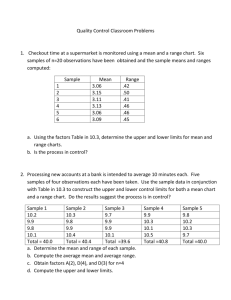
Topic 7
advertisement
Complaint Handling and Service Recovery Think of a time when, as a customer, you had a particularly satisfying (or dissatisfying) interaction with service provider. • When did the incident happen? • What specific circumstances led up to this situation? • Exactly what did the employee (or firm) say or do? • What resulted that made you feel the interaction was satisfying or (or dissatisfying)? • What could or should have been done differently? Complaints • Customers have a low propensity to complain. • Only about 4 % of customers with problems report those problems as complaints. • It is not important whether or not a service failure actually occurred, but rather, if it was perceived by the customer to have occurred. Impact of Service Failure The average customer who experiences a service failure tells nine or ten others about the failure. Customer Response Following Service Failure Service Failure Take Action Do Nothing Switch Providers Complain to Provider Complain to Family & Friends Switch Providers Complain to Third Party Stay with Provider Stay with Provider Entry Points for Complaints • Employees serving customers face-to-face or by phone • Intermediaries acting for original supplier • Managers contacted by customers at head/regional office • Complaint cards mailed or placed in special box • Complaints passed to company by third-party recipients – consumer advocates – trade organizations – legislative agencies – other customers Components of an Effective Service Recovery System Do the Job Right the First Time Effective Complaint Handling Identify Service Complaints -Conduct Research -Monitor Complaints -Develop Complaints as Opportunity Culture Resolve Complaints Effectively Develop Effective Systems and Training in Complaints Handling Learn from Recovery Feedback Increased Satisfaction and Loyalty Conduct Root Cause Analysis Act Quickly Service Recovery Strategies Fail-safe the Service Service Recovery Strategies Treat Customers Fairly Learn from Recovery Experiences Pricing • • • • High Price Price Increases Unfair Pricing Deceptive Pricing Inconvenience • Location/Hours • Wait for Appointment • Wait for Service Causes Behind Service Switching Core Service Failure • Service Mistakes • Billing Errors • Service Catastrophe Service Encounter Failures • • • • Uncaring Impolite Unresponsive Unknowledgeable Response to Service Failure • Negative Response • No Response • Reluctant Response Service Switching Behavior Competition • Found Better Service Ethical Problems • • • • Cheat Hard Sell Unsafe Conflict of Interest Involuntary Switching • Customer Moved • Provider Closed Source: Sue Keaveney Unhappy Customers’ Repurchase Intentions Unhappy Customers Who Don’t Complain 9% Unhappy Customers Who Do Complain Complaints Not Resolved Complaints Resolved 19% 54% 82% Complaints Resolved Quickly Percent of customers who will buy again after a major complaint (over $100 in losses) Source: Adapted from data reported by the Technical Assistance Research Program. Service Guarantees • guarantee = an assurance of the fulfillment of a condition (Webster’s Dictionary) • for products, guarantee often done in the form of a warranty • services are often not guaranteed –cannot return the service –service experience is intangible –(so what do you guarantee?) Service Guarantees Help Promote and Achieve Service Loyalty • Force firms to focus on what customers want • Set clear standards • Compensation highlights cost of service failures • Require systems to get, act on, customer feedback • Reduce risks of purchase and build loyalty • Builds “marketing muscle” Characteristics of an Effective Service Guarantee Unconditional The guarantee should make its promise unconditionally - no strings attached. Meaningful It should guarantee elements of the service that are important to the customer. The payout should cover fully the customer's dissatisfaction. Easy to Understand and Communicate For customers - they need to understand what to expect. For employees - they need to understand what to do. Easy to Invoke and Collect There should not be a lot of hoops or red tape in the way of accessing or collecting on the guarantee. Reasons companies do NOT offer guarantees: Reasons companies do NOT offer guarantees: – too many uncontrollable external variables – fears of cheating by customers – costs of the guarantee are too high Over-compensating concerns? • Service providers should probably be more concerned about under-compensating complaining customers than over-compensating them. • Track the customers who are given compensation for reported complaints. Service Guarantees • service guarantees work for companies who are already customer-focused • effective guarantees can be BIG deals - they put the company at risk in the eyes of the customer • customers should be involved in the design of service guarantees • the guarantee should be so stunning that it comes as a surprise -- a WOW!! factor • “it’s the icing on the cake, not the cake” Recovery • Service providers need to decide on policy for service recovery. • Will all customers with a particular type of problem be given the same service recovery? Recovery Do • • • • • • Acknowledge problem Apologize Take responsibility Explain causes Lay out options Compensate/ upgrade Don’t • Ignore customer • Blame customer • Leave customer to “fend for him/herself” • Downgrade • Act as if nothing is wrong • Pass the buck Early Communication Early Recovery • The service company must decide when and how to appropriately open communication with customers in the service process. • Communication with the customer throughout the service delivery process can decrease the magnitude and expense of service failures • Failure to communicate early in the service process can allow small customer concerns to grow into large problems. • If complaints are resolved in a timely manner, 95% of the time the customer will return. Ways to Increase Customer Communication • Actively solicit feedback. • Offer a channel of communication that is open to customers through the service process. Retaining Customers When Things Go Wrong • Track and anticipate recovery opportunitiesThe customer who complains is your friend? • Take care of customer problems on the front line. • Solve problems quickly. • Empower the front line to solve problems. • Learn from service recovery. Effective Recovery Skills • • • • Hear the customer’s problems. Improvise Bend the rules from time-to-time Employees must have the authority, usually within certain defined limits, to solve the customer’s immediate problem. When service customers have been disappointed on the first try, doing it right the second time is essential to maintaining customer loyalty OOPS! Service Recovery Discussion Develop guidelines for an effective complaint handling policy for a service organization in the industry you selected to study this session. Summary of Guidelines for Effective Problem Resolution • Act fast • Give benefit of doubt • Admit mistakes but don’t be defensive • Clarify steps to solve problem • Understand problem from customer’s viewpoint • Keep customers informed of progress • Don’t argue • Consider compensation • Acknowledge customer’s feelings • Persevere to regain goodwill