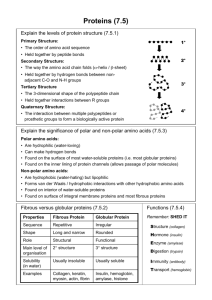
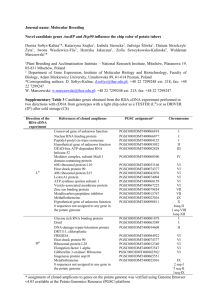
Protein: Amino Acids
advertisement

Protein: Amino Acids Chapter 6 Amino Acid “R” Amino Acids • Essential amino acids –i.e. indispensable amino acids – PVT. TIM HALL (or PVT. MAT HILL) • Nonessential amino acids –i.e. dispensable amino acids • “Conditionally” essential amino acids An Essential Amino Acid Nonessential Amino Acids Proteins Remember Condendation? • Dipeptide • Tripeptide: Yes...it’s three of ‘em. Proteins • Polypeptide Proteins • Amino acid sequences – With 20 different amino acids you can say a lot! Protein shape and function Proteins • Protein denaturation – uncoiling • heat or acid hydrolysis. – loss of function Protein Digestion • Stomach –HCl activated pepsinogen (proteolytic enzyme) –Pepsinogen* pepsin –Pepsin hydrolyzes proteins! *Proenzyme-an inactive form of enzyme! Protein Digestion • Small intestine –Proteases-more hydrolysis! •Intestinal and pancreatic –Peptidases Protein Digestion in the GI Tract Protein Absorption • Carriers • Capillaries • Absorption misconceptions – Enzyme/amino acid supplements Protein Synthesis • Sequencing errors Roles of Proteins • Building material –Growth –Maintenance Roles of Proteins • Enzymes Roles of Proteins • Hormones Roles of Proteins • Regulation of fluid balance –Edema • Acid-base regulation –Acidosis –Alkalosis Transport Proteins One of the most important proteins in your body! The Sodium-Potassium Pump in action! Roles of Proteins • Immunity –Antibodies –Antigens Protein Metabolism • Protein turnover –Amino acid pool • Nitrogen balance –Positive nitrogen balance –Negative nitrogen balance Protein Metabolism • Using amino acids to make proteins • Using amino acids to make nonessential amino acids Protein Metabolism • Using amino acids to make other compounds –Neurotransmitters Protein Metabolism • Using amino acids for energy and glucose • Deamination-removal of NH3 • Using amino acids to make fat Protein Quality • High-quality proteins • Digestibility –Animal (90%) vs. plant (70%) • Amino acid composition –Limiting amino acid Protein Quality • Reference protein • Complementary proteins Protein Quality • PDCAAS – Proteindigestibilitycorrected-aminoacid-score Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM) • Acute PEM • Chronic PEM Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM) • Marasmus • Kwashiorkor • Marasmus-kwashiorkor mix Protein-Energy Malnutrition (PEM) • Infections –Dysentery • Rehabilitation-can they recover? Health Effects • Heart disease • Cancer • Adult bone loss –osteoporosis Health Effects • Weight control • Kidney disease? Recommended Intakes Daily Value –50 g protein •10% of a 2000 kcal diet • RDA –0.8 g/kg/day –10% - 35% of energy intake Recommended Intakes • Adequate intake • Protein in abundance Supplements • Protein supplements • Amino acid supplements Vegetarian Diets Vegetarian Diets • Diet planning –Protein •Lacto-ovo-vegetarians •Meat replacements –Texturized vegetable protein-basically soybeans Vegetarian Diets • Vitamins and minerals – Lactovegetarians-easier to meet calcium/vit. D requirements – Vegans-supplements likely needed. – Omega-3 fatty acids also needed. Vegetarian Diets • Vegetarian diets through the life span –Pregnancy and lactation –Infancy –Childhood and adolescence