Greece - Historymrcrino59
advertisement

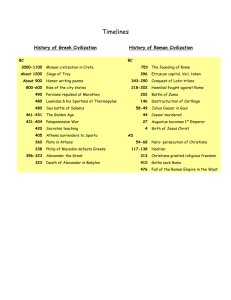
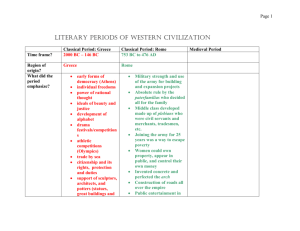
Ancient Greeks – Greece arose through migrations of many people many surrounding civilizations – Two major tribes arise… 1. Mycenaens 2. Dorians From these two tribes two great states will appear 1. Sparta 2. .Athens What does Hellenic Mean? Through cultural diffusion of people traveling from Egypt, and Mesopotamia a rich mixture of culture arose and formed early Greek or HELLENIC Culture. Greeks called their religion Hellas 1200s B.C. Rise of the Polis – Polis means “City State” – City States--- independent cities Have their own governments and cultures Built in the same area but independent of one another. Life in Ancient Greece Religion Greeks were Polytheistic Worshipped major Deities in the Pantheon Greeks believed different Gods controlled different aspects of life The Pantheon Zeus King of Gods God of Sky, lightning rain; Hera Goddess of Marriage virtue, women, childbirth Athena Patron Goddess of Athens, War Hermes and Protector of Flocks Shepherds, travelers; Aphrodite Goddess of Love and Beauty Apollo Artemis Poseidon God of Prophecy, Medicine, archery, courage and wisdom Goddess of the hunt protectress of youth beauty Producer of thunder shaker of the earth God of the Sea Various Festivals took place in honor of certain gods and goddesses. Delphi Temple Location of the built in honor of Apallo Became a religious and commercial center. Persian Wars 546 B.C. Cyrus the Great of Persia conquers Ionia. (Western Turkey) 499 b.c. Ionia revolts Darius I Persian King. Puts down revolt. Ionians were aided by Athenians 490 B.C. Darius tries to punish Athens for helping Ionia Athens Xerxes Defeats Darius’ army at the battle of Marathon. Darius’ son Xerxes After Persian Wars Attacked Athens 480 b.c. Sparta aided Athens Defeated Persians at the Battle of Salamis Athens formed the Delian League Delian League Alliance of many Greek City States Athens came to control the league Sparta Refused to join Set up their own alliance known as Peloponnesian League Athens and Sparta Athens and Sparta were the two greatest City States of Ancient Greece. 1200s-800s B.C. Life during these times was Chaotic. Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey were written during this time Sparta Location: Peloponnesus Founders: Dorians Economy: Agriculture Labor: Helots (slaves) Social Order: Military Society Military Training begins at Age 7. Ages 20-30 Men did military field service Ages 30-60 Men married and lived in barracks Athens Location: Attica Penin Founders: Mycenaeans Economy: Seafaring traders Labor: Commoners Social Order: Private Educ males 7-18 Math, literature, music, and Rhetoric. Military Service 18-20 Age of Pericles Pericles 461-429 B.C. Golden Ages of Greece New Interest in The Arts Parthenon and Acropolis both built during this time Greek Philosophy Philosophers Scholars who analyze the process of reason. These men refused to believe that the world was controlled by the Gods Democritis Studied Composition of matter and the Atom Hippocrates Studied and applied philosophy to physics, biology, and chem Pythagoras applied Philosophy to geometry music theory and astronomy Sophists Sophists Philosophers who turned their away from science and philosophy and studied politics, law and rhetoric. Many philosophers rejected sophist ideas. Said they were narrow minded and materialistic. Anti-Sophists Focused their studies on truth, justice ethics and beauty Socrates Plato Aristototle Philosophers Socrates Socratic Method Three Famous AntiSophist Socratic Method Teaching through questioning. Never giving answers. Socrates Put to Death For corrupting the youth of Athens Plato Student of Socrates Wrote “Platos Republic” Described the perfect ruler as a philosopher monarch The Academy Platos school. Science, Math, Ethics, Logic Rhetoric Teacher of Aristotle Aristotle 384-322 B.C. Focused his teachings on logic. Excellence is an art won by training and habituation. We do not act rightly because we have virtue or excellence, but we rather have those because we have acted rightly. We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act but a habit. Studied in the Academy for over 20 years King Philip Macedonia Invited Aristotle to tutor his son Alexander Alexander the Great Became a great student of Aristotle 335 B.C. Alexander the Great Established the Lyceum Son of Philip II of Macedonia 356-323 B.C. Became Ruler of Macedonia after his father was assassinated in 336. After Alexanders death in 323 his empire was broken up into Macedonian, Asian, and Egyptian dynasties. Alexander was only 20 Alexander became a very accomplished military general and conquered one of the largest empire of the time. Other Types of Philosophy 1. Cynicism 2. Stoicism 3. Epicurianism Cynicism Happiness is achieved by cultivating virtue and self-control Stoicism Happiness is achieved by controlling emotion and having a reasonable outlook on life Epicurianism Knowledge is based on your senses Spread of Hellenistic Civilization Hellenistic Refers to the blend of culture after the power of the city-state faded and Alexander took over much of the territory. Hellenistic Scholars 1. Euclid 2. Aristarchus 3. Archimedes Euclid Geometry Aristarchus Earth Orbits the Sun Archimedes Simple Machines water displacement ROME Latin Tribe Founded Rome in 753 B.C. 7th to 1st Cent B.C. Military Generals conquered the entire Italian Peninsula, Sicily, and Carthage. Government during this time, government went from monarchy to republic to dictatorship Etruscan Kings Overthrown 509 B.C. Overthrown by the Senate. Birth of the Roman Republic By 200s B.C. Rome had conquered most of Northern Africa, Greece and the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Romans adopted many parts of Greek Culture Architecture Built the Circus Maximus and Colosseum Circus Maximus could hold up to 250,000 people. Roman Government Patricians Wealthy Romans who controlled the Senate Created the Laws Consuls Two were elected annually Military Generals served as the Executive Branch Plebians Second class common citizens paid taxes, did military service but no voice in government By 400s B.C. Plebians demanding a say in government. Demanding laws be written down and made public 450 B.C. Laws of the twelve Tables Created. Laws of Twelve Tables Laws of Rome, written and placed in the forum Became the basis of the Roman legal system Plebians Granted the right to have and assembly. their assembly was known as the Assembly of Tribes Tribunes 366 B.C. elected reps of the A of T who could address their concerns in the senate Tribunes could be elected as consuls 287 B.C. Assembly of Tribes granted the right to make the laws in the Senate Punic Wars 264-146B.C. Between Rome and Carthage for territory. Second Punic War Most Famous Hannibal---General of Carthage Scipio---General of Rome Hannibal Tries a sneak attack on Rome Marched thousands of men and forty elephants over the Alps, to attack Rome from the North. most of the elephants died attack failed Third Punic War 149-146 B.C. Rome destroys Carthage, sells people into slavery End of Roman Republic 1st Century--- Much warfare and high taxes. Wealthy Landowners were the only ones making money on their Latifundias Latifundias Large Roman Estates Political Unrest Gaius Marius and Lucius Sulla Marius 104-100 B.C. Created Professional Army Sulla Overthrew Marius and took over in 88 B.C. Sulla 70 B.C. Got rid of all plebians from leadership. Gnaeus Pompey, Marcus Crassus and Julius Caesar Form the FIRST TRIUMVIRATE Restored Stability to Rome. Crassus Caesar Pompey Feared Caesars Power Dies in Battle. 53 B.C. Conqueres Northern Europe Afraid he would overthrow the government. Pompey and the Senate ordered Caesar to leave his army and return to Rome Caesar Battles Pompey 49-45 Civil War Chases Pompey through Egypt and through Northern Africa, and back to Europe into Spain. Conquers Pompey While in Egypt he makes Cleopatra His Mistress and Queen. 44 B.C. Senate makes Caesar Dictator for Life Reforms of Caesar Changed Tax Structure Redistributed Land Expanded Citizenship Reformed the Calendar Fear of Caesar 44 B.C. Senate feared his power and popularity. Caesar is assassinated by members of the Senate Civil War Again Marc Antony, Marcus Lepidus, and Octavian were supporters of Caesar 2nd Triumvirate These men defeated Caesars enemies Octavian Caesars Nephew Removed Lepidus from Power and Began Civil war with Marc Antony Octavian Chased Antony down to Egypt. Marc Antony had take Cleopatra as his Mistress Battle of Actium 31 B.C. Marc Antony and Cleopatra defeated by Octavian Roman Republic Comes to an End 27 B.C. Octavian Takes on Title Caesar Augustus (Exalted Emperor) Continued Caesars Reforms Oversaw the Golden Age Otherwise known as the Pax Romana. 200 Years of Roman Peace Secured the Borders Created Road Network Postal System Encouraged Roman Art and Architecture