Accounting Theory: Roles & Approaches Presentation
advertisement

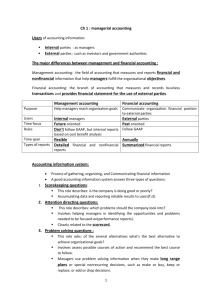
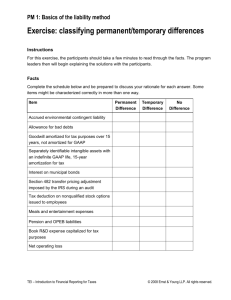
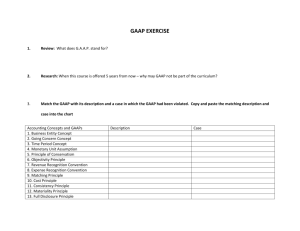
Accounting Theory: Roles and Approaches Lectured by S. Sutthachai Accounting Department Faculty of Management Science Khon Kaen University A Theory: Definition A theory: ‘a set of interrelated constructs (concepts), definitions, and propositions that present a systematic view of the phenomenon by specifying relationships among variables with the purpose of explaining and predicting the phenomenon’ A theory includes propositions linking concepts in the form of hypotheses to be tested. A Theory: Definition Elements of a theory include: Concepts: the main units of a theory and it is devised to refer to identifiable characteristics or phenomena. : The better the concept, the better the theory. : A formation of concept starts from the idea or percept generating a concept designated by terms. A Theory: Definition Elements of a theory include: Propositions: establish relation between the concepts of a theory. : designated by a sentence. : characterized by 1) the number and degree of predicates; and 2) the degree of generality. A Theory: Definition Elements of a theory include: Hypotheses: a proposition about a relationship whose truth or falsity is yet to be determined by an empirical test. : Confirmation of a theory is the extent to which a hypothesis is capable of being shown to be empirically true, that is, of describing the real world accurately : Falsification?? Functions of a Theory Descriptive function: using the constructs or concepts and their relationships so as to provide the best explanation of a given phenomenon and the forces underlying it. Delimiting function: selecting the favorite set of events to be explained and assigning a meaning to the formulated abstractions of the descriptive stage. Functions of a Theory Generative Function: the ability to generate testable hypotheses or to provide hunches, notions, and ideas from which hypotheses could be developed. Integrative Function: the ability to present a coherent and consistent integration of the various concepts and relations of a theory. Evaluation of a Theory A theory is evaluated to prove the adequacy of what it proposes. Criteria to evaluate a theory??? Accounting Theory: Definition Accounting theory: A set of broad principles that: 1) provides a general frame of reference by which accounting practice can be evaluated; and 2) guides the development of new practices and procedures. Accounting Theory: Definition Accounting theory should explain and predict accounting phenomena. The primary objective of accounting theory is to provide a basis for the prediction and explanation of accounting behaviour and events. Accounting Theory: Definition Accounting theory should have 3 elements: 1) encoding of phenomena to symbolic representation; 2) manipulation or combination according to rules; and 3) translation back to real-world phenomena. Formation of Accounting Theories Accounting practitioners and researchers draw on different images of accounting to elaborate different theories of accounting. Views of accounting: Accounting as an ideology Accounting as a language Accounting as a historical record Formation of Accounting Theories Views of accounting (continue): Accounting as current economic reality Accounting as an information system Accounting as a commodity Accounting as mythology Accounting as rationale Accounting as imagery Accounting Theory: Approaches Deductive Approach: it moves from general (basic proposition about the accounting environment) to the particular (accounting principles first and accounting techniques second). Accounting Theory: Approaches Deductive approach used in formulating a conceptual framework of accounting: Specifying the objectives of financial statements Selecting the ‘postulates’ of accounting Deriving the ‘principles’ of accounting Developing the ‘techniques’ of accounting Accounting Theory: Approaches Inductive Approach involves 4 stages: Recording all observations Analysis and classification of these observations to detect recurring relationships (‘likes’ and ‘similarities’) inductive derivation of generalizations and principles of accounting from observations that depict recurring relationships testing the generalizations. Accounting Theory: Approaches Ethical Approach: the concepts of fairness: fair, unbiased and impartial presentation justice: equitable treatment of all interested parties true: true and accurate accounting statements without misrepresentation. Accounting Theory: Approaches Sociological Approach: Social Welfare the social effects of accounting techniques Socioeconomic accounting: to encourage the business entities that function in a free-market system to account for the impact of their private production activities on the social environment through measurement, internalisation, and disclosure in their financial statements. Accounting Theory: Approaches Economic Approach: General Economic Welfare the choice of different accounting techniques depends on their impact on the national economic good. Accounting policies and techniques should reflect ‘economic reality’ and the choice of the techniques should depend on ‘economic consequences’. A Role of Accounting Theories Accounting Theories A Conceptual Framework Accounting Principles, Concepts and Postulates Accounting Techniques GAAP Accounting Standards Accounting Policies GAAP GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles): a guide to the accounting profession in the choice of accounting techniques and the preparation of financial statements in a way considered to be good accounting practice. GAAP Conditions under which an accounting method will be deemed as generally accepted: The method will be in actual use; The method would have support in the pronouncement of the professional accounting societies; The method would have support in the writing of a number of respected accounting teachers and thinkers. GAAP Examples of pronouncements of the professional accounting societies!!!! In a new situation, what methods would be generally accepted???? GAAP Little GAAP and Big GAAP A little GAAP for smaller and/or closely held businesses. A big GAAP is for large companies What is the definition of ‘small businesses’? Accounting Standards What are the differences between GAAP and accounting standards??? Accounting Standards Accounting standards consist of 3 parts: A description of the problem to be tackled. A reasoned discussion or ways of solving the problems. in line with discussion or theory, the prescribed solution. Accounting Standards Reasons to establish standards are: to ensure quality of financial information to be guidelines and rules to be database for a government to generate interests in principles and theories. Accounting Standards Who should set accounting standards? Theories of regulation: Public-interest theories Interest-group or capture theories The the political ruling-elite theory of regulation economic theory of regulation Accounting Standards Who should set accounting standards? The free-market approach The private-sector approach The public-sector regulation of accounting standards Accounting Standards Standard-setting approach for developing countries The Evolutionary Approach The Transfer of Technology Approach The Adoption of International Accounting Standards Accounting Standards Standard-setting Procedures (IASB Due Process): Setting the agenda Project planning Development and Publication of a discussion paper Development and publication of an exposure draft Development and publication of an IFRS Procedures after an IFRS is issued Accounting Policies The specific accounting principles and the methods of applying those principles that are judged by the management of the entity to be the most appropriate in the circumstances to present fairly financial position, changes in financial position, and results of operations in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.