mec13039-sup-0009-AppendixS1
advertisement

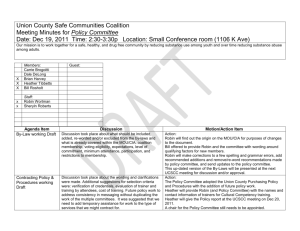
Appendix S1 New Zealand robin MHC class II B primer design We initially used primers MHCABSF1 and MHCABSR2 (Miller & Lambert 2004) to amplify all of exon 2 (260 bp) plus 43 bp of intron 2 in 12 contemporary robins from North and South Island populations following published protocol (Miller & Lambert 2004). We resolved amplified products on 2% agarose 1× TAE gels stained with SYBR Safe® (Invitrogen™) against a 100 bp ladder (GeneRuler™, Fermentas). We excised bands of expected size and used the Ultra-Sep Gel Extraction kit (Omega Bio-Tek) to purify the DNA. We then sequenced robin MHC products using the BigDye Terminator v3.1 RR100 sequencing kit (Invitrogen) on an ABI 3730xl Genetic Analyser (service provided by Genetic Analysis Services at Otago, New Zealand). We edited and aligned sequence chromatograms with CLUSTALW (Thompson et al. 1994) implemented in GENEIOUS v5.6.5 (Biomatters 2012) alongside 46 SI robin RNA sequences from Miller & Lambert (2004a,b; Genbank accessions: AY428561 - AY428568; AY730420 AY730460; Fig. A1). We relied on IUPAC ambiguity codes where base calls were ambiguous. Based on conserved regions near the 3` end of exon 2, we designed the new reverse robin primer PetMHCIIEx2R1 (5`-3`: TCG-GCG-MTC-CAC-GMK-GAACGG-GG; Fig. A1). Fig. A1 part1 Fig. A1: Sequences used to design the robin MHCIIB reverse primer, PetMHCIIEx2R1. References Biomatters (2012) Geneious version 5.6.5 created by Biomatters. Available from http://www.geneious.com. Miller HC, Lambert DM (2004) Genetic drift outweighs balancing selection in shaping post-bottleneck major histocompatibility complex variation in New Zealand robins (Petroicidae). Molecular Ecology 13, 3709-3721. Thompson J, Higgins D, Gibson T (1994) CLUSTAL-W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positionspecific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Research 22, 4673-4680.