Introduction to LEDs
advertisement

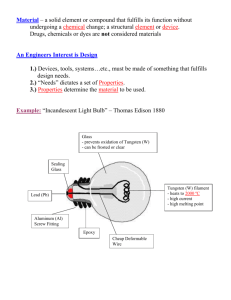
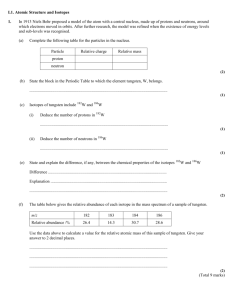
Xiaoyu Sun 24012083 2008-12-2 1 Intro – what is led How does it works Where it uses Advantages and disadvantages Green city 2008-12-2 2 Photo from www.mulelighting.com Photo from www.gizmowatch.com Photo Credit 2008-12-2 sandstep via Flickr 3 2008-12-2 4 2008-12-2 5 When current flows across a diode, negative electrons move one way and positive holes move the other way. 2008-12-2 6 The holes are at lower energy level than the free electrons, so when a electron falls it loses energy. 2008-12-2 7 The energy is emitted in the form of a light photon. The wavelength depends on the band gap energy of the materials forming the p-n junction. 2008-12-2 8 Direct band gap Indirect band gap 2008-12-2 9 Indicators and signs Lighting Smart lighting Non-visual applications 2008-12-2 10 2008-12-2 11 Left: A supermarket in Switzerland Right: Parking garage in Raleigh, NC 2008-12-2 12 Smart lighting Non-visual applications 2008-12-2 13 • • • • • Efficiency Color Cost Lifetime On/Off time Dimming Cool light Shock resistance Focus Toxicity 2008-12-2 14 High price Temperature dependence Voltage sensitivity Area light source 2008-12-2 15 Raleigh, NC Toronto, Canada Ann Arbor, MI 2008-12-2 16 Roughly estimation: Assume φ = 45 lm I = 350 mA V = 3.42 V luminous efficacy 45 lm/(0.35 A x 3.42 V) = 38 lm/W (From the website of U.S. department of energy) 2008-12-2 17 Category Type Overall luminous efficacy Overall luminous efficiency Incandescent 5 W tungsten incandescent (120 V) 5 0.7% 40 W tungsten incandescent (120 V) 12.6 1.9% 100 W tungsten incandescent (220 V) 13.8 2.0% 100 W tungsten glass halogen (220 V) 16.7 2.4% 100 W tungsten incandescent (120 V) 16.8 2.5% 2.6 W tungsten glass halogen (5.2 V) 19.2 2.8% white LED 10-90 1.5% - 13% white OLED 102 15% Prototype LEDs Up to 161 Up to 25% Light-emitting diode 2008-12-2 18 Color Wavelength (nm) Voltage (V) Semi-conductor Material Infrared λ > 760 ΔV < 1.9 GaAs, AlGaAs Red 610 < λ < 760 1.63 < ΔV < 2.03 AlGaAs, GaAsP, AlGaInP, GaP Orange 590 < λ < 610 2.03 < ΔV < 2.10 GaAsP, AlGaInP, GaP Yellow 570 < λ < 590 2.10 < ΔV < 2.18 GaAsP, AlGaInP, GaP 500 < λ < 570 InGaN / GaN, 2.18 < ΔV < 4.0 GaP, AlGaInP, AlGaP Green 2008-12-2 19 Color Wavelength (nm) Voltage (V) Semi-conductor Material Blue 450 < λ < 500 ZnSe, InGaN 2.48 < ΔV < 3.7 SiC/ Si as substrate Purple multiple types 2.48 < ΔV < 3.7 Violet 400 < λ < 450 2.76 < ΔV < 4.0 InGaN Ultraviolet White λ < 400 Broad spectrum Blue w/red, white w/ purple 3.1 < ΔV < 4.4 diamond (C), AlN, AlGaN, AlGaInN ΔV = 3.5 Blue/UV diode with yellow phosphor 2008-12-2 20 2008-12-2 21 2008-12-2 22 Reference: [1] S. S. Iyer 1, Y. -H. Xie. Science 2 April 1993: Vol. 260. no. 5104, pp. 40 – 46. Light Emission from Silicon [2] Nobuyoshi Koshida, Hideki Koyama. Efficient Visible Photoluminescence from Porous Silicon. [3] http://en.wikipedia.org [4] http://electronics.howstuffworks.com 2008-12-2 23