Two-point threshold
advertisement

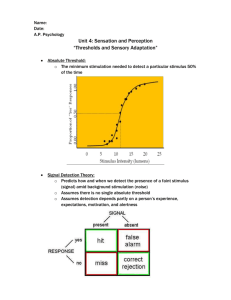
Lady Bugs and Cell Phones Research Methods in Psychology Then and Now Presented in PSY 3384 University of The Incarnate Word February 24, 2005 Harold Rodinsky MSc. Research Methods • Our curiosity leads us – To ask a question – About some • Observation • Our first task – Is to define • The observation of interest – So that we can.. Research Methods – Creating An operational definition • That allows us • To evaluate our observations – Rather than • Speculate about our observation Observation • • • • • • I see students walking to class A lady bug lands on the arm of one of the students The student doesn’t realize the ladybug is on her arm one her friends tell her about the Lady Bug OBSERVATION OF INTEREST………… Why didn’t the student know that the Lady Bug was on her arm? How to Define the Observation • We could speculate – The student was to busy to notice !!! • Speculation provides no information about our question • What can we measure ? – the weight of the lady bug Operational Definition • Does measuring the Lady Bug – tell us • why the student didn’t sense the lady bug – Or does the weight of the ladybug – raise another question ? The Beginning of Experimental Psychology • British Empiricists – Sensations were the only source of knowledge • Bessel demonstrated – Individual differences • In sensation & perception • Physiologists – Were defining the • structure & function • of the senses The Inquiry of Experimental Psychology • With these advancements in place – It was time to experiment with – And measure – The MIND • To methodologically – and scientifically investigate • The subjective • Experience of sensation The First Four • Credited with the application – Of experimental research methods – To the study of the mind • • • • Herman von Helmholtz Ernst Weber Gustav Fechner Wilhelm Wundt Herman von Helmholtz (1821-1894) • Researcher in many fields – Physics – Physiology – Experimental Psychology • Speed of neural impulse • Reaction times for sensory nerves • Theory of color vision Ernst Weber (1795-1878) • Weber did research – On the perception – Of weight • This lead to – Two-point threshold • minimum distance • Between sensations • That can be detected – This work lead to • Just Noticeable Difference • Smallest difference between weights • that can be detected Weber’s Contributions • Discrimination of two sensations – Depends on a ratio between them – Not absolute difference between weights • Not a direct correspondence – Between sensation and perception – Did not appreciate this in terms of psychology • Weber’s work the measurement of sensation – Still in use today Gustav Fechner (1801-1887) • Studied many fields – Proposed two ways to measure Sensation • First – Is the stimulus present – Or absent ? (yes/no) • Second – Measure the intensity – of stimuli – When reported as present and is called – Absolute Threshold – Differential Threshold • The least amount of change that gives rise to a new sensation Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920) • Father of Modern Psychology – Formalized psychology into academic discipline – Set up first laboratory for psychological research • Research focus CONSCIOUS EXPERIENCE – Social Psychology – Stages of cognitive development » Expressed in art, literature, myth » Social customs and morals Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920) • Father of Modern Psychology – Formalized academic discipline – first laboratory for psychological research – Research focus CONSCIOUS EXPERIENCE Absolute Threshold • Lady bug – Absent or present ? • Above or below • Absolute threshold • If the Lady Bug isn’t noticed – It is below – absolute threshold • Can we discriminate – Between one and two lady bugs? Discrimination Experiment • Lets’ find out – We need • • • • Cotton balls Paper cups 12 participants 12 assistants Two Point Threshold • What if two Lady Bugs – land on your arm ? • Weber’s research – “…there is a threshold – Where you can’t tell • If it is two lady bugs • Or one lady bug Two-Point Experiment • Lets measure – The two-point threshold – We need • • • • • • 4 participants 4 blindfolds 4 dividers 4 rulers 4 assistants 1 blackboard Results • Absolute Threshold – Subject to individual differences • Was the lady Bug detected – Yes/no – If no below threshold – If yes above threshold • Discrimination Test – The smallest change in stimuli • That is detectable • Two-Point Threshold – Subject to individual differences • By two-point threshold testing – We can measure • the smallest distance between two points – That is detectable Discussion Absolute Threshold • Absolute Threshold – Do I feel the key depress when I press it? – OR • Do I select – Key sound option • So I can HEAR • Rather than feel • the key has been depressed Discussion Discrimination • The smallest change in stimuli detectable – Are the keys uniform – All the same ? – OR • Are there slight • Differences • So we can sense the difference? – Look at your #5 Key Discussion Two-Point Threshold • How far apart are the keys on my cell phone? – Can I feel the difference between keys – Or do I feel just one key? Summary Discussion • The research methods we demonstrated – Are from the earliest days in the history of psychology • These studies answer fundamental questions – Produce fundamental theories • That are still pertinent today – Used in designing consumer products – In medical testing