ScarRes
advertisement

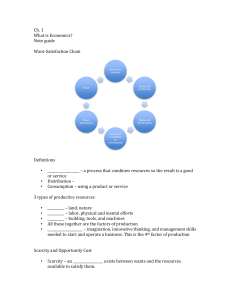
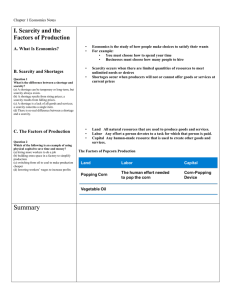
SCARCITY & RESOURCES The Factors of Production SCARCITY Scarcity limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants. This is the basic problem of economics. Scarcity is not the same as a shortage. Shortage when a good or service is unavailable, suppliers will not or cannot offer the good or service (it may not actually be that scarce). All resources are limited and are subject to scarcity. RESOURCES The three types or resources are: Land Labor natural resources that are used to make goods and services. the effort that people devote to a task for which they are paid. Divided into physical and human. Capital any human-made resource that is used to create other goods and services. FACTORS OF PRODUCTION Entrepreneurship is an individual’s ability to start a new business, to introduce new product and techniques, and to improve management techniques. Entrepreneurship combined with the three types of resources (Land, Labor & Capital) make up the Factors of Production. The factors of productions are then used to produce Goods and Services. TRADE-OFFS & OPPORTUNITY COST A trade-off is defined as an alternative that we sacrifice when we make a decision. This applies to individuals, families, corporations and societies. People face trade-offs. Every decision involves choices, more of one good means less of another. Example: The most desirable alternative given up when we make a decision is called the opportunity cost. The Cost of something is what you give up to get it. Whatever we choose to do, we could have chosen to do something else instead. Some costs are obvious such as out-of-pocket expenses, other costs are less obvious but must be included in total opportunity cost. Only actions have costs; if there is no choice there is no cost. Cost is subjective. THINKING AT THE MARGIN Thinking at the Margin involves deciding whether to do or use one more additional unit of some resource. Rational people think at the margin. Economics assumes that people act rationally. That they try to act so as to gain the most benefit for themselves compared to the costs. Microeconomics focuses on small (marginal) changes, such as the cost or benefit of a small increase or decrease. If the benefits outweigh the costs - do it! PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES A Production Possibilities Curve is a graph that shows alternative ways to use an economy’s resources. PPCs show alternative ways to use an economy’s productive resources. Guns and butter! The Production Possibilities Frontier is the line on a production possibilities graph that shows the maximum possible output PPC CURVE INCENTIVES & SUBSTITUTES People respond to incentives If rational people compare costs and benefits, then changes in either one may change decisions People respond to incentives like changes in prices All actions have substitutes Principle of substitution: when the opportunity cost in an activity increases, people substitute other activities in its place. The closer the substitute, the greater is the degree of switching that takes place when the opportunity cost changes For example, skiing is a substitute for skating; drinking Coke is substitute for drinking Pepsi