Chapter 12
advertisement

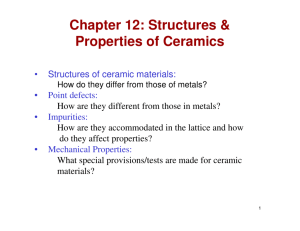
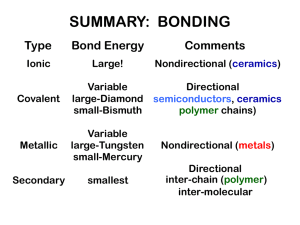
CHAPTER 12: STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF CERAMICS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... • Structures of ceramic materials: How do they differ from that of metals? • Point defects: How are they different from those in metals? • Impurities: How are they accommodated in the lattice and how do they affect properties? • Mechanical Properties: What special provisions/tests are made for ceramic materials? Chapter 12- 1 CERAMIC BONDING • Bonding: --Mostly ionic, some covalent. --% ionic character increases with difference in electronegativity. • Large vs small ionic bond character: Adapted from Fig. 2.7, Callister 6e. (Fig. 2.7 is adapted from Linus Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd edition, Copyright 1939 and 1940, 3rd edition. Copyright 1960 by Chapter 12- 2 Cornell University. IONIC BONDING & STRUCTURE • Charge Neutrality: --Net charge in the structure should be zero. Cation Anion --General form: The anion is larger than cation. • Stable structures: --maximize the # of nearest oppositely charged neighbors. Adapted from Fig. 12.1, Callister 6e. Chapter 12- 3 COORDINATION # AND IONIC RADII • Coordination # increases with Issue: How many anions can you arrange around a cation? (covalent) Zinc Sulfide Adapted from Fig. 12.4, Callister 6e. SiC, ZnTe (ionic) Adapted from Fig. 12.2, Callister 6e. Also MgO, MnS, LiF, and FeO (ionic) Adapted from Table 12.2, Callister 6e. Adapted from Fig. 12.3, Callister 6e. Like a BCC structure Chapter 12- 4 Two interpenetrating FCC lattice, one composed of anions and the other of cations Chapter 12- Close packing of anions Octahedron Tetrahedron Chapter 12- EX: PREDICTING STRUCTURE OF FeO • On the basis of ionic radii, what crystal structure would you predict for FeO? Cation Al3+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Ca2+ Table 12.3 in textbook Anion O2ClF- • Answer: r cation 0.077 r anion 0.140 0.550 based on this ratio, --coord # = 6 --structure = NaCl Data from Table 12.3, Callister 6e. Chapter 12- 5 AmXp STRUCTURES r cation 0.100 0.8 • Consider CaF2 : r anion 0.133 (Fluorite) • Based on this ratio, coord # = 8 and structure = CsCl. • Result: CsCl structure w/only half the cation sites occupied. • Only half the cation sites are occupied since #Ca2+ ions = 1/2 # F- ions. Adapted from Fig. 12.5, Callister 6e. Chapter 12- 6 Two types of cations AmBnXp STRUCTURES Example: Barium Titanate (BaTiO3) Chapter 12- 6 Ceramic Density Calculations Number of formula units within the unit cell n( AC AA ) VC N A Sum of the atomic weights of all anions in the formula unit Example: density of Sodium Chloride Formula is NaCl n´=4 (because there are 4 Na atoms and 4 Cl atoms within a unit cell) VC=a3=(2(0.102E-7)+2(0.181E-7))3=(0.566E-7)3 4(22.99 35.45) 3 2 . 14 g / cm (0.566 E 7)3 (6.023E 23) a=2rNa++2rClChapter 12-