Chapter 1
advertisement

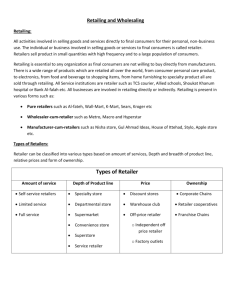
Retailing & Wholesaling Chapter 13 Top 10 Retailers in America 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Wal-Mart Kroger Home Depot Sears K-Mart Albertson’s Target J.C. Penny Costco Safeway Sales (in billions) $ 193.295 $ 49.000 $ 45.738 $ 40.937 $ 37.028 $ 36.762 $ 36.362 $ 32.649 $ 32.164 $ 31.976 http://www.stores.org/archives/2001top100_1.html Change (00-01) +15.9% +8.0% +19.0% +3.7% +3.1% -1.9% +9.5% +0.4% +17.1% +10.8% What is Retailing? Retailing - Includes all the activities Involved in Selling Goods or Services Directly to Final Consumers for Their Personal, Non-business Use. Retailing can be done in stores (store retailing) or out of a store (nonstore retailing) such as: Direct mail Catalogs Telephone Home shopping shows Internet Top 10 Internet Retailers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 eBay Amazon.com Dell Buy.com Egghead.com Gateway Quixtar uBid Barnes & Noble Outpost US Sales $ 3.5-3.7B $ 1.7-1.9B $ 1.1-1.3B $ 7-800M $ 5-600M $ 5-600M $ 4-450M $ 275-325M $ 275-325M $ 2-250M http://www.stores.org/eng/archives/00top100int_1.html Classification of Retailing Amount of Service Self-Service, Limited-Service and Full-Service Retailer Product Line Length and Breadth of the Product Assortment Relative Prices Pricing Structure that is Used by the Retailer Retail Organizations Independent, Corporate, or Contractual Ownership Organization Classification of Retailing: Amount of Service Self-Service Retailer Provide Few or No Services to Shoppers Limited-Service Retailers Provide Only a Limited Number of Services to Shoppers Full-Service Retailers Retailers that Provide a Full Range of Services to Shoppers Classification of Retailing:Product Line (Tab. 13.1) Store Description Specialty Stores Narrow Product Line, Deep Assortment Department Stores Wide Variety of Product Lines i.e. Clothing, Home Furnishings,… Supermarkets Wide Variety of Food, Laundry, & Household Products Convenience Stores Limited Line of HighTurnover Convenience Goods Classification of Retailing:Product Line (Tab. 13.1) Store Superstores Description Large Assortment of Routinely Purchased Food & Nonfood Products Discount Stores Standard Merchandise at Lower Prices Off-Price Retailers Changing Collection of Higher-Quality Goods at a Reduced Price Warehouse Clubs Limited Selection of Brand-Name Grocery Items, Appliances Classification of Retailing:Relative Prices Higher Prices and Offer Higher-Quality Goods and Superior Customer Service Regular Prices and Offer Normal-Quality Goods and Average Customer Service Low Prices and Offer Lower-Quality Goods and Little Customer Service Discount Stores “Off-Priced” Retailers Catalog Showrooms Classification of Retailing:Retail Organization Merchandising Conglomerates Corporate Chain Voluntary Chain Franchise Organizations Retailer Cooperatives Retailer Marketing Decisions Retailer Strategy • Target Market • Retail Store Positioning (Fig. 13.1) Retailer Marketing Mix •Product and service assortment •Prices •Promotion •Place (location) Product Assortment and Services Decisions Product Assortment • Width and Depth of Assortment • Quality of Products • Product Differentiation Strategies Services Mix Key Tool of Non-price Competition for Setting One Store Apart From Another Store’s Atmosphere • Physical Layout • “Feel” That Suits the Target Market and Moves Customers to Buy Retailer’s Price, Promotion, & Place Decisions Price Decisions Target Market, Product & Service Assortment, Competition Promotion Decisions Using Advertising, Personal Selling, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, & Direct Marketing to Reach Customers Place Decisions Shopping Centers, Central Business Districts, or Power Centers, or Online Shopping The Future of Retailing New Retail Forms and Shortening Retail Lifecycle Growth of Non-store Retailing Increasing Intertype Competition Rise of the Megaretailer Growing Importance of Retail Technology Global Expansion of Major Retailers Retail Stores as “Communities” or “Hangouts” The Wheel of Retailing High Margin High Price High Status 1 3 2 1 2 3 3 4 Low Margin Low Price Low Status 2 1 = Discount 2 = Superstore 3 = Warehouse Club 4 = Combination Store 1 ELECTRONIC COMMERCE DEFINITION: Exchange of information, goods, service, and payments by electronic means. History of E-Commerce E-commerce actually began in the 1970s when larger corporations started creating private networks to share information with business partners and suppliers. This process is called Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). Prodigy was running text ads and selling flowers in the early '80s. The first documented Online sale in 1994 was what? A CD E-Commerce Today Some major product categories have paved the way: travel services ($5.95 billion in 1999 sales), computer hardware and software ($5.8 billion), books ($1.7 billion), gifts and flowers ($730 million), music ($540 million), and apparel and footwear ($460 million), (eMarketer in Business 2.0 Jan 2000). E-Commerce Services Today In 1999, the online market size for business services was estimated at $22 billion. Primary service categories include financial ($7.3 billion, 1999), professional ($4.4 billion), administrative support ($3.9 billion), corporate travel ($5 billion), and telecommunications ($1.5 billion). By 2003, Forrester Research predicts that online services will represent nearly 8 percent of the overall sector hardly a drop in the bucket. Future of E-Commerce eMarketer, an Internet technology (IT) research and reporting firm, estimates that the dollar figure for ecommerce will rise from approximately U.S. $18 billion in 1998 to U.S. $294 billion in 2002. US Or maybe $184 billion by 2004. (Forrester, Business 2.0 Jan 2000) In Europe, consumers' internet purchases will jump from: US $2.9 billion in 1999 to US $174 billion in 2005. Online business-to-business e-commerce is projected to speed past $1 trillion in annual revenue by 2003 Future Trends to Watch in E-Commerce Women take control. Women make or influence 80 percent of household sales in the United States, according to WomanTrend, despite the fact that they make up 51 percent of the population. The untapped get tapped. Two highly touted markets $509 million health and beauty, and $513 million grocery still lag behind expectations. More "click and mortar." Traditional retailers Circuit City, Crate and Barrel, Sears, Toys R Us, Wal-Mart, and Federated Department Stores missed the boat in 1995 and 1996, but rest assured they "get it" now, and are attempting re-entry, this time around with more money and smarts. Watch out. Still a Long Way To Go Andersen Consulting and Forrester Research both show shopping cart abandonment rates of 25%. E-commerce still accounts for less than 1% of total retail sales Pure plays are struggling to maintain cash flow and are either: Folding Cutting back Being bought at cheap prices Security Issues are Important Discussion Connections Online retailers provide an alternative to shopping the old fashioned way. Discuss the differences in shopping for books and music at www.Amazon.com vs. Barnes & Noble Booksellers. Discuss the differences in shopping for groceries at www.peapod.com vs. your local grocery store. Which do you prefer and why? What is Wholesaling? All the activities involved in selling goods and services to those buying for resale or business use. Wholesaler - those firms engaged primarily in wholesaling activity. Wholesalers buy mostly from producers and sell mostly to: Retailers, Industrial consumers, and Other wholesalers. Why are Wholesalers Used? Wholesalers are Often Better at Performing One or More of the Following Channel Functions: Management Services & Advice Market Information Risk Bearing Selling and Promoting Wholesaler Functions Financing Buying and Assortment Building Bulk Breaking Warehousing Transportation Types of Wholesalers Merchant Wholesaler Independently Owned Business that Takes Title to the Merchandise it Handles. Manufacturers’ Sales Branches and Offices Wholesaling by Sellers or Buyers Themselves Rather Than Through Independent Wholesalers. Brokers/ Agents They Don’t Take Title to the Goods, and They Perform Only a Few Functions. Wholesaler Marketing Decisions Wholesaler Strategy • Target Market • Service Positioning (Fig. 13.1) Wholesaler Marketing Mix • Product and service assortment • Prices • Promotion • Place (location) Trends in Wholesaling Consolidation within the Industry is Reducing # of Wholesalers Distinction Between Large Retailers and Wholesalers Blurs Wholesalers Will Continue to Increase the Services Provided Wholesalers Are Beginning to Go Global