Cancer
advertisement
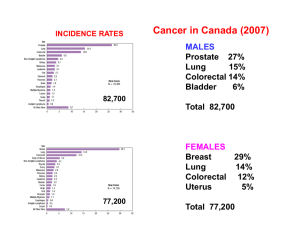
Cancer What is cancer? “Abnormal, uncontrolled growth of cells, which, if left untreated, can ultimately cause death.” (American Cancer Society) Terminology: Benign Malignant Metastasis In situ Cells and Cancer Two-stage model of cancer development: Initiators Accumulation of DNA mutations “Genetic insults” Promoters Do not cause cancer but help it grow Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors “Good” = proto-oncogene “Bad” = oncogene Tumor suppressors OR vs US: Cancer Incidence (CDC) OR vs US: Cancer Deaths (CDC) Non-Specific Warning Signs CAUTION: C: changes in bowel or bladder habits A: a sore that doesn’t heal U: unusual thickening or discharge T: thickening or lump in the breast or any other part of the body I: indigestion or difficulty swallowing O: an obvious change in wart or mole N: a nagging cough or hoarseness Cancer Staging T: The extent of primary tumor N: absence of presence of lymph node involvement M: presence of distance metastasis Stages: I, II, III, IV Five year “Gold standard” Types of cancer: Leukemia Involve blood-forming cells (white blood cells) which are chiefly in bone marrow. Acute, chronic (National Cancer Institute) Types of cancer: Sarcoma Connective & fibrous tissue Examples: muscle, bone, cartilage, membranes covering muscle/fat Source: cancerhelp.org.uk Types of Cancer: Lymphomas Involve lymph nodes Hodgkins, non-Hodgkins Source: newsimg.bbc.co.uk Types of Cancer: Carcinoma Epithelial cells Cover external body surfaces or line internal tubes and cavities Most common type Examples: skin, breast, uterus, prostate, lungs, GI tract Source: media.collegepublisher.com Lung Cancer Lung Cancer continued Types: Non-small cell Small cell Symptoms: Most lung cancers are silent When symptoms occur: Cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, loss of appetite, blood in sputum. Lung Cancer: Risk Factor Most common malignant disease worldwide Leading cause of cancer deaths. Tobacco smoke accounts for approximately 90% of all lung cancers. According to the WHO, decreasing current smoking rates by 50% could prevent 20-30 million deaths before 2025 and 150 million deaths by 2050. Breast Cancer Breast Cancer The most frequently diagnosed cancer in women. Risk factors: Age, female gender, personal family history (National Cancer Institute, 2005) Types of Breast Cancer Ductal cancer Most common type of breast cancer Lobular cancer Inflammatory breast cancer Breast Cancer: Risk Factors Gender 100x more common in women Age Genetics BRCA1 BRCA2 Diet Alcohol Physical activity Menarche Pregnancies Breast-feeding Menopause Mammograms (National Cancer Institute, 2005) Screening / Prevention Mammogram recommendation Starting at age 40 (unless family or personal history) and every year as long as “in good health.” BSE (Breast Self-Exams) Starting at age 20, every month Clinical breast exam every year Chemoprevention Her2neu marker Prostate Cancer Prostate Cancer The most common cancer for men. Lifetime risk: 1 in 6 Risk of dying: 3% Risk Factors / Screening Age Strongest risk factor Race / ethnicity Diet PSA blood test Red meat High-fat dairy Genetics DRE – digital rectal exam Good news Prostate cancer is not always life threatening Colorectal Cancer Colorectal Cancer More common in Western societies. Almost 100% preventable with screening and polyp removal. Colorectal Cancer: Risk Factors Age Smoking Over 50 Alcohol Diet Diabetes (type 2) Physical inactivity Obesity Link stronger in men Increased risk Less favorable outcome Screening Colonoscopy Recommended first colonoscopy at age 50; every 5-10 years Unless family history / personal symptoms Good news: colon cancer usually slow growing Other screenings: FOBT (Fecal Occult Blood Test) sDNA (Stool DNA tests) Skin Cancer Sun Safety Quiz “I can’t get skin cancer, because my normal routine (such as work, drive to work, hobbies, and vacations) doesn’t include any outdoor activities” False “If I’m wearing sun screen, I can stay in the sun as long as I want.” False “Getting a ‘base tan’ at an indoor tanning salon is a good way to prevent sunburn when I go to the beach later this summer.” False (American Cancer Society) Skin Cancer Three types of skin cancer: Basal cell carcinoma Most common type of skin cancer Squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma Deadliest form of skin cancer Skin Cancers Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer However…. Basal cell and squamous cell are not reported to cancer registries Basal cell About 8 of 10 skin cancers Squamous cell About 2 of 10 skin cancers Source: skin cancer foundation Melanoma – ABC’s Source: skin cancer foundation Skin Cancer: Risk Factors SUN (Obviously!) Specifically UV exposure Age / Gender Before age 40 – higher risk for women After age 40 –higher risk for men Melanoma is one of the common cancers in people younger than 30. Smoking Skin Cancer Prevention “Slip, Slop, Slap … and Wrap” (ACS) Wrapping up chronic diseases Responses differ from person to person Grief Loss of body part, control, independence, security, certainty of future Physical / Mental fatigue Depression Shock / disbelief Denial Anger Communication: A few do’s and don’ts Be “other-oriented” Please avoid cliches! “I know what you’re going through” “Everything will be okay” “Well we all have to die sometime” It’s not about you Listen and listen some more The patient is the boss It’s their decision Offer specific help