Module 7 – Strategic Planning
advertisement

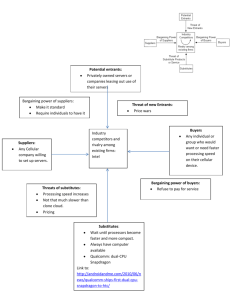
Module 7 – Strategic Planning Chapter 4 Learning Objectives LO1 Summarize the basic steps in any planning process LO2 Describe how strategic planning should be integrated with tactical and operational planning LO3 Describe how strategy is base on analysis of the external environment and the firm’s strengths and weaknesses. LO4 Discuss how companies can achieve competitive advantage through business strategy 4-2 Learning Objectives (cont.) LO5 Describe the keys to effective strategy implementation LO6 Explain how to make effective decisions as a manager. LO7 Summarize principles for group decision making. 4-3 Basic definitions • Strategy – “pattern of actions and resource allocations to achieve the goals of the organization” Basic Definitions • "Strategy is the direction and scope of an organization over the long-term, and which enables the organization to achieve advantage through its configuration of resources within a challenging environment, to meet the needs of markets and to fulfill stakeholder expectations.” To rephrase that…… • Direction: Where is the business trying to go in the long-term? • Markets and scope: Which markets should a business compete in and what kind of activities are involved in such markets? • Advantage: How can the business perform better than the competition in those markets? To rephrase that…… • Resources: What resources (skills, assets, finance, relationships, technical competence, facilities) are required in order to compete? • Environment: What external, environmental factors affect the businesses' ability to compete? • Stakeholders: What are the values and expectations of those who have power in and around the business? Basic definitions • (Stakeholders) – A person, group, or organization that has direct or indirect stake in an organization because it can affect or be affected by the organization's actions, objectives, and policies. – Employees, govt., owners, the community….. Basic definitions • • • • (Stakeholders) Strategic goals/objectives Strategic management Strategic planning Strategic vs. tactical vs. operational In a nutshell • Where are we now? • Where do we want to go? • How will we get there? Whole bunch of nutshells….. • • • • Corporate strategy Business strategies Functional strategies Operating strategies In another nutshell…… Your strengths Expected environmental changes Resource allocations Your weaknesses Expected reactions by competitors The Strategic Management Process S/W O/T 4-15 Sources of sustainable competitive advantage • • • • • Valuable Rare Difficult to imitate Non-substitutable “organized” (?) Core competencies The Strategic Management Process 4-17 SWOT example • SWOT in action Corporate strategies • • • • Concentration Vertical integration Concentric diversification Conglomerate diversification Business strategy • Porter’s 5 Forces PORTER’s 5 FORCES MODEL Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Barriers to entry • • • • • • • • Access to inputs Economies of scale Government policy Brand identity Switching costs Access to distribution Expected retaliation Proprietary products PORTER’s 5 FORCES MODEL Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Buyers Bargaining power of buyers Buyer power • • • • • • Buyer volume Buyer information Brand identity Product differentiation Buyer concentration vs. industry Price sensitivity PORTER’s 5 FORCES MODEL Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Buyers Bargaining power of buyers Threat of substitutes Substitute products Threat of substitutes • Switching costs • Buyer inclination to substitute • Price-performance trade-off of substitutes PORTER’s 5 FORCES MODEL Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers Suppliers Buyers Bargaining power of buyers Threat of substitutes Substitute products Supplier power • • • • Supplier concentration Differentiation of inputs Cost relative to total purchases Switching costs PORTER’s 5 FORCES MODEL Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Bargaining power Industry competitors of suppliers Suppliers Buyers Rivalry among existing firms Threat of substitutes Substitute products Bargaining power of buyers Intensity of competitor rivalry • • • • • • • Very high strategic stakes Large number of firms Diversity of rivals Slow market growth High fixed cost Short shelf-life Low switching costs Advantage Target Scope Low Cost Product/Service Uniqueness Broad (Industry wide) Cost Leadership Strategy (Sam’s) Differentiation Strategy (Toyota) Narrow (Market segment) Focus Strategy (low cost) (Dollar General) Focus Strategy (differentiation) (Tiffany’s) Strategies for Gaining Sustainable Competitive Advantage • Cost leadership –Requires efficiency throughout –Same price, higher margins –Lower price, greater mkt share –All wages low? – Threat? Strategies for Gaining Sustainable Competitive Advantage • Differentiation – TREAD SOFTLY – Customer service, technological superiority – Changing the rules – Increased costs means must have higher price Strategies for Gaining Sustainable Competitive Advantage • Focus – Unique market niche – Premium price/differentiation – Great customer loyalty (why?) – Ex: Bad-credit finance companies, big & tall men’s shops, petite dress shops Does it work???? • Criticism #1 – Assumes the world will "hold still while a plan is being developed and then stay on the predicted course while that plan is being implemented." • Criticism #2 – Manage by objective measures of hard data, • Criticism #3 – Inflexibility – Focus on goals set, not goals that should be set • Criticism #4 – Monkey see, monkey do…. – Bellbottoms and pet rocks