Making
Decisions:
Artificial
Intelligence
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
is the science of making machines imitate
human thinking and behavior.
• Reasoning
• Learning
• Being able
to adapt
• Ability to
solve a
problem
Comparing a DSS to Artificial
Intelligence
• Decision Support System (DSS)
– User actively involved with the system.
– Relies on user expertise. The user must understand
problem situation and what needs to be done.
– The user makes the ultimate decision/choice.
• Artificial Intelligence
– User not as actively involved because all of the expertise
is built into the system.
– The system makes the ultimate decision/choice.
Robotics
A mechanical device equipped with simulated human
senses and capable of taking actions on its own.
• Expert Systems are computerized advisory programs
that imitate the reasoning process of experts. They
consist of a knowledge base and a set of rules for
applying that knowledge base to a particular situation.
Most common form of AI in business.
• Neural Networks mimic the way the brain works,
analyzing large quantities of data and information to
establish patterns and infer relationships.
• Genetic algorithms mimic the evolutionary, survivalof-the-fittest process to generate increasingly better
solutions to a problem. Genetic algorithms work to find
the best/optimal answer.
• Intelligence agents accomplish a specific task for the user.
AN EXPERT SYSTEM
is an artificial intelligence system that
applies reasoning capabilities to reach a
conclusion.
An expert system captures expertise from a
human expert and applies it to a problem.
Tricks of the trade
Knowledge base
Reasoning Process
Expert Systems
• Programming is in the form of Rules, If-Then
statements, and Reasons
• Decision Support System guides you, but you
must reason through the problem.
• Expert Systems : you provide the facts, it solves
the problem.
– Recommendation from some expert systems is a
probability or other type of “score.”
• Used as diagnostic and prescriptive.
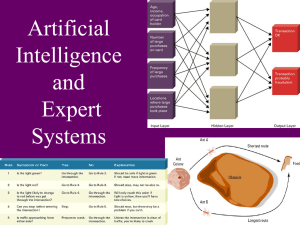
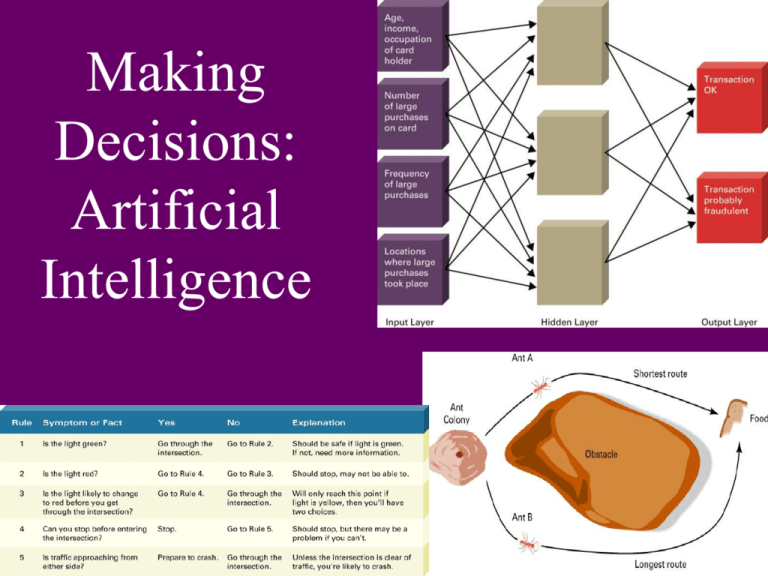
Expert System Rules for a Bank Mortgage Application
Example of Medical
Expert System for lung
cancer treatment
If lung capacity is high
AND X-ray results are positive
AND patient has fever
AND patient has coughing
THEN surgery is necessary.
If tumor has spread
OR contraindications to surgery exist
THEN surgery cannot be performed
Traffic Light Expert System
Expert Systems
• Expert Systems are computerized advisory programs
that imitate the reasoning process of experts. They
consist of a knowledge base and a set of rules for
applying that knowledge base to a particular situation.
• EXPERT SYSTEMS apply rules to solve a problem.
– The system uses IF statements and user answers to
questions in order to reason just like a human does.
– It takes something the users doesn’t know and applies rules
to indicate what to do.
• Expert Systems: ask a series of questions to determine
what is “known.”
Easy
Diagnosis
Medical
Expert
System
WHAT EXPERT SYSTEMS CAN DO
• Can handle massive
amounts of information
and they can provide
new information.
• Can draw conclusions
from complex
relationships
• Can explain their
reasoning or suggested
decisions
• Provide consistency in
decision making.
• Improve customer
service.
• Reduce errors and costs.
• Provide portable
knowledge
WHAT EXPERT
SYSTEMS CAN’T DO
• Handle all types of domain expertise. Human
experts might not fully be aware of the
process that they use. Can’t put everything
into machine form.
• Can’t solve problems in areas not designed
for. Can’t learn to solve new things.
• Apply common sense or judgment to a
problem
Expert Systems Perform Diagnostic
and Prescriptive Tasks Like
•
•
•
•
•
•
Expert System used
Auditing and tax planning
by American
Diagnosing illnesses
Express’ Optima
Card program.
Managing forest resources
VB Loan
Evaluate credit and loan applications
System
Computer help desk diagnosis assistance
Rules to follow when directing air traffic
Smartflow
Acquired Intelligence
Whale Watcher
Douglas Fir Cone and Seed
Exsys Corvid
Which Dog Breed is best for you?
Marathon Race Advisor
Albuquerque Restaurant Advisor
Web Support
Camcorder Selection
Ethical Questions and the Use of
Expert Systems
• An expert system will act as it is programmed. If
you program in bias, then the system will be
biased.
• The expert system is consistent, which is easily
defended in court.
• Can distinguish between good and bad, but may
not be able to distinguish between degrees of
good.
• Expert Systems are computerized advisory
programs that imitate the reasoning process of
experts.
– EXPERT SYSTEMS apply rules to solve a problem.
– Expert Systems: ask a series of questions to determine
what is “known.”
• Neural Networks mimic the way the brain works,
analyzing large quantities of data and information to
establish patterns and infer relationships.
– They recognize patterns
• They can “see” subtle, hidden and newly emerging patterns
within large amounts of complex data.
A NEURAL NETWORK
is an artificial intelligence system which is
capable of learning because it’s patterned
after the human brain. Uses parallel
processors.
A neural network simulates the human ability to
classify things based on the experience of seeing
many examples.
Pattern Recognition
Learn by looking at a data set and finding patterns in it.
NEURAL NETWORKS
• Typically used to combat attempts at fraud
•
Credit card fraud or insurance fraud.
• Able to detect money laundering attempts.
• Working in conjunction with X-ray machines, can be
used to detect weapons and other forbidden items.
• Often used to make investment decisions (stocks,
bonds, futures markets, etc.)
•
Can also detect inefficiencies in financial markets
Learn by looking at a data set and finding patterns in it.
A Neural Network Can Perform
Pattern Recognition Tasks Like
• Distinguishing different chemical compounds
• Detecting abnormalities in human tissue that may
signify disease
Analyze travel
patterns to detect potential drug smuggling.
• Analyze handwriting to detect forgeries.
• Detecting credit card and insurance fraud
• Track habits of insurance customers and predict
which ones might not renew their policies
• Virus Detection Software by IBM
• Neugent monitors 1,200 data points in the Allstate
Insurance network every 5 seconds, trying to
predict a potential problem in/with the network.
Neural networks attempt to mimic the structure and
functioning of the human brain. They contain input, output
and hidden layers. The hidden layers use various weights of
strength to classify and categorize things. As the system
learns, it can change the classification weights.
Neural networks can adjust or change themselves
over time based upon data input regarding
successful and unsuccessful mortgage applications.
Neural networks can adjust themselves as they
“learn”. Expert systems follow fixed rules.
Neural Networks serve as Learning Systems
• Allows the computer to change how it functions or
reacts to situations based on the feedback it
receives.
• There are computer games with learning abilities.
• 20Questions www.20Q.net
• Fuzzy logic and neural networks are often
combined to express complicated and subjective
concepts (that are vague and ambiguous) in a form
that makes it possible to simplify the problem and
apply rules with some degree of certainty.
Fuzzy Logic
• Fuzzy Logic: a special field of computer science that
allows for shades of gray and does not require
conditions to be black/white, yes/no, or true/false.
• A mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective
information so that ambiguous information such as
“short/long” or “hot/cold” or other “non-exact areas usable
in computer systems
• Applications
–
–
–
–
–
–
Google’s search engine (your perception of a topic frames your query)
Washing machines that wash until the water is “clean”
Antilock brakes and subway/tram control systems
Auto focus cameras
Temperature sensors attached to furnace controls
Medical equipment that automatically makes corrections based
upon patient vital signs.
• EXPERT SYSTEMS apply rules to solve a problem.
– The system uses IF statements and user answers to questions in order
to reason just like a human does.
– It takes something the users doesn’t know and applies rules to indicate
what to do.
– Expert Systems: ask a series of questions to determine what is
“known.”
• NEURAL NETWORKS recognize/learn patterns and can apply
that learning to the unknown.
– It is either taught by someone or teaches itself. After it is taught to
recognize the pattern, it can adjust itself to reflect new learning.
– Neural networks: system is “guessing” based upon examples and
patterns found in the data set- trying to figure out what category
something fits in.
• GENETIC ALGORITHMS generate several generations of
solutions, with each generation resulting in a better solution to
the problem.
A GENETIC ALGORITHM
is an artificial intelligence system that mimics
the evolutionary, survival-of-the-fittest
processes to generate increasingly better
solutions to a problem.
Begin running Car evolution genetic algorithm
Genetic algorithms produce several generations
of solutions, choosing the best of the current set
for each new generation.
THE CONCEPTS OF EVOLUTION
IN GENETIC ALGORITHMS
• SELECTION - or survival of the fittest. The
key is to give preference to better outcomes.
• CROSSOVER - combining portions of good
outcomes in the hope of creating an even
better outcome.
• MUTATION - randomly trying combinations
and evaluating the success (or failure) of the
outcome.
Seeking an optimal configuration.
Genetic Algorithms Can Generate Lots of
Solutions As In
• Deciding which combination of projects a firm should invest in,
given limited investment dollars.
• Generating solutions to routing problems
– How much cable or track to lay?
– What path/route should your delivery vehicles take?
• Used to optimize production schedules (make the best use of your
production resources)
• Investment companies use them to generate optimal
stock/bond portfolios by considering different combinations of
stocks and bonds .
• Clothing manufacturing: cutting a piece of fabric so as to
generate the least amount of waste.
The Traveling Salesman
• EXPERT SYSTEMS apply rules to solve a problem.
– The system uses IF statements and user answers to
questions in order to reason just like a human does.
– It takes something the users doesn’t know and applies rules
to indicate what to do.
• NEURAL NETWORKS recognize/learn patterns and
can apply that learning to the unknown.
– It is either taught by someone or teaches itself. After it is
taught to recognize the pattern, it can adjust itself to reflect
new learning.
• GENETIC ALGORITHMS generate several
generations of solutions, with each generation
resulting in a better solution to the problem.
• Expert Systems: ask a series of questions to
determine what is “known.”
• Neural networks: system is “guessing” based
upon examples and patterns found in the data
set- trying to figure out what category
something fits in.
AN INTELLIGENT AGENT
is a software entity that senses its environment and
then carries out some operations on behalf of a user,
with a certain degree of autonomy, and in doing so,
employs knowledge or representation of the user’s
goals or desires.
The Agent will take your profile and preferences and
then go out and work on your behalf.
Characteristics of an intelligent agent
Autonomy: can act without you telling them what to do
Adaptivity: can change itself and what it does based upon
your changing characteristics.
Sociability: can communicate and interact with other
agents that it encounters.
Types of Intelligent Agents
• Information Agents: search for information and bring it back to you (from the
Internet or a database)
– Buyer agents, shopping bots, search and filtering agents, Googlebots that scour the
Internet locating and indexing sites that ultimately appear in search results when you do a
Google search.
– The SuperFetch feature (search feature) found in Vista
• Monitoring and Surveillance Agents: constantly observe and report back on
what they see.
– Applications software agents monitor the activities of software users and offer
suggestions for improvement.
– Wizards and the Microsoft Office Assistant (Clip It)
• User Agents: act as a personal assistant by taking action on your behalf.
Examples include sorting and prioritizing email, filling out forms on the Web
automatically for you, and automatically storing your information.
• Data Mining agents operate in a data warehouse by sifting through the data, trying
to discover trends, relationships and patterns through the use of multidimensional
statistical analysis.
Based On
Starting
Information
AI System
Problem Type
Expert
Systems
Diagnostic or
prescriptive
Strategies of
experts
Expert’s
know-how
Neural
Networks
Identification,
classification,
prediction
The human
brain
Acceptable
patterns
Genetic
Algorithms
Biological
Optimal solution evolution
Set of
possible
solutions
Intelligent
Agents
Specific and
repetitive tasks
Your
preferences
One or more AI
techniques
• A relational database stores information in a series of two
dimensional tables.
• Data warehouses are multidimensional, containing layers of
rows and columns. Each dimension is an attribute of
information.
Data-mining agents perform
multidimensional analysis in data
warehouses
• Cube – common term for the representation of multidimensional information (layers, rows, columns)
• Info in an Excel spreadsheet and a relational
database (Access) appears in the form of a two
dimensional table of rows and columns.
• By adding a Page Field to a Pivot Table, you
can add another dimension of information: 3-D
(rows and columns and layers).
– Creating a 3-dimensional Pivot Table in Excel is a
means of conceptually building a data warehouse.
Page fields represent the depth layer
• Pivot Tables can help you see relationships in
the data
Extra Credit
Opportunities
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
©2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved
• This type of system is used to find the very best, or
optimal answer? It is based on evolutionary
concepts
– The Genetic Algorithm
• What type of system is based on pattern
recognition? Due to its pattern recognition abilities,
it is capable of learning. It can detect forgeries and
new viruses it has never seen.
– The Neural Network
• This type of system can reason through a process. It
is used for diagnostic and prescriptive types of tasks.
– The Expert System
• This is a highly interactive system where you have to know what
you are doing to effectively use it. It is used to solve nonprogrammed decisions (unstructured problems) where there are
several possible correct answers. Spreadsheet what-if analysis is
an example of what this system can do.
– Decision Support System
• Data mining agents conduct multi-dimensional analysis of the data
found in a ______________.
– Data warehouse
• Buyer agents, shop bots and googlebots are examples of what type
of agent?
– Information agents
• The Microsoft Office Assistant wizard (Clip It) is an example of
what type of agent?
– Monitoring and surveillance agent
• As you move from lower to upper levels in an
organization, information needs move from ___________
in nature to __________.
– Transactional in nature to analytical
Decision support systems
Transactional decisions
Ad-hoc decisions
Nonprogrammed decisions
Programmed decisions
Analytical decisions
(these are the answers)
• ____________ have well-defined relationships and are
easily quantifiable while _________________ may have
several answers that will work, and they are not easily
quantifiable.
• If you are trying to find the very best solution
given the constraints provided, you are using a
technique called ___________
– optimization
• If you want to find a good solution, one that
satisfies all your decision criteria, without
necessarily being the best solution., you are using
a technique called _____________.
– satisficing
The End
Natural Language Processing
• Allows the computer to understand and react to
statements and commands made in a “natural”
language, such as English.
– Often used to replace telephone answering menu
systems. Have also been used to make dictations and text
files from speech.
• Three Levels of Natural Language Processing
– Command recognition
– Discrete voice recognition: recognizes dictated speech
with pauses between words.
– Continuous voice recognition: when a system recognizes
natural speech and understands its meaning.
Jane saw a letter on the desk. She quickly read it.
Vision Systems
• Used to capture, store, and retrieve visual images
and pictures.
• Used in fingerprint identification, identifying
people based on facial features, robotics, and by
the Post Office to sort mail
Learning Systems
• Allows the computer to change how it functions or
reacts to situations based on the feedback it
receives.
• There are computer games with learning abilities.
• 20Questions www.20Q.net
Components of Expert Systems
The Inference Engine
• Processes the domain expertise and your
problem facts to reach a conclusion.
– This is where the expert system does its “reasoning.”
The Knowledge Base
• Stores all relevant data, information, rules,
cases, or relationships that the expert system
uses.
– IF THEN, ELSE statements
– Cases: find cases in the knowledge base similar to
the problem or situation at hand, and then modify the
solution of the existing case to fit the new/current
problem or situation.
COMPONENTS OF AN EXPERT
SYSTEM
• KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION - used by the
knowledge engineer to build the expert system.
– Knowledge may also come from books, reports,
databases, data warehouses, diagrams, etc.
• USER INTERFACE - used to run a
consultation. You interact with the system.
• EXPLANATION FACILITY - stores the “Why?”
information.
– Consultation: The user can ask the system to
explain the logic that underlies a question.
A Self-Organizing Neural Network: finds patterns and
relationships in vast amounts of data by itself.
Back-propagation neural networks are trained by
someone. You teach the neural network by example.
Neural networks attempt to
mimic the structure and
functioning of the human
brain. They contain input,
output and hidden layers.
The hidden layers use
various weights of strength
to classify and categorize
things. As the system learns,
it can change the
classification weights.