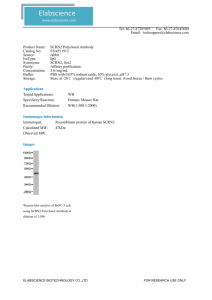
46,XX,inv(2)(p21q31)
advertisement

CYTOGENETIC PRACTICE I NO. 435- COURSE: HEREDITY Key words: congenital and acquired chromosomal aberrations, abnormalities of chromosomal number, structural chromosome rearrangements balanced and unbalanced, partial monosomy, partial trisomy, terminal and intersticial deletions, duplication, reciprocal translocation, Robertsonian translocation, inversion pericentric and paracentric, insertion, dicentric chromosome, ring chromosome, marker chromosome (structuraly abnormal extra chromosome), isochromosome, derivative chromosome, recombinant chromosome, unequal crossing over, meiotic recombination, double minutes, homogeneously staining regions (HSRs), Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1), microdeletion (contiguous gene) syndromes, chromosome instability syndromes, ovarian teratoma, hydatiform mole, prenatal and postnatal cytogenetic examination, amniocentesis (AMC), chorionic villus sampling (CVS), cordocentesis. Review of some cytogenetic abbreviations and symbols (according ISCN -International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature) p short arm q long arm cen centromere h heterochromatin s satellite ter terminal end of arm del deletion dup duplication t translocation inv inversion i isochromozome ins insertion r ring chromosome dic dicentric chromosome mar marker chromosome mat maternal origin pat paternal origin der derivative chromosome rec recombinant chromosome : break and loss of a part of chromosome distal to break :: break and reunion (in detailed description) + before number of chromosome = trisomy - before number of chromosome = loss of chromosome, monosomy / for separations of different cell lines in mosaic p12 site of break on the short arm (according scheme of G banding) q13 site of break on the long arm (according scheme of G banding) 1. Describe types of aberrations. Which karyotypes will be probably connected with normal phenotype? 45,XX,der(14;21)(q10;q10) 46,XX,der(14;21)(q10;q10),+21 45,XX,der(21;21)(q10;q10) 46,XX,der(21;21)(q10;q10),+21 46,XY,inv(3)(q21q26) 46,XX,inv(2)(p21q31) 46,XX,rec(2)dup(2p)inv(2)(p21q31) 46,XX,rec(2)dup(2q)inv(2)(p21q31) 46,XX,dup(1)(q22q25) 46,XX,dup(1)(q25q22) 46,XX,ins (5;2)(p14;q22q32) 46,XY,del(5)(p13) 46,XY,del(5)(q15q22) 46,X,i(X)(q10) 46,XX,i(17)(q10) 46,XX,r(9)(p24q34) 46,XX,t(2;18)(p13;q21) 46,XY,der(18)t(2;18)(p13;q21)mat 46,XY,der(2)t(2;18)(p13;q21)mat 45,X[10]/47,XXX[10]/46,XX[30] 46,XX/46,XY 47,XY,+mar 47,XX,+21/46,XX 2. Describe possible origin of karyotype 49,XXXXX? 3. The woman has hemophilia and cytogenetic examination is recommended. Why? (This woman is not daughter of hemophilic man and woman carrier of hemophilia). 4. Explain karyotype 46,XX in male phenotype? 5. A baby girl has testes in the inguinal canals. What is her disorder? What karyotype would you expect to find in the child? 6. A child with ambiguous genitalia is found to have 21- hydroxylase deficiency.What karyotype woud you expect to find in the child? 7. A newborn girl has lymphoedema on feet. Why the cytogenetic analysis is recommended? 8. A woman – carrier of balanced translocation 14/21 - has a child with Down syndrome. What is the risk of Down syndrome for another child a) theoretic risk, b) real risk? 9. A woman – carrier of balanced translocation 21/21 - has a child with Down syndrome. What is the risk of Down syndrome for another child a) theoretic risk, b) real risk? 10. Parents of a child with translocation form of Down syndrome have both normal karyotypes. What is the risk of the same abnormality for the next pregnancy? 11. In what case and what type of cytogenetic analysis is recommended? • 29 year-old pregnant woman with 41 year-old husband • 39 year-old pregnant woman with 29 year-old husband • 20 year-old pregnant woman with 53 year-old husband • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with free trisomy 21 • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 46,XX,der(14;21)(q10;q10),+21 • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 46,XY,der(21;21)(q10;q10),+21 • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 45,XY,der(14;21)(q10;q10) • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 45,X • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 46,X,i(Xq) • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had previous child with karyotype 46,XY, del(6)(p13) • 30 year-old pregnant woman who has had three spontaneous abortions • husband of woman who has had three spontaneous abortions 12. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of amniocentesis (AMC) and chorionic villus sampling (CVS). 13. Prenatal cytogenetic examination at 10 weeks´ gestation reveal more chromosome abnormalities than those obtained in at 16 weeks´gestation. Explain this situation. 14. What are the indications for postnatal and prenatal cytogenetic analysis ? 15. What is the difference in triploid product of fertilisation arising by fusion of a) haploid ovum and diploid sperm, b) diploid ovum and haploid sperm, c) arising by dispermy? 16. What is the reason of origin of a) numerical, b) structural chromosomal aberrations? 17.Why we cannot detect all trisomies in newborns? Can you see autosomal monosomies in newborns? If not, why? 18. Can you describe cytogenetic manifestation of fragile X and condition of fragile X manifestation in cultivated cells? 19. Explain why the same deletion on chromosome 15 can lead in one case to Prader Willi and in other case to Angelman syndrome? Karyotype assembly from photograph