The Hispanic Caribbean
advertisement

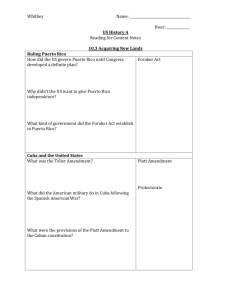
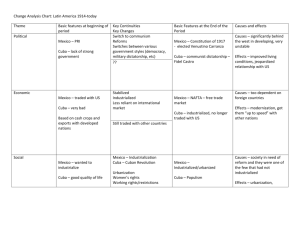
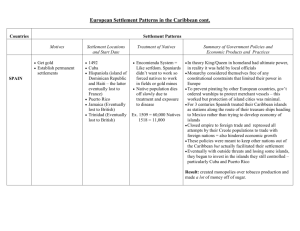
The Hispanic Caribbean Chapter 8 Geography & Environment North American & Caribbean Plates Geology 1. North American Plate • Limestone Plateau – Cuba, Yucatan, Florida – Karst landscape – sinkholes, caverns, karst towers, subterranean rivers – Sierra de los Organos (Cuba) – Sierra de Escambray (Cuba) – Fertile soils – sugarcane 2. Caribbean Plate • Uplifted fault-block mountains (Granite) – Sierra Maestra (Cuba) • Pico Turquino – 1,975 m (6,476 ft.) – Cordillera Central (Dominican Republic) • Pico Duarte – 3,083 m (10,164 ft.) – Cordillera Central & Sierra de Luquillo (Puerto Rico) Republic of Cuba Population: 12 million Population: 9 million Commonwealth of Puerto Rico Population: 4 million Historical Geography & Economic Development • Pre-Columbian culture – Ciboney • Once in Cuba – Arawak/Taíno • Once in Cuba, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico – Caribs • Today in Dominica • Black Caribs in Central America – Zambos – Vocabulary: • Bohío – hut • Hurricane, barbeque • Spanish conquest – Santo Domingo (Hispaniola/Hispañola) • Founded by Bartholomew Columbus in 1496 • 1st European city and 1st Spanish capital in the Americas – Havana (Cuba) • Principal gateway to the New World for Spanish trade • Mercantile trading system – stopover to and from mainland ports of Veracruz, Cartagena, Colón (Acapulco, Lima) • Became more important than Santo Domingo and San Juan • Independence from Spain & U.S. Hegemony – 1865 – Santo Domingo – 1898 – Cuba & Puerto Rico – Spanish American War Economy • Sugarcane – Spain – importation of African slaves – United States investment after the Civil War • Slavery abolished until 1878 (Puerto Rico) & 1886 (Cuba) – Cultivation and Processing on Plantations • Small family plantations gave way to large landholdings • Sugar mills: trapiches, ingenios, and centrales • Sugar, molasses, and rum • Other crops and livestock – – – – Tobacco Indigo Coffee Cattle ranching U.S. Hegemony & the “Yankee Years” • Spanish American War – 1898 – Cuban revolution for independence • José Martí, Antonio Maceo, and Máximo Gómez – U.S.S. Main explosion in Havana Harbor – T. Roosevelt and the “Rough Riders” – San Juan Hill • Puerto Rico – U.S. territory in 1901 • Cuban “independence” in 1902 – Platt Amendment – mediated “sovereignty” – Guantánamo Bay Naval Base • Camp X-Ray – in order to avoid U.S. law toward prisoners – Dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista – 1933 - 1944, 1952 - 1959 • Dominican Rep. – U.S. intervention – – Dictatorship of Rafael Trujillo – 1930 – 1961 – Marines landed in 1965 Cuban Revolution • Fidel Castro • 26 of July Movement – 1953 – Moncada Barracks • Che Guevara – Return to Cuba on the Granma • Revolution of 1959 • U.S. Embargo – 1960 – Helms-Burton Act of 1996 • Bay of Pigs Invasion – 1961 • Cuban Missile Crisis – 1962 Contemporary & Social Geography • Cuba – “Revolution” continues • • • • • Education Healthcare Provision of food and consumer goods – bodegas Housing Committees for Defense of the Revolution (CDRs) – Special Period of 1990s • Tourism • Self-sufficiency • Remittances from exiles • Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico – Tourism • Advantages – State and regional economic options – A clean industry – Educational • Disadvantages – Disjunctive development – Degrades fragile environmental resources – Inauthentic representations of native cultures Tourism: A Mixed Blessing? MEXICO ¡Ándale! Chapter 9 Historical Landscapes of Mexico • Pre-Columbian – Teotihuacán – Tula (Toltecs) – Tenochtitlán (Aztecs) • Tlaxcala • Purepecha (Tarascans) • Spanish Colonial – Hernán Cortez vs. Moctezuma – Haciendas – Silver and gold mining in the Bajío region • Independence and Republican Period – “Grito de Dolores” – Dolores (near Guadalajara) Historical Landscapes of Mexico – 1821 – independence from Spain for Mexico and Central America – Mexican-American War – 1846 • Gen. Zachary Scott Taylor – Monterrey (1846) • Gen. Winfield Scott – Mexico City (1847) • Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) – present border between Mexico & U.S.l – French Intervention – Emporer Maximiliam I (1861 – 1867) – Modernization of Mexico and the Railroads – President Benito Juárez – “Pax Porfiriato” (1876 – 1911) – President Porfirio Díaz • Mexican Revolution – Pancho Villa (North) & Emiliano Zapata (South) • Constitution of 1917 – Expropriation and the Ejido Regions of Mexico 1. Independent North • • • Borderlands Arid Northwest Humid Gulf Lowlands 2. Central Mexico • • Central Metropolitan Axis El Bajío 3. Southern Poverty Belt • • • • Southern Mountains Chiapas Yucatán Tourist Fringe “Club Mex” • • • Mayan Riviera Pacific Resorts Baja California Regions in Mexico Mexican Plateau 1. Mesa Central - Valle de Mexico – Neovolcanic Range • Pico de Orizaba – 18,490 ft. • Popocatepetl Volcano – 17,887 ft. • Paricutin & Colima – Mexico City – Guadalajara (Mexico’s 2nd largest city), Puebla, Morelia – El Bajío (Guanajuato, Querétaro, San Miguel de Allende) • Spanish colonial mining centers Regions in Mexico 2. Mesa del Norte – Coahuila, Chihuahua, Sonora Deserts – mesquite, cacti, agave, creosote – Northern Borderlands (Mexamerica) – Monterrey (Mexico’s Pittsburgh): 3rd largest city in Mex. – Mining and manufacturing – Saltillo, Monclova, Chihuahua, Torreon, Durango, Hermosillo, San Luis Potosi – “Silver Belt” – Zacatecas, Durango, Parral, Chihuahua – Haciendas – Ranching – Mexican Border towns – Matamoros, Reynosa, Nuevo Laredo, Ciudad Juarez, Nogales, Mexicali, Tijuana – Maquiladoras – Mormons and Mennonites • Sierra Madre Oriental – sedimentary (mostly karst – i.e. limestone) • Sierra Madre Occidental – volcanic origin (mostly crystalline – i.e. granite) – Copper Canyon – Chihuahua Central America Chapter 10 Physical Environment • Caribbean & Cocos Plates • Sierra de los Cuchumatanes • Central American volcanic axis – – – – Guatemala: Agua Vol., Fuego Vol., Lake Atitlán El Salvador Nicaragua: Concepción, Momotombo, Masaya Costa Rica: Arenal, Poás, Irazú • Lake Nicaragua – Freshwater sharks – San Juan River • 49 Gold Rush • Caribbean Lowlands – humid tropical • Pacific Lowlands – tropical wet-and-dry • Highlands in Guat. and C.R. – tierra fría and páramo – Mt. Chirripó • Wildlife: resplendent quetzal, toucans, parrots, tree sloths, capuchin & howler monkeys, and many others Historical and Contemporary Geography • • • • • United Provinces of Central America (1823 – 1840) Highlands: Coffee farms – fincas (Costa Rica vs. El Salvador) Caribbean Lowlands: Bananas – Standard/United Fruit Company Guatemala and Costa Rica: Tourism Costa Rica, Panama, Nicaragua: Expatriots from N. America & Europe United States as regional hegemony (Gringos) – “Yankee Years” • Monroe Doctrine • President Theodore Roosevelt “The Bully” – Panama Canal – "Carry a Big Stick and use it..." – Rough Riders and San Juan Hill (Cuba) • Good Neighbor Policy – President Franklin D. Roosevelt • Alliance for Progress – President John F. Kennedy Guatemala • Jacobo Arbenz – democratic leader of Guatemala • United Fruit Co. of Boston – “The Octopus” – Bananas • CIA and Operation Success – deposed Arbenz • John Foster Dulles (Advisor to President Dwight Eisenhower) • URNG – Guatemalan National Revolutionary Unity Historical and Contemporary Geography Nicaragua • Río San Juan and Lake Nicaragua – Trans-isthmian route for 49ers in California Gold Rush – Potential canal prior to Panama Canal • William Walker – filibuster from Nashville, Tennessee & established Nicaragua as a slave empire – President of Nicaragua 1856 – 1857 – Captured by British and executed by Hondurans • • • • • • • • U.S. Marines – 1912 – 1933 Augusto César Sandino – rebel leader Anastasio “Tacho” Somoza García – Nicaraguan National Guard Anastasio “Tachito” Somoza Debayle Pedro Joaquín Chamorro – journalist assassinated by Somoza Debayle Revolution in Nicaragua – 1979 Violeta Chamorro (FSLN Junta member, President in 1990) Daniel Ortega (FSLN Junta member, President in 1980s, current President since 2006) • FSLN “Sandinistas” – Sandinista National Liberation Front • “Contras” – Contra-Sandinistas (illegal funding and support by President Ronald Reagan) Historical and Contemporary Geography El Salvador • Civil War • Assassination of Archbishop Oscar Romero in 1980 • FMLN – Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front • U.S. military advisors Costa Rica • Juan Santamaria – pushed W. Walker out of C.R. in 1856 • Civil War – Figueres vs. Calderón (1948) – Abolished military – Public healthcare • Oscar Arias – Nobel Peace Prize (1987) – Ending conflicts in Central America Panama – independence in 1903 • Canal – completed in 1914 – Canal Zone reverted to Panamanian sovereignty in 2000 • Gen. Manuel Noriega – U.S. Invasion in 1989 Caribbean Lowlands • Mosquito (Miskito) Coast/Mosquitia – British loggers (mahogany) • Black Caribs/Garifuna of Honduras Physical Environment Guatemala Costa Rica ¡Pura vida!