Taxonomy
advertisement

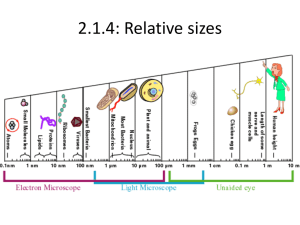
http://assets.natgeotv.com/Shows/10406.jpg In this unit, the summary is shown in blue, and the underlined words are vocabulary; the animation and video hyperlinks are shown in orange. TPS How would you classify your shoes? If you had to create a cladogram [see below] to show the evolution of shoes, how would you do it? http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1b/Identical_cladograms. svg/250px-Identical_cladograms.svg.png When you go shopping in the grocery store, similar items are often placed on the same aisle. Why? They are most often related to each other. In science, classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. Scientists classify the diverse number of organisms on the planet in order to learn and study from them into hierarchical groups (from general to more specific categories). In this unit you will learn how scientists classify living things; the science of taxonomy. Von Linne [AKA Carolus Linnaeus] was the Swedish biologist who in the mid1700’s developed the biological system of classification. ◦ 7 taxonomic levels [or taxa] ◦ kingdom to species http://www.ub.uit.no/northernlights/images/linne06d.jpg Scientists give animals Latin/Greek names in classification which consists of two parts: ◦ genus + species [specific epithet]. Often use Latin because it is universal [worldwide] and not widely spoken, therefore, the meaning is not likely to change. In Latin, nomenclatura = ◦ nomen "name"+ calare "to call" EX Tyrannosaurus rex translates to “tyrant lizard” and “king.” http://nerdywithchildren.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/trex-fossil.jpg http://hqwalls.org/t_rex_dinosaur_wallpaper-wallpapers.html http://www.unmaskingevolution.com/images/imaginative.gif Always in italics Genus name is written 1st, capitalized Species name is written 2nd, NOT capitalized EX scientific names ◦ Homo sapiens (modern man) ◦ Felis domesticus (common housecat) http://bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu/People/Grad_Students/hui fangq/food/HuifangCookings/edited/crawfish.jpg 1. A Latin name eliminates confusion caused by regional name differences. ◦ EX crayfish, crawdad, mudbug are all common names for…. ◦ Cambarus bartoni http://wdfw.wa.gov/wlm/game/cougar/graphics/cougar4.jpg ◦ Mountain lion, panther, cougar and puma are all common names for... ◦ Felis concolor 2. organizes large amounts of information 3. Classification also reveals (or shows) evolutionary relationships between organisms http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/19/Phylogenetic_Tree_of_Life.png Phylogeny – evolutionary relationships among organisms Biologists now group organisms according to phylogeny (lines of evolutionary descent), not just physical characteristics. Create a mnemonic to remember the sequence of taxons from general to specific ◦D ◦K ◦P ◦C ◦O ◦F ◦G ◦S http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_DiCeGX2-bR8/TKI_zgN01QI/AAAAAAAAAFs/myAAROvR80/s1600/Taxanomy+5.5.2.JPG http://ag.arizona.edu/pubs/garden/mg/entomology/images/p4large.gif Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species http://www.whoi.edu/cms/images/tree_550_74474.jpg Domain is the most recently added 8th taxonomic level, which is even more inclusive than a kingdom. There are three domains shown above. ◦ Two are prokaryotic, one is for eukaryotes. Domains in the News Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Three domains of life: ◦ Archaea & Bacteria contain only prokaryotes. ◦ Eukarya contains all eukaryotes. Take notes from the following slides in a Venn diagram. http://culturingscience.files.wordpress.com/2010/09/3-domains-of-life.jpg Members of the domain Archaea are bacteria [prokaryotes] that live in very extreme environments (hot volcanic springs, black organic mud, etc) and many can only survive in the absence of oxygen! http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Grand_prismatic_ spring.jpg Archaea were first found in extreme environments, such as volcanic hot springs. Pictured here is Grand Prismatic Spring of Yellowstone National Park. According to the Mayo Clinic there are more than 2,000 strains of salmonella bacteria, but only a dozen or so make people sick. Salmonella is most often contracted by eating raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs. Image Regular everyday bacteria [prokaryotes] belong to domain Bacteria. EX Salmonella All of the organisms that have a nucleus [eukaryotes] are included in Domain Eukarya. This domain includes a variety of life forms in 4 kingdoms: ◦ Protist ◦ Fungi ◦ Plant ◦ Animal Domain Animation http://www.biocentrum.dtu.dk/upload/institutter/bic/biocentrum/studievalg/his_archaea_fot3_3 80.jpg When organisms are newly discovered, they are identified, sorted, and categorized into one of the three domains. Basis of classification: 1. Type of cell 2. Number of cells 3. Mode of nutrition Take notes from the following slides in your NovaMind App. http://1.bp.blogspot.com/y_abocOeLKk/TpuITAAu8VI/AAAAAAAAHuw/SJdeqGFpZ8E/s1600/six+kingdoms+tree+of+li fe+.gif Prokaryote Eukaryote Unicellular = one-celled Multicellular = many-celled Autotroph = “self-feeder”, photosynthetic or chemosynthetic Heterotroph = “different-feeder”, consumer or decomposer Motile = organism moves Sessile = stationary, does not move Eubacteria – bacteria common to “YOU” and me ◦ Cell Type: Prokaryotic, Unicellular ◦ Energy: Autotrophic and heterotrophic Archae bacteria – live in harsh environments (highly salty or acidic, high temperatures) ; mostly anaerobic w/out oxygen ◦ Prokaryotic ◦ Unicellular ◦ Autotrophic only http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/Courses /bio101/labquiz2/prokaryote.jpg http://www.dirtworks.net/Images/NeptunesHarvest/Kelp.jpg Protist – lack complex organ systems; require moist environments; first appeared in the fossil record 200 million years ago! ◦ Eukaryotic w/ cell walls ◦ Unicellular & Multicellular ◦ Autotrophic & heterotrophic EX amoebas, algae, kelp http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/Mic hael.Gregory/files/Bio%20102/Bio%20102%2 http://4.bp.blogspot.com/360Hzs1e75w/TaiqOZ0s7MI/AAAAAAAAAC4/xUXmW6Q6qoY/s1600/Slime _mold%2528ms-07%2529.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a0/Slime_Mold_On_Deadwood.JPG Fungi – EX Molds, mildews, and mushrooms; first appeared in the fossil record 400 million years ago! ◦ Eukaryotes w/ cell walls of chitin ◦ Unicellular & multicellular ◦ Heterotrophic decomposers http://www.shutterfreaks.com/albums2/album225/mu shroom.jpg http://howtobuildahouseblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/Black-Mold.jpg n 1692 some teenage girls in Salem, Massachusetts, accused a West Indian slave named Tituba and two white women of practicing witchcraft. By April the girls began to denounce others as witches, including a former minister. In total close to 150 people were accused. "Both women and men, such as George Jacobs, stood trial for witchcraft in Salem, Politics. Vol. 1. Detroit: Gale, 2008. U.S. History In Context. Web. 20 Feb. 2013. 1692." Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. History: Government and Plants – oxygen producers; create their food using photosynthesis (thus the green color). ◦ Non-motile (do not move) ◦ Eukaryotes w/ cell walls of cellulose ◦ Multicellular ◦ Autotrophs EX mosses, ferns, flowering and cone-bearing plants http://www.mccullagh.org/db9/d30-2/jellyfish-7.jpg Animals - At the microscopic level, animal cells are different; they do NOT have cell walls. ◦ Eukaryotes ◦ Multicellular ◦ Heterotrophs EX sponges, jellyfish, worms, insects, humans http://www.dnr.state.wi.us/org/caer/ce/eek/critter/watercritter/images/keymap_ template.gif Taxonomists have dichotomous keys to help to identify organisms; a guide. A dichotomous key consists of several pairs of descriptive statements to help identify an unknown organism. Dichotomous key animation Derived characters – characteristics found in recent parts of a lineage through cladistics; used to construct cladograms. Cladograms show evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms. Caldogram animation Crab Barnacle Limpet CLASSIFICATION BASED ON VISIBLE SIMILARITIES