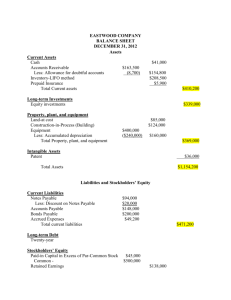
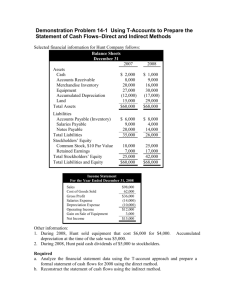
Final Exam Review Chapter 12-13 In its most basic form, the
advertisement

Final Exam Review Chapter 12-13 1. In its most basic form, the earnings per share ratio is calculated as a. dividends paid on common stock divided by the average number of outstanding common shares. b. net income divided by the average number of outstanding common shares c. total dividends paid divided by the average number of total stock shares d. net income divided by average stockholders' equity. Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 2. A company reported net income of $6 million. During the year the average number of common shares outstanding was 3 million. The price of a share of common stock at the end of the year was $5. There were 400,000 shares of preferred stock outstanding on average and no dividends were declared. The EPS is approximately: a. $.40 b. $1.76 c. $1.86 d. $2.00 3. The Price/Earnings Ratio is approximately: a. 2 b. 2.5 c. 2.84 d. 12.50 4. The return on equity ratio is calculated as: a. dividends paid divided by the average book value of stockholders' equity. b. net income divided by the average number of outstanding common shares c. dividends divided by the average number of total shares. d. net income divided by the average stockholders' equity 5. All else equal, when companies make stock repurchases a. EPS falls, ROE rises b. EPS rises and ROE stays the same c. EPS rises and ROE falls d. EPS and ROE both rise 6. Which of the following would be included in the calculation of net cash flows from operating activities? a. Cash proceeds from sales b. Cash received from an issuance of bonds c. Dividends paid to stockholders d. Cash used to purchases of equipment 7. Which of the following would be included in the calculation of net cash flows from investing activities? a. Cash proceeds from sales b. Cash received from an issuance of bonds c. Dividends paid to stockholders d. Cash used to purchases of equipment 8. Which of the following would be included in the calculation of net cash flows from financing activities a. Cash proceeds from sales b. Cash paid of another corporation’s stock c. Dividends paid to stockholders d. Cash used to purchases of equipment 9. A change in a company's cash account is equal to the: a. changes in liabilities and stockholders' equity plus or minus the change in noncash assets. b. changes in liabilities minus the changes in stockholders' equity and noncash assets. c. Change in stockholders’ equity minus the change in noncash assets and liabilities d. change in noncash assets minus the changes in liabilities and stockholders' equity. 10. When the indirect method is used, if prepaid expenses fall during the accounting period, the change in prepaid expenses is: a. Added to the change in the cash c. Added to net income account d. Subtracted from the change in the cash b. Subtracted from net income account 11. The supplies account falls and accounts payable rises during an accounting period. When the indirect method is used, what does the company do with the changes in these accounts to calculate net cash flows from operating activities? a. Both are added to net income b. The change in accounts payable is added to net income; the change in supplies is subtracted. c. Both are subtracted from net income. d. The change in supplies is added to net income; the change in accounts payable is subtracted. Consider the following information: Net income $20,000 Depreciation 3,000 Increase (decrease) in accounts receivable 1,000 Increase (decrease) in prepaid rent (400) Increase (decrease) in accrued liabilities 900 Cash paid to purchase office equipment 4,000 12. The company would report a net cash inflow from operating activities of: a. $17,500 c. $21,500 b. $18,500 d. $23,300 13. Almost all U.S. companies use the indirect method of preparing the statement of cash flows: a. because most users of the financial statements do not understand the direct method. b. in spite of the Financial Accounting Standard Board's stated preference for the direct method. c. because it usually requires less space in the annual report. d. so that stockholders cannot determine how much cash was spent on executives' salaries. 14. Inventory rises and accounts payable rises during the accounting period. When the direct method is used to determine the net cash flow from operating activities, how would these changes affect cash flow calculations? a. The changes in each account are both added to net income b. The change in inventory is subtracted from cost of goods sold and the change in accounts payable is added to cost of goods sold to find the cash paid to suppliers. c. The changes in each account are both subtracted from net income. d. The change in inventory is added to cost of goods sold and the change in accounts payable is subtracted from cost of goods sold to find the cash paid to suppliers. 15. When a company uses the direct method to determine the net cash flow from operating activities, cash flows from operating activities will: a. be identical to the amount reported using the indirect method. b. be larger if there is a net cash inflow and smaller if there is a net cash outflow compared to the amount reported using the indirect method. c. always be larger than the amount reported using the indirect method. d. be larger if there is a net cash outflow and smaller if there is a net cash inflow compared to the amount reported using the indirect method. 16. When the direct method is used to determine the net cash flow from operating activities, the following adjustments must be made to income tax expense to determine total income tax payments: a. add all changes in income taxes and income taxes payable. b. add decreases in income taxes payable and subtract increases in income taxes payable. c. add increases in income taxes payable and subtract decreases in income taxes payable. d. subtract all changes in income taxes payable 17. Your company owned equipment with a book value of $120,000 that was sold during this accounting period for $30,500 in cash, and purchased new equipment for $148,000. Your company would record: a. a credit of $30,500 and a debit of $148,000 to the cash account for a net cash outflow of $117,500. b. a debit of $148,000 and a credit of $89,500 to the cash account for a net cash outflow of $58,500. c. a debit of $30,500 and a credit of $148,000 to the cash account for a net cash outflow of $117,500. d. a debit of $89,500 and a credit of $148,000 to the cash account for a net cash outflow of $58,500 18. Cash transactions relating to the purchase and sale of which types of assets affect a company's cash flows from investing activities? a. All of a company's assets. b. All of a company's assets except inventory. c. All of a company’s non-current assets. d. Only property, plant and equipment. 19. Which of the following represent cash inflows from financing activities? a. Issuing stock in exchange for another company's shares b. Paying a bond's face value at maturity c. Issuing long-term bonds at a discount. d. Receiving interest on promissory notes 20. A company issues $1 million of new stock and pays $200,000 in cash dividends during the year. In addition, the company took advantage of falling interest rates to borrow $1.5 million in a new bond issue and paid off existing bonds with a face value of $2 million. The company bought 500 of another company's $1,000 bonds at a $100,000 premium. The net cash flow from financing activities is: a. Inflow of $500,000 b. Outflow of $200,000 c. Outflow of $100,000 d. Inflow of $300,000 21. Company X paid Company Y $1.35 million for a new plant. During the same accounting period, Company X experienced the following changes in its balance sheet: cash fell $350,000, accounts receivable rose $321,300, inventory rose $275,800, property, plant, and equipment rose $752,900, and bonds payable rose $1 million. The net cash flow from financing activities is: a. Inflow of $1.35 million c. Inflow of $1 million b. Outflow of $350,000 d. Inflow of $752,900 22. The net cash flow from operating activities is an inflow of $37,042, the net cash flow from investing activities is an outflow of $16,831, and the net cash flow from financing activities is an outflow of $26,397. If the beginning cash account balance is $11,283, what is the ending cash account balance? a. $5,097 b. -$6,186 c. $38,759 d. $27,476 23. Company X has a capital acquisitions ratio of 1.42 while Company Y has a capital acquisitions ratio of 7.28. Which of the following could be true? a. If Company X and Y are in different industries, these ratios may reflect the different production needs of the industry. The ratio cannot really be compared across industries. b. Company Y may be more efficient at managing cash flows. c. Company Y may be lagging in adopting new technology which could hurt future sales. d. All of the above 24. If net cash flow from operating activities is unchanged, but net income is rising, the quality of income ratio is: a. rising, which may signal that revenue is being recorded later and/or expenses earlier than in the past. b. falling, which may signal that revenue is being recorded later and/or expenses earlier than in the past. c. falling, which may signal that revenue is being recorded earlier and/or expenses later than in the past. d. rising, which may signal that revenue is being recorded earlier and/or expenses later than in the past. 25. Oberlin Co. had sales revenue of $500,000 this year and $400,000 last year. As a consequence, its year over year percentage change in sales is: a. 20% b. 25% c. 50% d. 100% 26. The following information comes from the balance sheet and income statement of the Rocket Co. for the years 2xx9 and 2xx8: 27. 28. 29. 30. What is the current ratio as of December 31, 2xx9? a. .70 b. 1.43 c. 1.80 What is the net profit margin for the year ended December 31, 2xx9? a. 7.6% b. 11.8% c. 19.4% What is the times interest earned ratio for the year ended December 31, 2xx9? a. 2.2 b. 5.2 c. 6.2 What is the debt-to-assets ratio as of December 31, 2xx9? a. .55 b. .65 c. 1.54 Which ratio is a test of liquidity? a. Net profit margin b. Inventory turnover d. 3.98 d. 21.7% d. 8.0 d. 1.80 c. Times interest earned d. Debt to assets 31. Which ratio is not a test of profitability a. Gross profit margin c. Earnings per share b. Fixed asset turnover d. Current ratio 32. If a company increases the selling price of the product it sells and all other data on the financial statements remains the same, which of the following ratios will be unaffected? a. Fixed asset turnover c. Inventory turnover b. Net profit margin d. Earnings per share