KINGDOM PROTISTA

Chapter 9: Section 1
Protist- An organism that lives in a moist or wet habitat
Contains organisms that don’t fit anywhere else!
ALL PROTISTS
Have a nucleus (eukaryotic)
SOME PROTISTS
Single celled/Many celled
Make food/Consume food
Otherwise known as ALGAE
All-
contain chlorophyll make own food
Some-
Single-celled/many-celled
Are not green b/c a different pigment covers chlorophyll
Divided into 6 phyla according to their pigments and how they store food
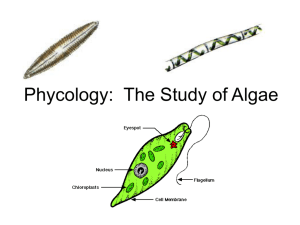
Common name- Euglenas
Characteristics:
Single-celled
Pigment is chlorophyll
Stores food as carbohydrates
No cell wall, but thick layer inside cell membrane
Moves using flagella (whip like tail)
Has an eyespot that respond to light
Common name- Diatoms
Characteristics:
Single-celled
Stores food as oil
Golden-brown pigment & chlorophyll
Cell wall is a glasslike shell made from silica
Common name: Dinoflagellates
Characteristics:
Single-celled
Stores food as oil & starch
Red pigment & chlorophyll
Move with 2 flagellum causing it to spin
Many produce a chemical that causes them to glow!
Common name: Green Algae
Characteristics:
Single-celled and many-celled
Store food as starch
Contains only chlorophyll
Common name: Red Algae
Characteristics:
Most are many- celled
Store food as starch
Contain red pigment that absorbs minimal light
Common name: Brown Algae
Characteristics:
Many-celled
Store food as starch
Brown pigments & chlorophyll
Diatom shells are used in paints & make up
(make it shiny) and toothpaste (make it abrasive)
Red Algae is used in pudding and toothpaste
(makes them creamy & smooth)
Brown Algae is used in ice cream & marshmallows (makes thick) and is eaten in sushi & salads
A main food source for herbivores of the water
Provides oxygen through photosynthesis
Otherwise known as PROTOZOA
All single-celled organisms
Can’t make their own food (heterotrophs)
Contain special vacuoles for digesting food & ridding excess water
Four phyla based on method of movement
Common name: The Amoebas
Use a temporary extension of the cytoplasm called a pseudopod to:
Move- extend a section out and drag forward
Eat- extension surrounds the food particle (endocytosis)
Common name: Flagellates
Move by whipping one or more flagella
Common name: Ciliates
Move by using cilia
Short threadlike fibers that beat back/forth
Have two nuclei
Feed through an “oral groove”
Have no way of moving on their own
Only survive as a parasite
Plasmodium is the protist that causes
Malaria
Good- Consuming bacteria
Example: Waste water treatment
Bad- Disease causing
Examples: African Sleeping Sickness, Malaria, dysentery (diarrhea)
The amoeba that causes acute diarrhea!
Trysanopoma among red blood cells in someone with Sleeping Sickness
Have features of protists and fungi
ALL
Reproduce using spores
Obtain energy from decomposing organic materials
At times use pseudopods to move and feed like an amoeba
Most of their life is spent acting like a fungus
Feeding on decaying matter and producing spores
Protist like b/c reproductive spores have flagellum to move
Fungus like b/c they grow as a mass of threads over a plant or animal, digest it and then absorb its nutrients