Early Agricultural Civilizations
advertisement

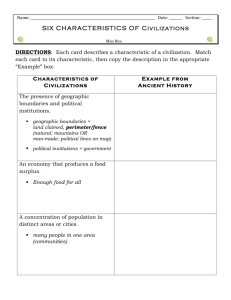
6th Grade UBD - Unit 2 - Early Agricultural Civilizations The Growth of Civilization- Agriculture allowed early humans to settle in larger communities. As populations grew, signs of civilization began to appear. Interactions Among Civilizations- Early civilizations were located in areas that could support agricultural communities. Civilizations that were near one another exchanged goods and ideas. Early humans often lived alone or in small groups. This made it difficult to survive. Over time, however, they began to live in larger groups and create settlements. They also began working together to ensure the basic needs of all those in the group were met. What other advantages might living in a large group have? (5 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your answer with theirs. What things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes) Agriculture provided a steady food source. Cities were supported by nearby farms. People living in cities could specialize, or do only certain kinds of work they enjoyed. Specialization of labor created social classes. Central governments developed to manage the larger populations. Civilizations developed cultures that over time included written languages. Food is one of the main needs for life. Until this need is met, most of a person’s thoughts and actions are directed toward locating food. The development of agriculture— producing crops and raising farm animals—provided a steady food supply people could rely on. With a steady food supply, more people could settle in one place. They began to build stronger and longer-lasting homes and live in larger communities. They began to develop civilizations. Key Term Civilization- A society with cities, a central government, job specialization, and social classes. As the population grew, other changes in people’s lives began to occur. People began to live together in larger communities. These communities could be fed by the neighboring farms. In large communities, workers do not have to meet all their needs themselves. This lets people specialize in certain jobs. The division of labor allowed early humans to become skilled at certain tasks. They now had time to do things they wanted to do. Key Term SpecializationThe development of skills in a specific kind of work. During this time, people created pottery. Artists and craft workers made jewelry, paintings, and carvings. Items such as jewelry and carvings were not needed to survive and therefore are considered luxury items. Key Term Luxury ItemSomething that gives pleasure but is not necessarily needed to live. Specialization of labor created a new feature of civilizations—social hierarchy. A social hierarchy is a system in which people are ranked in different classes, one above the other. Key Term Social HierarchyThe division of society by rank or class. There were fewer members in the top class than at the bottom. In early civilizations, power was usually concentrated in the small ruling class at the top, made up of government and religious leaders. A person’s class was determined by the role they filled. At first, people could move to a new class if their role changed. Over time, the social systems in many civilizations became more rigid and people had little chance of moving to a higher class. Video- Social Classes Cities are usually the center for culture, religion, government, and the invention of new tools. As larger numbers of people began to live together, it became important to have good leaders. Leaders were needed to settle conflicts and direct large tasks. Rulers took charge of big project and wrote laws that told how to solve problems among members of the community. Culture is the beliefs, behaviors, and knowledge of a society. Culture is passed on from the older members of the society to the younger ones. Clothing, music, entertainment, and even architecture are part of culture. Key Term Architecture- The discipline dealing with the principles of design and construction of buildings. An important mark of a civilization is its ability to share its culture. This is particularly true of its knowledge. The organization of religion and the invention of written languages were major cultural advances that took place in early civilizations. Members of ancient civilizations faced many dangers. Bad weather destroyed crops. Illness and injuries that would be minor today often led to death. To help explain these hardships, people often believed they were at the will of higher beings, or gods. They looked to stories and legends to understand how the gods affected the world they lived in. Members of ancient civilizations usually followed the same religion. They marked the same special events. They honored the same gods. They held religious ceremonies in the same way. Early civilizations often had a social class of priests and priestesses. These people controlled the holy customs. They were believed to have special connections to the gods. Religion united the members of a civilization. Key Term Religion- An organized collection of beliefs, cultural systems, and world views that relate humanity to the supernatural, and to spirituality. Key Term MonotheismThe belief in one god. Key Term PolytheismThe belief in many gods. Before writing was invented, people could share information only by speaking. Often, older people told younger people what they knew. Written language played several important roles. People used written records to keep track of floods and the times to plant. They wrote down details about the goods they bought and sold. Writing could provide information about laws and customs Most well-known civilizations have recorded information about themselves in writing. As a result, researchers can study those civilizations today. Video- Writing of Ancient Civilizations Rivers were a source of water for crops, fresh water for drinking, and fish for food. Rivers provided a method of transportation. Geographic features like deserts, mountains, and oceans sometimes kept civilizations from spreading. As a result of war and trade, civilizations exchanged stories, tools, and ideas about science and religion. As agriculture grew more important, it became necessary for early humans to settle in places where they could regularly find water. For this reason, many of the earliest civilizations arose near natural sources of water. Video- The Nile Where Egypt Began Civilizations traded with each other. They also fought wars with each other. As a result of such meetings, civilizations often shared parts of their cultures. They heard each other’s stories. They learned from each other about tools, science, and religious ideas. In some areas, different civilizations were located near each other. When two or more civilizations often wanted the same resources. Both trade and war were common. Fighting brought many changes in leaders. Cities provided early humans with the main things they needed to live. Cities also encouraged culture to develop. Even today, cities continue to be very important to the success of civilizations. What has been the “muddiest” point so far in this lesson? That is, what topic remains the least clear to you? (4 minutes) Work with a neighbor and compare your muddiest point with theirs. Compare what things are the same and what things are different? (3 minutes)