Two-stage batch adsorber design using pseudo-second
advertisement

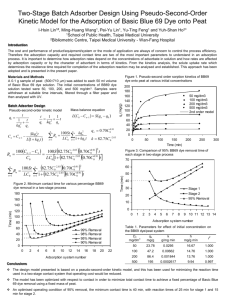
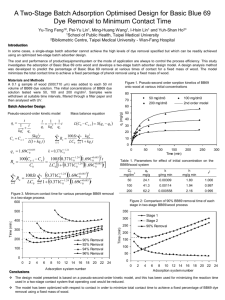
Two-Stage Batch Adsorber Design Using Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model for the Adsorption of Acid Blue 25 Dye onto Peat Pei-Yu Lin1#, Ming-Huang Wang1, Yu-Ting Feng1, I-Hsin Lin1 and Yuh-Shan Ho2* 1School of Public Health, Taipei Medical University 2Bibliometric Centre, Taipei Medical University - Wan-Fang Hospital Introduction Batch adsorber design has mainly concentrated on reducing adsorbent costs, which is particularly relevant when expensive sorbent materials such as active carbon, silica, zeolites and resins are used. But for cheaper adsorbents minimizing the contact time for a fixed percentage of pollution removal using a fixed mass of adsorbent will result in being able to process more batches of polluted wastewater per day, thus enabling the required treatment plant items to be reduced in size, with a decrease in the plant capital cost. This paper studies the adsorption of Acid Blue 25 dye onto peat and develops a two-stage batch adsorber design model. Methods A 0.5 g sample of peat (500-710 m) was added to each 50 ml volume of Acid Blue 25 (AB25) dye solution. The initial concentrations of AB25 dye solution tested were 20, 50, 100 and 200 mg/dm3. Samples were withdrawn at suitable time intervals, filtered through a filter paper and then analysed AB25 concentration using UV. Results Pseudo-second-order kinetic model Cn Cn1 t 1 1 t qt kqe2 qe 100 St n kqn2 Rn LC0 n1 1 kqn t n1 n k 12.3C 01.86 n 0.157C t 0.157C t 0.839 2 0 0.839 0 100St n 12.3C01.86 0.157C LC0 n1 1 12.3C01.86 0.157C 0.839 2 0 0.839 0 1.86 0 1.86 0 n t 350 80% Removal Stage 1 Time (min) 250 300 250 200 89% Removal 86% Removal 83% Removal 80% Removal 150 100 50 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Adsorption system number Figure 1: Comparison of 80% AB25 removal time of each stage in two-stage AB25/peat process 300 450 400 100Cn1 Cn 100S 12.3C C0 LC0 1 12.3C R n 1 LC0 Cn1 S qn q0 350 Skqn2t L1 kqn t q e 0.157C 00.839 Rn Figure 2. Minimum contact time for various percentage AB25 removal in a two-stage AB25/peat process Time (min) t 1 t 2 kqe qe qt Mass balance equation Stage 2 Table 1. Parameters for effect of initial concentration on the AB25/peat system C0 mg/dm3 qe mg/g k g/mg min h mg/g min r2 20 1.85 0.0442 0.152 0.999 50 4.40 0.0110 0.213 0.999 100 7.76 0.00156 0.0941 0.994 200 12.7 0.000747 0.121 0.924 Conclusions 200 The design model presented is based on a pseudosecond-order kinetic model, and this has been used for minimizing the reaction time used in a two-stage contact system that operating cost would be reduced. 150 100 The method proposed in this study enables the contact time in a two-stage batch adsorber to be minimized to achieve a fixed percentage of Acid Blue 25 removal using a fixed mass peat. 50 0 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Adsorption system number An optimised operating condition, the minimum contact time is 191 min, with reaction times of 100 min for stage 1 and 91 min for stage 2.