BIOL 197L * Lab #7: INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY AND ANATOMY I
advertisement

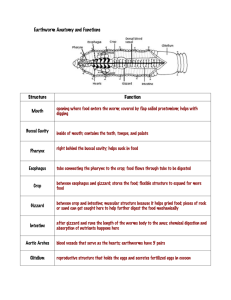
BIOL 197L – Lab #7: INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY AND ANATOMY I Which phyla did we study in class? And what genera represented these phyla? Cnidaria Hydra sp. Platyhelminthe Dugesia sp. Mollusca Venus sp. Annelida Lumbricus sp. What phylum does this organism belong to? What genus does this organism belong to? Which life form is represented here? What is the other life form? Cnidaria Hydra Polyp (sedentary) Medusa (free-swimming) Other types of organisms that represent the phylum Cnidaria: • • • • Jellyfish Sea anemones Corals Hydrozoans What symmetry do cnidarians show? Radial symmetry What type of body plan do cnidarians show? Diploblasty • Two germ layers: • Ectoderm • Endoerm What internal space acts as the central digestive cavity? Gastrovascular cavity Is the gastrovascular cavity a complete or an incomplete gut? The gastrovascular cavity is an incomplete (or blind) gut Identify: Gastrovascular cavity Identify: Tentacles What are the stinging cells of the tentacles called? Nematocysts • Used to paralyze and entangle prey • The tentacles push food through the mouth opening Identify: Mouth How do members of the genus Hydra reproduce? Asexually and sexually (hermaphroditic) What is the asexual method called? Budding Note that budding occurs from the gastrovascular cavity Identify: Tissue What germ layer is it derived from? Epidermis Derived from ectoderm Identify: Tissue What germ layer is it derived from? Gastrodermis Derived from endoderm What acellular substance joins the tissue tissues? Mesoglea Is this Hydra a male or female? What is the structure that produces this type of gamete called? Male (note the multiple spermaries) Testes (spermaries) Is this Hydra a male or female? What is the structure that produces this type of gamete called? Female (note that only one ovary is present – as opposed to multiple spermaries in males) Ovary Identify: Identify: Tentacles (The outer layer) Identify: Tentacles Epidermis The middle layer Identify: Tentacles Epidermis Mesoglea Identify: Tentacles Epidermis Mesoglea Flagellum Identify: Tentacles Mouth Epidermis The inner layer Mesoglea Flagellum Identify: Tentacles Mouth Epidermis Gastrodemis Mesoglea Flagellum Identify: Tentacles Mouth Epidermis Gastrodemis Mesoglea Gastrovascular Cavity Flagellum Identify: Identify: Tentacles (Containing nematocysts) Identify: Tentacles (Containing nematocysts) Mouth Identify: Tentacles (Containing nematocysts) Mouth Asexual bud What phylum does this organism belong to? What genus does this organism belong to? Platyhelminthe Degusia sp. • Free-living flatworms • AKA planarians What type of symmetry does Degusia sp. show? Bilateral symmetry What is the term that is used to describe the evolutionary milestone that resulted in the anterior concentration of nervous tissue, in other words the presence of a head? Cephalization What body type does Degusia show? Acoelomate Identify: Structure Purpose Auricle (ear-like structure) Contains a variety of sensor cells, chiefly of touch and chemical detection Identify: Structure Purpose Eye spots Detect light Identify: Structure Purpose Pharynx Feeding structure Identify: Identify: Ventral nerve Cords Identify: Ventral nerve Cords Pharynx Identify: Gastrovascular Cavity Ventral nerve Cords Pharynx Identify: Gastrovascular Cavity Ventral nerve Cords Pharynx Eyespots Identify: Gastrovascular Cavity Ventral nerve Cords Pharynx Eyespots Ganglia Identify: Gastrovascular Cavity Ventral nerve Cords Pharynx Eyespots Auricles Ganglia Identify: Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Cilia Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Cilia Lateral branch of gut Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Cilia Endoderm Lateral branch of gut Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Cilia Endoderm Mesoderm Lateral branch of gut Identify: Pharyngeal chamber Pharynx Cilia Endoderm Mesoderm Ectoderm Lateral branch of gut What phylum does this specimen belong to? What genera represented this phylum? Mollusca Venus sp. Most mollusks share what four characteristic features? 1) Foot – locomotion and 2) Visceral mass – housing of organs 3) Mantle – Secretes the shell 4) Shell – protection (CaCO3 which is made of twp parts, called valves) What type of symmetry does Venus exhibit? Bilateral symmetry What body type does Venus exhibit? Triploblastly What type of body cavity does Venus exhibit? Coelomate Determine the anatomical positions: Determine the anatomical positions: Dorsal Determine the anatomical positions: Dorsal P o s t e r i o r Determine the anatomical positions: Dorsal Ventral P o s t e r i o r Determine the anatomical positions: Dorsal A n t e r i o r Ventral P o s t e r i o r Identify: Identify: Pericardium Identify: Pericardium Posterior adductor muscle Identify: Pericardium Posterior adductor muscle Mantle Identify: Labial palp (the mouth is located here) Pericardium Posterior adductor muscle Mantle Identify: Labial palp (the mouth is located here) Anterior Adductor muscle Pericardium Posterior adductor muscle Mantle Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Umbo Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Umbo Mantle Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Posterior Adductor muscle Umbo Mantle Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Umbo Mantle Anterior Adductor muscle Identify: Note that this image is flipped, so the anterior is the right side, and the posterior is the left side. You can see this by noting the position of the umbo. Umbo Mantle Anterior Adductor muscle Foot Identify: (The green substance) Identify: (The yellow substance) Digestive gland Identify: Gonads Digestive gland Identify: Gonads Digestive gland Gills Identify: Gonads Digestive gland Gills Visceral mass Identify: Gonads Digestive gland Gills Visceral mass Foot Identify: Gonads Digestive gland Gills Visceral mass Mantle Foot What phylum does this animal belong to? What genus represented this phylum? Annelida Lumbricus sp. What type of symmetry does Lumbrius demonstate? Bilateral symmetry What body type does Lumbricus show? Triploblasty How does Lumbricus reproduce? What type of body cavity does Lumbricus have? Coelomate Sexually; Lumbricus is a hermaphroditic, and transfer sperm when mating (they do not self-fertilize) Identify: Identify: Prostomium Identify: Prostomium Mouth Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Male gonopore Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Male gonopore Sperm groove Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Male gonopore Sperm groove Genital chaetae Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Male gonopore Sperm groove Clitellum Genital chaetae Identify: Prostomium Peristomium Mouth Chaetae Seminal receptacles Female gonopore Male gonopore Sperm groove Clitellum Genital chaetae Tubercle Identify: Identify: Identify: Pharynx Identify: Identify: Identify: Identify: Identify: