Ancient World History
advertisement

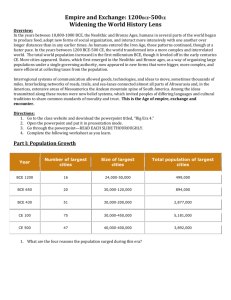
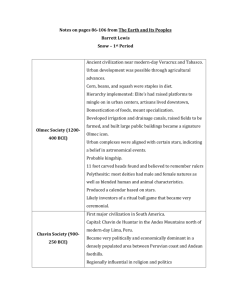
Prehistory to 1500 Foundations of Civilization Neolithic Revolution Middle Asia: Mongols Core Civilizations Middle East: Muslim Empires Five Major World Religions South/East Africa: Great Judaism Hinduism Buddhism Christianity Islam China: Qin and Han Empires India: Maurya and Gupta Empires Mesoamerica: Maya, Aztec, Inca Zimbabwe, Swahili city-states West Africa: Songhai, Mali, Ghana Western/European: Ancient Greece & Roman Empires One side 500BCE – 1450 CE Other side 1450CE - present Development of civilization, sources of power Development of world religions Regional trade: Silk Roads, Mediterranean Sea, Trans- Saharan, Indian Ocean sea lanes New technologies Growth of bureaucracy/state practices Cross cultural interactions, technological and cultural transfers Beginning about 10,000 years ago Emergence of permanent agriculture Emergence of pastoralism (domesticating animals) At different times, in: Mesopotamia Nile River Valley & Sub-Saharan Africa Indus River Valley Yellow River Papua New Guinea Mesoamerica Andes Transformation of human societies Work cooperatively for agriculture, more food=more ppl Specialization of labor, new classes of artisans, warriors, elites: Hierarchical social structures Improvements in agriculture, trade, transportation: Pottery Plows Woven textiles Metallurgy Wheels and wheeled vehicles All civilizations have in common: Agricultural surpluses that allowed for specialization Cities Complex institutions, like bureaucracies, armies, religions Social hierarchies Long-distance trading relationships 6. 5. 5. Olmec: modern south-central Mexico 6. Chavin: modern day Peru Maurya Empire: Chandragupta Maurya 303 BCE 2000 miles, northern India Grandson Asoka & his Edicts Fell apart by 185 BCE Dharma is good, but what constitutes Dharma? (It includes) little evil, much good, kindness, generosity, truthfulness and purity. Pilar Edict Nb2 (S. Dharmika) And noble deeds of Dharma and the practice of Dharma consist of having kindness, generosity, truthfulness, purity, gentleness and goodness increase among the people. Rock Pilar Nb7 (S. Dharmika) All religions should reside everywhere, for all of them desire selfcontrol and purity of heart. Rock Edict Nb7 (S. Dhammika) Here (in my domain) no living beings are to be slaughtered or offered in sacrifice. Rock Edict Nb1 (S. Dhammika) Contact (between religions) is good. One should listen to and respect the doctrines professed by others. Beloved-of-the-Gods, King Piyadasi, desires that all should be well-learned in the good doctrines of other religions. Rock Edict Nb12 (S. Dhammika) Chandra Gupta and two heirs 3rd: Chandra Gupta II, 40 years of incredible achievements Classical Age of Hindu and Buddhist art and literature, for example: Author Kalidasa Kama Sutra First base-10 numeral system Sun-centered astronomy Plastic surgery, cataract surgery Developed over centuries; pre-1500 BCE 1 billion Hindus worldwide; 900 million in India Collection of different beliefs rather than rigid rules Complete freedom of belief Basic precepts include: dharma, samara, karma, moksha, Brahman Thousands of gods Shiva Brahma Vishnu Based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, known as Buddha once he achieved enlightenment Born about 563 BCE (Mauryan Empire) Encompasses variety of traditions, precepts: ethical life, mindfullness Approximately 350-500 million Buddhists in the world Three Jewels: the Buddha, the Dharma (the teachings), the Sangha (community) Variety of Chinese dynasties rose and fell 2000BCS+ During time of turmoil, various philosophies arise: Confucius (551 BCE): 5 basic relationship around which to organize society, filial piety Laozi (~553BCE): Daoism – “the way” – finding the natural order of things Legalism: strong, harsh leader necessary to rule over ppl Yin and yang: 2 powers that represent natural rhythms of life Rises in 221 BCE, based on legalism Emperor Shi Huangdi unifies China Centralization Great Wall of China: 1400 miles long Ends 206 BCE 202 BCE – 225 CE, ruled thru mandate of heaven Centralized gov’t, large bureaucracy Civil service : intellectual + literary jobs impt Paper invented 105 CE: more bureaucracy! Expanded thru assimilation China’s Golden Age: today, Chinese refer to themselves as ethically Han 800BCE to 146 BCE (when came under Roman rule) Iliad and Odyssey date from 800BCE 776 BCE first Olympics Sappho Pythagoras “Classical Greece”: 480-323BCE (until Alexander dies) Hippocrates Plato Socrates Thucydides Hellenistic Greece: 323-146BCE Euclid Archimedes 3 - 5 slide ppt on a trade route: Silk Roads: Harrison Mediterranean Sea trade routes: Ben Trans-Saharan trade routes: Jackie Indian Ocean sea lanes: Elliana Mongols: Zur x Swahili City-states: Lucas x Great Zimbabwe: Aaron x Aztec: Sophia Inca: Chloe x Maya: Rachel x Mali: Rebecca When? Where? Who? Significance? What traded? Use maps and lots of images… Email me your slides by Monday at noon: powerpoint ONLY (.ppt) Village of Rome settled sometime in 8th century BCE Roman Republic: 509 BCE – 27 BCE 451 BCE Twelve Tables est. Roman Republic laws Dominant people on Med. Sea by 200BCE Julius Caesar, First Triumvirate, then invaded, dictator, assassinated Octavian Second Triumvirate, then Emperor Roman Empire: 27 BCE – 476CE Good emperors, bad emperors…lots of emperors Pax Romana: 27BCE-180CE (Pompeii?) Constantine (313CE): converts empire to Christianity Empire divided into Eastern and Western: 395CE End of empire: 476CE when last Western emperor dethroned by barbarian Huns Abraham: father of Judaism, Christianity & Islam Lived around ~1800BCE Abraham roamed Egypt/Canaan/Mesopotamia, made first covenant with God for protection and obedience Moses: around 1200BCE led Hebrews out of slavery in Egypt, got 10 commandments New covenant with god Wandered, settled in Canaan (Palestine) Kingdom of Israel est. 1020BCE, ups and downs First Temple destroyed 586 BCE, exile to Babylon for 70 yrs Jews return, rebuild, various ups and downs Roman Empire conquers Second Temple destroyed by Rome in 70CE, diaspora begins Monotheistic God all knowing, all powerful Sacred Text: Torah – generally, but also means: Tanakh: is an acronym to include the Torah (Jewish “law”), the Nevi’im (“prophets” -- history of Israel), and Ketuvim (“writings”-- of faith and devotion) Torah: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, Deuteronomy Nevi’im: Joshua, Judges, Samuel, Kings, Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel and lesser prophets Ketuvim: Psalms, Proverbs, Job, Song of Solomon, Ruth, Lamentations, Ecclesiastes, Esther, Daniel, Ezra, Nehemiah, Chronicles Mishnah: around 100 Rabbi Judah brought together oral traditions of discussions on the Torah in a written collection Talmud: Entire collection of oral sermons, stories and parables on the Torah, a commentary on Jewish law that forms the backbone of a Jew’s scholarly and religious life (compiled in the Middle Ages) CE Jesus born 4 – 6 BCE, starting at age 30, miracles reported Taught monotheism, personal relationship to God, based on 10 Commandments, gathered disciples Gospels claim J rose after death=Messiah=eternal life for all, disciples spread teachings Pax Romana common languages excellent Roman roads Christians persecuted until Constantine; by 380CE official religion of Roman Empire Great diversity in church, disciples write Gospels Christian Bible: Hebrew Bible/”Old Testament” + Gospels/”New Testament” Roman capital moved to Constantinople 312 CE Byzantine Empire: 395CE-1453CE Emperor Justinian Connection to Western world, but (almost) in Eastern world Schism in Christianity: 1054 CE divides Western Christianity (Pope, Catholic) and Eastern Christianity (Patriarch, Eastern Orthodox— Greeks, Russians, etc.) Constantinople center of Eastern Orthodox Church Muhammad the Prophet: born 570CE, became convinced Gabriel spoke to him as last of the prophets Islam=submission to the will of Allah Muslim=one who has submitted Ka’aba as house of worship for Abraham (and others) already in Mecca, but hostile to Muhammad Went to Medina (“city of prophet”), showed good leadership, gained followers, battled Mecca, won 630CE : Muhammad dedicates Ka’aba to Allah Muhammad dies two years later after nearly unifying Arabia under Islam Monotheistic, individual responsibility Holy book: Qur’an (references J/C texts & origins) Sunna=example Muhammad’s life; Qur’an+Sunna= shari’a: body of law for applying God’s will to daily life Five Pillars: duties to demonstrate submission to God Faith (Shahadah): "There is no God but Allah, and Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah." Prayer (Salat) Alms (Zakat) Fasting (Sawm): holy month of Ramadan Pilgrimage (Hajj) Umayyads: 661 – 750CE beginning of hereditary succession of caliph moved capital to Damascus (trade center) Worldly life, excesses of wealth Abbasids: 750 – 1258CE Moved capital to Baghdad Bureaucracy, centralized gov’t, strongly religious Various smaller indep Muslim states existed, but all linked by religion, trade Golden Age of learning: Baghdad House of Wisdom, universities, arts, medicine, engineering: Renaissance Kingdom of Zimbabwe: 1220CE – 1450CE Controlled the Ivory and Gold trade Expansive Empire with over 150 Tributaries Rigid 3-tiered social system Until modern times Great Zimbabwe was the largest stone structure in Southern Africa Trading states along the east coast of Africa, stretching from Kenya to Mozambique Earliest Swahili culture formed in the 6th century BCE Major cultural advances: 900 CE introduction of organized religion (Islam) unique language Shirazi Era: 900CE-1400CE (approx) Golden age of expansion and trading Traded local resources, most notably gold and ivory, other luxury items Connected inner Africa with Indian Ocean trading networks Fell in 1500s as Portuguese rose ~830CE-1235CE With domestication of camel, trans-Saharan trade in gold, salt & ivory routes enriched area No written history; origins of empire uncertain—most info comes from merchants Pre-Islamic, monarchy, stable economy and military (~200,000 soldiers) Traveler wrote of king: He sits in audience or to hear grievances against officials in a domed pavilion around which stand ten horses covered with gold-embroidered materials. Behind the king stand ten pages holding shields and swords decorated with gold, and on his right are the sons of the kings of his country wearing splendid garments and their hair plaited with gold. The governor of the city sits on the ground before the king and around him are ministers seated likewise. At the door of the pavilion are dogs of excellent pedigree that hardly ever leave the place where the king is, guarding him. Around their necks they wear collars of gold and silver studded with a number of balls of the same metals 1230CE – 1340CE Sundiata 1340CE – 1591CE Muslim empire, conquered Mali Largest African empire: 1.4 million sq km Trans-Saharan trade based in empire Gold, ivory, salt Clan system, universities, center of learning & commerce in Timbuktu Established 2000BCE, lasts as a people and culture to present Trade crucial factor: type varied, from long-distance trading spanning the length of the region, to small trading between farm families Each Region had exclusive resources: Highlands = granite and obsidian. Lowlands = cotton, animal skins, feathers, beeswax Northern Yucatan = salt Jade = eastern Guatemala Quetzal feathers = Highland cloud forests Cocoa = west coast Developed civilization: writing, cities, extensive religion, empire of millions 1438CE – 1533CE Developed civilization: quipu, arts, religion, architecture Extensive economy & trading: potatoes, maize, llamas, ducks, cotton, alpaca wool, silver, ceramics & especially gold Tribute-based empire, complex mythology/religion (human sacrifice), calendar, architectural and artistic accomplishments—base of today’s Mexico culture Triple Alliance: three cities Tenochtitlan (Mexico City), Texcoco and Tiacopan, Lead by Emperor Moctezuma Merchants called pochteca Traded gold, silver, cloth and cotton, animal skins, agriculture, wild game, and woodwork At various times the empire controlled modern day China, Korea, Mongolia, Iran, India, Turkestan, Burma, Vietnam, Thailand, and Russia late 1100'sCE, Temujin, a Mongol chieftain later known as Genghis Khan, unified nomadic tribes into a superior fighting force conquered largest geographical empire in history Mongol armies ruthlessly eliminated any resistance in their conquest Inflicted terror and destruction everywhere including the slaughter of entire city populations Established roads connecting Russia and Persia with eastern Asia Greatly increased contact between cultures and promoted trade, religiously tolerant Brought printing, paper, gunpowder, and the compass from China to Europe Began in Han Dynasty: 206BCE Extended 4000 miles Networked Eurasian landmasses & connected China with Europe & areas between Disintegrated after Mongols: 1360CE Last shipped silk : 1400CE Controlled by different empires at different times and places Goods traded: China (silk, perfume, spices, medicines) India (spices, ivory, textiles, gems, pepper) Roman Empire (gold, silver, wine, glassware) Other traded: religion & philosophies (Buddhism esp.),disease (Black Plague), technology (compass, gunpowder) Trade has existed in Mediterranean Sea for millennia Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Muslims Height: 1300s1800s, Italian City-states (jump started Renaissance) Traded: silk, spices, opium Peak: 700CE-1400CE Dominated by Muslim traders & West African empires Traded: gold, salt, ivory, spices Linked West African gold with Renaissance, linked Muslim world together, contributed to creating civilizations in West Africa Always trade in Indian Ocean: based on monsoon season Ancient Rome traded with India Height: 800-1600CE Indians, Swahili city-states, Muslim Empires controlled Traded gold, spices, gems, ivory, other luxury items 1600CE Portuguese took over; world focus switches to Atlantic Early Middle Ages: 476 – 1000CE High Middle Ages: 1000CE – 1300CE Late Middle Ages: 1300CE – 1453CE Early Middle Ages: (“Dark Ages” if any are) depopulation, deurbanization, and increased barbarians North Africa and Middle East become Islamic Towards 800CE, feudalism helps move away from subsistence agriculture & urbanization of Northern and West Europe Religious art & architecture flourished Crusades Nation building Chivalry, courtly love Laws: Justinian Code, mathematics of Fibonacci, philosophy of Thomas Aquinas, paintings of Giotto, poetry of Dante and Chaucer, travels of Marco Polo, architecture of Gothic cathedrals like Calamity: climate change=famine, up to 75 years of it Black Death: toll as high as ½ of population in some places, towns hard hit Prices of labor rose as laborers died, workers felt right to greater earnings=popular uprisings Period of stress in society=creative social, economic and technological developments Church divided against itself (1057CE Great Schism) Further nation building Spread of Black Death