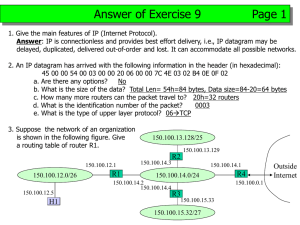
7. Refer to the exhibit. Which value will be configured for Default
advertisement

1. Which IP address can be assigned to an Internet interface? A. 10.180.48.224 B. 9.255.255.10 C. 192.168.20.223 D. 172.16.200.18 2. What will happen if a private IP address is assigned to a public interface connected to an ISP? A. Addresses in a private range will be not routed on the Internet backbone. B. Only the ISP router will have the capability to access the public network. C. The NAT process will be used to translate this address in a valid IP address. D. Several automated methods will be necessary on the private network. E. A conflict of IP addresses happens, because other public routers can use the same range. 3. When is it necessary to use a public IP address on a routing interface? A. Connect a router on a local network. B. Connect a router to another router. C. Allow distribution of routes between networks. D. Translate a private IP address. E. Connect a network to the Internet. 4. When a DHCP server is configured, which two IP addresses should never be assignable to hosts? (Choose two) A. network or subnetwork IP address B. broadcast address on the network C. IP address leased to the LAN D. IP address used by the interfaces E. manually assigned address to the clients F. designated IP address to the DHCP server 5. The network administrator has asked you to check the status of the workstation’s IP stack by pinging the loopback address. Which address would you ping to perform this task? A. 10.1.1.1 B. 127.0.0.1 C. 192.168.0.1 D. 239.1.1.1 6. Which command is used to see the path taken by packets across an IP network? A. show ip route B. show route C. traceroute D. trace ip route 7. Refer to the exhibit. Which value will be configured for Default Gateway of the Local Area Connection? A. 10.0.0.0 B. 10.0.0.254 C. 192.223.129.0 D. 192.223.129.254 8. Which of the following describe private IP addresses? (Choose two) A. addresses chosen by a company to communicate with the Internet B. addresses that cannot be routed through the public Internet C. addresses that can be routed through the public Internet D. a scheme to conserve public addresses E. addresses licensed to enterprises or ISPs by an Internet registry organization 9. What layer in the TCP/IP stack is equivalent to the Transport layer of the OSI model? A. B. C. D. Application Host-to-Host Internet Network Access 10. Which of the following services use UDP? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A. B. C. D. DHCP SMTP SNMP FTP HTTP TFTP 1, 3 and 6 2 and 4 1, 2 and 4 All of the above 11. Which class of IP address provides a maximum of only 254 host addresses per network ID? A. B. C. D. Class A Class B Class C Class D 12. Which of the following allows a router to respond to an ARP request that is intended for a remote host? A. Gateway DP B. Reverse ARP (RARP) C. Proxy ARP D. Inverse ARP (IARP) 13. What is the address range of a Class B network address in binary? A. 01xxxxxx B. 0xxxxxxx C. 10xxxxxx D. 110xxxxx 14. What protocol is used to find the hardware address of a local device? A. RARP B. ARP C. IP D. ICMP . 15. What is the subnet mask of a point to point link? A. 255.0.0.0 B. 255.255.255.255 C. 255.255.248.0 D. 255.255.255.248 E. 255.255.255.252