Basic Problems in Economics - Spartanburg County School District
advertisement

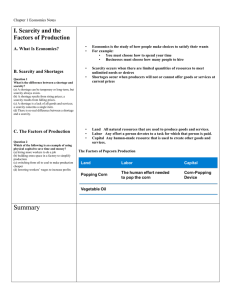
Basic Problems in Economics Economics The study of how individuals, families, businesses, and societies use limited resources to fulfill their unlimited wants. Wants vs. Needs A need is anything that you need to survive- Basic survival- Seven things A want- anything else- a nonnecessity People have unlimited wants but limited resources People have to make choices Choices Choices- how are you going to divide your resources? Businesses do the same thing- what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce People must make choices because of the problem of scarcity Problem of Scarcity People have to make choices because everything that exist is scarce Scarcity is the most basic problem in economics Scarcity is that something that you need or want is not readily available Different from a shortage- you can get more just out temporarily Scarcity always exist Factors of Production We use the factors of production to make products or services Factors of production are how we are going to use these resources to make a product or service – 1. Land- natural resources – 2. Labor- workers- human resources- make goodstouch- services are actions – 3. Capital- when you use goods and services to create another good or service Combined LLC- more valuable- Diamonds Capital also increases productivity- produce more things – 4. Entrepreneurship- start a new business a person is called an entrepreneur – 5. Technology- new factor- changes every thing Trade offs Trade Offs- sacrificing one good or service to purchase or produce another – If you buy a DVD, you are exchanging your money for the right to own the DVD Opportunity cost- value of the next best alternative given up for the alternative that was chosen Time is a scarce resource and when you give it, you are making a trade-off; and when you study, you are giving up other certain things (ex. Going to the mall…talking to friends) Any time that you make a tradeoff, you lose…you lose the next best alternative – Ex. National level Congress votes $220 Billion for new roads, or it could have been used for higher education Production Possibilities Curve Production Possibilities Curve- graph showing the maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced from a fixed amount of resources in a given amount of time. Used when you produce more than one type of product. Involves trade-offs The Classic example: – Trade off between military defense and civilian goods (guns and butter) Production Possibilities Curve What is the best balance between military spending and domestic programs? What kind of situations might arise that would cause you to change your answer? Continued on next slide. Economic Models Microeconomics- small- households Macroeconomics- large- The US Economy- activity that affects production, distribution, and the use of goods and services Theories are called economic models – They show visual representation of consumers, businesses, and other economic behavior – 1. Create a model – 2. Hypothesis – 3. Test – 4. Apply Economic Models Figure 1.10 Economic Models Graph A is an example of a model, and Graph B is a test of that model. Schools of Economic Thought Different views- Where you live affects the outcomes Values will affect the outcome Not in terms of good or bad – short term and long term outcomes