16Sampling Errors
advertisement

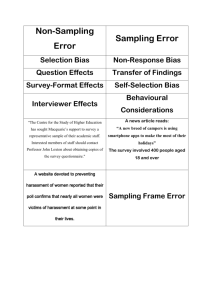
Business Research Methods Errors In Survey Research Surveys Surveys ask respondents for information using verbal or written questioning Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Random sampling error Total error Systematic error (bias) Random Sampling Error • Even though a representative sample is selected there is always a deviation between true population value & sample value • A statistical fluctuation that occurs because of chance variation in the elements selected for the sample. Systematic Error • Systematic error results from some imperfect aspect of the research design or from a mistake in the execution of the research Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Administrative error Systematic error (bias) Respondent error Respondent Error • Errors observed on respondents’ side • It is difficult to get respondents ’cooperation in getting answers that contain correct information • Two common types of respondent’ errors are - Non- Response Error - Response Bias Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Nonresponse error Respondent error Response bias Non response Error • Nonrespondents - people who refuse to cooperate --Not-at-homes --Refusals due to fear or personal preference Response Bias • A bias that occurs when respondents tend to answer questions with a certain slant that consciously or unconsciously misrepresents the truth Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Deliberate falsification Response bias Unconscious misrepresentation Deliberate Falsification • People knowingly misrepresent or give false answers when they are not certain about facts - Providing information by recall - For assuming a safe situation -To conceal personal information Unconscious Misrepresentation • People give wrong information due to ignorance -Misunderstanding a question -Prior inexperience to a subject Factors for Misrepresentation • Misrepresentation of answers either deliberately or unconsciously could be due to a number of factors • Factors are results of various biases in the nature of respondents Types of Response Biases Acquiescence bias Extremity bias Interviewer bias Auspices bias Social desirability bias Acquiescence Bias • A category of response bias that results because some individuals tend to agree with all questions or to concur with a particular position. Extremity Bias • A category of response bias that results because response styles vary from person to person; some individuals tend to use extremes when responding to questions while some tend to give neutral answers Interviewer Bias • A response bias that occurs because the presence of the interviewer influences answers. Facial expression, age, gender, tone, etc of the interviewer may play a role in inducing interviewer bias Auspices Bias • Bias in the responses of subjects caused by the respondents being influenced by the organization conducting the study. Social Desirability Bias • Bias in responses caused by respondents’ desire, either conscious or unconscious, to gain prestige or appear in a different social role. Information about educational qualification or income might be overstated to gain prestige Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Administrative error Systematic error (bias) Respondent error Administrative Error • Improper administration of the research task • Caused due to sample design error or other factors on personal front • Confusion • Neglect • Omission Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Data processing error Sample selection error Interviewer error Interviewer cheating Administrative Error • Sample selection error -improper sample design or sampling procedure execution. Mall intercept interviewers selecting only neatly dressed customers or only families with children ----Sample Frame error –frame is list of population units for sample selection. Error occurs if list does not match with target population (Incomplete list) ---Population Specification Error- Population itself defined incorrectly .To estimate market potential for electronic cars selecting population of only small car users Administrative Error • Interviewer cheating - filling in fake answers or falsifying interviewers • Interviewer error - field mistakes committed by interviewer while administering questionnaire or recording responses • Data processing error - incorrect data entry, computer programming, or other procedural errors during the analysis stage. Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Random sampling error Total error Systematic error (bias) Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Administrative error Systematic error (bias) Respondent error Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Nonresponse error Respondent error Response bias Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Deliberate falsification Response bias Unconscious misrepresentation Types of Response Biases Acquiescence bias Extremity bias Interviewer bias Auspices bias Social desirability bias Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Administrative error Systematic error (bias) Respondent error Tree Diagram of Total Survey Error Data processing error Sample selection error Interviewer error Interviewer cheating