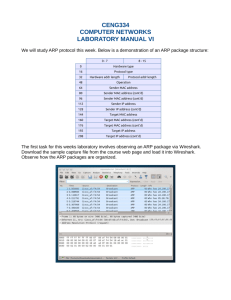
ARP Caching
advertisement

ARP Caching Christopher Avilla What is ARP all about? • • • • • • • • • Background Packet Structure Probe Announcement Inverse and Reverse Proxy Tools Poisoning MAC Flooding ARP Refresher • Determines a MAC when only IP address is known • Implemented in many types of networks • Most frequently used to translate IPv4 addresses into Ethernet MAC addresses • In the next generation Internet Protocol, IPv6, ARP's functionality is provided by the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). Packet Structure • • • • Simple message format One address resolution request or response Operation code for request (1) and reply (2) 4 addresses, the hardware and protocol address of the sender and receiver Internet Protocol (IPv4) over Ethernet ARP packet bit offset 0 16 32 48 64 80 96 0–7 8 – 15 Hardware type (HTYPE) Protocol type (PTYPE) Hardware address length Protocol address length (HLEN) (PLEN) Operation (OPER) Sender hardware address (SHA) (first 16 bits) (next 16 bits) (last 16 bits) 112 Sender protocol address (SPA) (first 16 bits) 128 (last 16 bits) 144 Target hardware address (THA) (first 16 bits) 160 (next 16 bits) 176 (last 16 bits) 192 Target protocol address (TPA) (first 16 bits) 208 (last 16 bits) Probe • ARP request constructed with an all-zero sender IP address • IPv4 Address Conflict Detection specification (RFC 5227). – First test to see if the address is already in use, by broadcasting ARP probe packets. Announcements • gratuitous ARP message – Updating other host's mapping of a hardware address when the sender's IP address or MAC address has changed – broadcast as an ARP request containing the sender's protocol address (SPA) in the target field (TPA=SPA), with the target hardware address (THA) set to zero. – An alternative is to broadcast an ARP reply with the sender's hardware and protocol addresses (SHA and SPA) duplicated in the target fields (TPA=SPA, THA=SHA). Announcements Cont. • Not intended to solicit a reply • Updates any cached entries in the ARP tables of other hosts that receive the packet. • Many operating systems perform gratuitous ARP during startup • Load balancing for incoming traffic • In a team of network cards, used to announce a different MAC address within the team that should receive incoming packets. Inverse ARP • Protocol used for obtaining IP addresses from MAC addresses • Used in Frame Relay and ATM networks • As ARP translates Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 addresses, InARP may be described as its inverse • Implemented as a protocol extension to ARP • Uses the same packet format from ARP with different operation codes. Reverse ARP • Translates Layer MAC addresses to IP addresses • Used to obtain the IP address of the requesting station itself for address configuration purposes • RARP is now obsolete. It was replaced by BOOTP, which was later superseded by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Proxy • Device on a given network answers the ARP queries for an IP address not on that network • The ARP Proxy is aware of the location of the traffic's destination • Offers its own MAC address in reply • "send it to me, and I'll get it to where it needs to go." • The "captured" traffic is routed by the Proxy to the intended destination via another interface or tunnel • Sometimes referred to as 'publishing'. Tools • ARPwatch – Generates a log of observed pairing of IP addresses with MAC addresses along with a timestamp when the pairing appeared on the network. • ARPing – The program tests whether a given IP address is in use on the local network, and can get additional information about the device using that address • Cain and Able Cache Poisoning • Update cache whenever an ARP request OR!!! Reply is received. • If the MAC address for the given IP has changed. Overwrite the old value • ARP replies are unicast • Used to set up man in the middle attacks • Allows attacker to monitor, intercept, and modify sessions MAC Flooding • ARP Cache Poisoning technique • For Network switches • When certain switches are overloaded they often drop into a "hub" mode. • The switch is too busy to enforce its port security features and just broadcasts all network traffic • Flood a switch's ARP table with a ton of spoofed ARP replies then packet sniff Why do we care? • Network Design • Security • Device Configuration – Advanced Devices – Nortel – Cisco – Allied Tellesis Conclusion • • • • • Packet Structure Probes and Announcements Extensions of the protocol Tools Threats Resources • http://www.packetnexus.com/docs/arppoison .pdf • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_Resoluti on_Protocol • http://www.watchguard.com/infocenter/edito rial/135324.asp