading European institutions – The SHARE section come together to share and discuss solutions for a diverse range of educational issues by posting blogs, sharing events, and engaging in thematic discussion – The IN-DEPTH section hosts eLearning Papers —provides an exhaustive list of EU-funded projects, and highlights the latest news about open education as well as the most relevant recently published scholarly articles Coursera Case http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coursera • Coursera started in 2012 working with Stanford University, Princeton, the University of Michigan, and the University of Pennsylvania, – – – – 12 partners were added in July 2012 17 more in September 2012 another 29 partner universities in February 2013 the current total number of partners is 108 • In January 2014, the State Department told Coursera to block access to its courses for users in Cuba, Iran and Sudan Founded 2012 • All courses offered by Coursera are "accessible for free“ • Coursera courses: – approximate from six to ten weeks long – with one to two hours of video lectures a week – provide quizzes, weekly exercises, and sometimes a final project or exam • Coursera reaches 839 courses in October 2014 • Coursera reaches 10 million users in 114 institutions in October 2014 • As of May, 2015, Coursera had more than 1000 courses from 119 institutions and 13 million users from 190 countries Coursera Case http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coursera • Coursera: is a for-profit educational technology company • List of ways to generate revenue, include: – verified certification fees – tutoring – sponsorships – tuition fees • In January 2013, Coursera announced that the American Council on Education had approved five courses for college credit • In May 2014, Antioch University announced that it was the first US institution to offer college credit for Coursera courses Coursera: behind the scenes filming By Ben Loveridge (Learning Environments) http://blogs.unimelb.edu.au/researchservices/2012/12/15/courserabehind-the-scenes-filming/ Photo: Coursera filming set-up showing autocue and Wacom Cintiq 24HD Touch (Credit: Ben Loveridge) General Preparation Notes for Filming Presentations (I) • Content creation – video segments of around six minute long are the optimal length for student engagement • Copyright – Use creative commons on flickr within your course to avoid expensive ongoing licensing – If you can’t find or create anything appropriate yourself, make sure any copyright in images or video has been cleared well in advance – Check out Astrid Bovell’s blog post on MOOC’s and the Copyright office • Programs for presenting content – Keynote / Powerpoint / PDF – Video now lives in a 16:9 world so make sure your presentations are set to 16:9 mode • in PowerPoint this is listed under the ‘page setup’ option • in Keynote it is listed in the ‘inspector mode’ so something like 1920×1080 is a good start General Preparation Notes for Filming Presentations (II) What to wear • Avoid wearing green (clashes with the green screen) or fine striped or patterned outfits (can cause strange visual effects). • Black and white clothing is not ideal • Solid muted tones and colours are ok – not too dazzling or bright • Avoid rattling jewellery • Wear clothing that a lapel mic can easily attach Style of delivery • Sitting or standing? • Are they presenting together or separately? • If standing then green screen or white background? (This affects if we use Screenflow vs recording to hard drive where picture is merged with background) • If sitting will you annotate slides with the Wacom? • Scripted with an auto cue, presenting from ‘notes view’ or off the top of the head? • Creating slides on Mac or PC (affects if we use Keynote vs Powerpoint) edX Case http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EdX https://www.edx.org • edX is a non-profit online initiative created by founding partners Harvard and MIT (in 2012) and runs on an open-source software platform (http://code.edx.org/) • edX has more than 3 million users taking over 300 courses online (of 22 October 2014) • Around 400 faculty and staff teaching courses and discussing topics online • Around 100,000 certificates earned by edX students • The source code can be found on GitHub • Topics include: – biology, business, chemistry, computer science, economics, finance, electronics, engineering, food and nutrition, history, humanities, law, literature, math, medicine, music, philosophy, physics, science, statistics and more edX Business Model https://www.edx.org • With the exception of professional education courses, edX courses are free for everyone • Some courses have a fee for verified certificates but are free to audit • In September 2014 edX announced a high school initiative • In October 2014 edX announced Professional Education courses • In March 2015 it partnered with Microsoft • In April 2015, edX partnered with Arizona State University to launch the Global Freshman Academy MOOCs from the Learners’ side • Available questions and requirements for learners before the registration to the course (Stanford as an example): https://class.stanford.edu/courses/Engineering/C S101/Summer2014/about • Registration for free • Videos, Chats, discussions, quizzes, exams, all the material available on the Internet, certificates Some Examples Courses on MOOCs • Financial Markets (Coursera): https://class.coursera.org/financialmarkets-002 • Introduction to Computer Science (edX): https://www.edx.org/course/introduction-computerscience-harvardx-cs50x#.VImAOCuUckM • Developing Android Apps (Udacity): https://www.udacity.com/course/ud853 • Intro to HTML and CSS (Udacity): https://www.udacity.com/course/ud304 Θέματα Εργασιών 1. Create a Mini Site with HTML5 specification including the <video> element (HTML5, JS) 2. Create a Mini Site on mobile with HTML5 specification including the <video> element (HTML5, JS) 3. Algorithms for video streaming & distribution (IEEE, papers, platforms, Google, YouTube, Netflix…) 4. Install the edX and create a Mini site for a lesson as an example 5. Moodle: • Installation, configuration • Create lessons – Plugin implementation for courses retrieval from a MOOC (using the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting) • Versal, create a course … References (I) • https://docs.google.com/forms/d/15W2EZhpoWaZEBeDXn_NYP95pcNBYK mzyMY-AqgJ-Z58/viewform • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coursera • http://blogs.unimelb.edu.au/researchservices/2012/12/15/courserabehind-the-scenes-filming/ • http://cit.duke.edu/blog/2012/10/what-does-it-take-to-prepare-a-dukecoursera-course/ • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EdX • http://code.edx.org/ • http://www.openuped.eu/ • https://www.udacity.com/ • https://www.udacity.com/nanodegrees References (II) • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Massive_open_online_course http://chronicle.com/article/The-Major-Players-in-the-MOOC/138817/ • http://bit.ly/1ginXMb • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coursera • https://www.coursera.org/course/ml • http://www.moneycrashers.com/netflix-hulu-amazon-comparison/ • http://blogs.unimelb.edu.au/researchservices/2012/12/15/courserabehind-the-scenes-filming/ • http://cit.duke.edu/blog/2012/10/what-does-it-take-to-prepare-a-dukecoursera-course/ • http://www.openuped.eu/ • https://iversity.org • https://www.udacity.com/ • https://www.udacity.com/nanodegrees • http://www.slideshare.net/iaindoherty/everything-you-need-to-knowabout-moocs-well-almost References (III) • http://www.slideshare.net/beboac/ichl-moo-cs • http://blogs.unimelb.edu.au/researchservices/2012/12/15/courserabehind-the-scenes-filming/ • http://code.edx.org/ • https://www.edx.org References • • • http://www.w3.org/TR/html5/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML5_video http://www.w3.org/TR/html5/embedded-content-0.html#the-video-element • http://blog.streamingmedia.com/2014/07/apples-cdn-now-live.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Content_delivery_network • • • • • https://moodle.org/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streaming_media http://www.w3.org/2010/05/video/mediaevents.html http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/video/basics/ http://blog.teamtreehouse.com/building-custom-controls-for-html5videos • http://www.openarchives.org/OAI/openarchivesprotocol.html