Psychology - Mr. Duez UNIT 4 - Cognition Language & Thought
advertisement

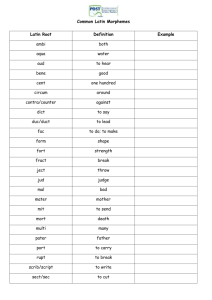
Language How do we Communicate? Its all about communication!!! Apes & Signing Honeybees seem to communicate Warm Up: "Curious blue ideas sleep furiously." At what level is this statement ambiguous? Don’t know this word??? Look it up! "Curious blue ideas sleep furiously." At what level is this statement ambiguous? SEMANTICALLY AMBIGUOUS: Semantics: the branch of linguistics and logic concerned with meaning. Ambiguous: unclear or inexact because a choice between alternatives has not been made. LANGUAGE complex communication system that involves the use of abstract symbols to convey unlimited messages. Human language can convey meaning about things that... haven't happened yet, happened in the past, may never happen. Because we can transcend time and space with language, we have an unlimited ability to communicate ideas. Language is an amazing gift ★ distinguishes humans from other species ★ essential to human cooperation ★ it is mysterious - how did it start, evolve, & change? ★ it is central to human life ★ we take it for granted Language has been found in EVERY society ever found. 6,000 different languages. “Man has an instinctive tendency to speak as we see in the babble of our young children while no child has an instinctive tendency to bake, brew, or write.” - Charles Darwin What can studying language help us understand about human behavior and the human mind? VSauce Video Link: "English" (6:58) Where does English come from? Language is an amazing gift Language is not thought. Do we have to have language to think? No. Can we have sophisticated cognition, cause and effect, objects, & intentions of others w/o speech Babies - before they have learned to speak Animals - chimps using sign language helped to show us that they were thinking At times, we ‘think’ without language. Spatial relations is a great example We use tacit (understood or implied) knowledge to understand language. Cognitive psych has shown us that long term memory remembers the ‘gist’ rather than the exact form of words. We don’t reproduce entire sentences we have heard. What sticks is abstract - meaning, content, semantics Language is an amazing gift Language can definitely impact thought though. It can impact the perception of a person who fumbles common grammar rules & syntax. Language is really 3 things: 1. Words (our personal dictionary) 2. Rules syntax- rules to assemble sentences; morphology- rules to create words from smaller portions; & phonology- rules to combine vowels & consonants into the smallest words 3. Interfaces (methods of communication) Structure of Language: Multi-layered process. Phonemes: smallest unit of sound in a language. All the letters of the alphabet are phonemes. In English we produce all the unique sounds that we are able to make by combining about 40-50 unique phonemes. Other languages make due with less. Hawaiian = 30 phonemes. Morphemes: smallest unit of meaning in a language. Small words: cat or walk Also: prefixes & suffixes If we add the letter s to cat, we now have two morphemes (cat(s)), and if we add-ing to walk, we have two morphemes (walk(ing)). "Unbreakable" 3 morphemes: un- (a bound morpheme signifying "not"), -break- (the root, a free morpheme), and -able (a bound morpheme signifying "do-able"). YouTube: Articulation of Phonemes Grammar: system of rules used in a language. Semantics: the way we understand meaning from words by their morphemes and from their context. ★ Adding an -s to the end of a word - referring to more than one ★ Words can have different meanings depending on the placement in a sentence or on the context. "I'm dying!" Very different meanings ★ when said by a person who is bleeding on the ground ★ versus an adolescent preparing for her first middle school dance. Syntax: rules that refers to the way we order words to create meaning. "Your new please away shoes put" …makes us confused, whereas “Please put away your new shoes" …is quite clear. How Do We Learn Language? Behaviorists exposed to environment, reinforcement, & repetition (Skinner-OC) Nativists Argue that we are "hardwired" to learn language & that humans are unique in that respect. (Social Learning Both sides have supporters, evidence isn't clear which is correct. Milestones in Language Acquisition AGE --> MILESTONE To 2 months --> Cooing 2 months to 12 months --> Babbling Approx. 12 months --> First word ( matching a simple sound: "DA") Approx. 16 months --> 2-word utterances (telegraphic speech) 2-6 years --> Add 6-10 new words a day; learn grammar. Over-extension. ("doggies" for ever 4-legged animal) Age 5 --> Overregularization: "I go-ed to the store." From Age 5 on --> Add words to vocabulary; learn subtleties of language. **Other languages show the same pattern of acquisition (not just English). A 40-year-old couple emigrate from Italy to the United States. They have an two daughters, one is 15 and the other is 7. Based on research that has investigated mastery of English as a second language, Which family member will master English first? 7-year-old daughter will master English more quickly. Language Development How many words do you think you know now? Probably close to 80,000 After age 1 you average 13 words a day. What made these Super Bowl commercials funny? The joke was “language acquisition” – funny/odd to see a baby talk like a trader. LANGUAGE & THOUGHT Do our words shape the way we think, or do we have ideas first and then look for ways to articulate them? Linguist Benjamin Whorf believed in… linguistic determinism: our words shape & restrict our thinking. Whorfian hypothesis Not THAT Worf! language affects thought, and the structure of the language itself affects cognition. Sapir-Whorf hypothesis: Language determines our experience of reality, and we can see and think only what our language allows us to see and think. For example, the Inuit are said to have many different words for snow, and their sophisticated snow vocabulary make it easy for them to communicate and understand each other. Therefore, they see and experience ‘snow-covered landscapes’ quite differently from the rest of us. Although the Inuit have many different words for snow, it does does not show that language determines reality, but instead suggests that reality determines language. The reason the Inuit have many words for snow is because of their environment, they live in snow. In contrast, the reason there are not many words for ‘snow’ in Australia is that it does not snow very often in Australia. Modern Family and how language can effect our view of others ●https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g68KgoHWupg Thinking and Problem Solving Do Animals think? Kohler: Insight Learning - Chimps can problem solve. It has been observed that the manner in which chimpanzees solve problems, such as that of retrieving bananas positioned out of reach, is not through trial-and-error. Instead, they were observed to proceed in a manner that was unwaveringly purposeful. Animals of quite a range of species are capable of solving a range of problems that are argued to involve abstract reasoning; Modern research has tended to show that the performances of Wolfgang Köhler's chimpanzees, who could achieve spontaneous solutions to problems without training, were by no means unique to that species, and that apparently similar behavior can be found in animals usually thought of as much less intelligent, if appropriate training is given. 4 STRATEGIES TO PROBLEM SOLVING 1. ALGORITHMS step-by-step approach. 2. HEURISTICS a procedure that has worked in the past and is seen as likely to work in the future. 3. MEANS-END ANALYSIS keeps in mind the final goal when setting sub-goals. 4. WORKING BACKWARD start with the goal state and work backward until you reach the present state. 4 STRATEGIES TO PROBLEM SOLVING ALGORITHMS step-by-step approach Some algorithms involve simple trial and error. If X is a possible solution to a problem, the algorithm for a solution might be stated: "Try X; if X works, then X = solution; if X doesn't work, then try next X." Clearly, this could go on as many times as there is another possible X. Algorithms guarantee a solution but can be very time consuming. 4 STRATEGIES TO PROBLEM SOLVING HEURISTICS a procedure that has worked in the past and is seen as likely to work in the future. Heuristics are "rules of thumb" based on past experiences. If the light in your room goes out, you could check the fuse box, change the lightbulb, check the wires in the wall or lamp, check the socket, and so on. Because experience suggests that the probability of the light bulb burning out is higher than the other choices, you try that first. Heuristics take less time than algorithms, but they may not result in a solution. 4 STRATEGIES TO PROBLEM SOLVING MEANS-END ANALYSIS final goal is in mind when setting subgoals ★ In planning your study for finals, you might start with math but will set a time limit because you have exams in three other subjects. ★ Will you need to spend the same amount of time on each? ★ What exactly do you need to focus on? 4 STRATEGIES TO PROBLEM SOLVING WORKING BACKWARD start with the goal state & work backward until you reach the present state. When a company wants to know how its competitor's product works, it will "reverse engineer" that product. This means beginning with the product and analyzing its construction to see what each part does. The company can then begin with its own parts and reconstruct a similar product. ★ After seeing several television programs on shark attacks, you start Examples of to think that such incidences are relatively common. When you go on Availability vacation, you refuse to swim in the ocean... WHY? Heuristic ★ After seeing news reports about people losing their jobs, you might start to believe that you are in danger of being let go. You start lying awake in bed each night worrying that you are about to be fired. ★ After read about lottery winners, you overestimate your own likelihood of winning the jackpot. You spending more money than you should each week on lottery tickets. ★ Your mother, next door neighbor and best friend have all been in a car accident this year. According to the availability heuristic, you will feel that your chances of being in an accident yourself are much higher.