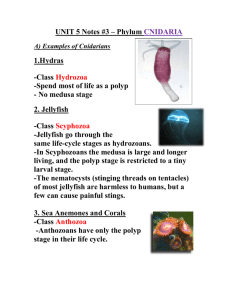
Class: Anthozoa (Sea anemone, corals)
advertisement

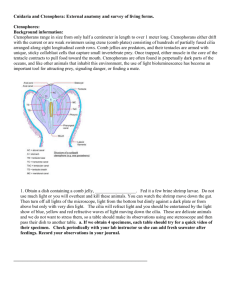
Cnidarians Kingdom: Animal Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Hydrozoa (Hydra & Portuguese man-of-war) Class: Scyphozoa (Jellyfish) Class: Anthozoa (Sea anemone, corals) Phylum Characteristics: General Characteristics 9000+ species Marine invertebrates All aquatic o Mostly marine, only a few live in fresh water Body Structure Radial Symmetry 2 cell layers (transparent), organized into separate tissues with specific functions Tentacles surround mouth Nemocysts (stinging cells) at ends of tentacles Dissolved oxygen in water enters cells directly (only 2 layers of cells) Life cycle Polyp : tube shape body, mouth surrounded by tentacles, usually sessile stage Medusa : body shaped like an umbrella, tentacles hang down, mobile stage Digestion Predators o plankton, small invertebrates (esp. crustaceans), plastic o larger jelly fish and sea anemone will eat small fish Use tentacles with nematocysts to stun/poison prey & tentacles contract and bring prey into mouth digested in gastrovascular cavity Gastrovascular Cavity o Lining of interior cavity has specialized cells, release enzymes for digestion over prey Gas Exchange Diffusion from water inside and outside organism Nervous system Nerve net: no control center (no brain), conducts nerve impulses from all over body, contraction of tentacles o Eating & swimming Skeleton Some from on outer covering of chitin (partial or nearly complete, open at oral end) Reproduction Asexually : budding, either polyp or medusa stage Sexually : medusa stage only Classes Hydrozoa (no internal division in gastrovascular cavity) Group: Hydroids o Hydra polyp stage dominant Group: Siphonophores o Portuguese Man-of-war Floating colonies Scyphozoa (four divisions in gastrovascular cavity) Jelly fish o Medusa stage dominant o Found in all oceans, some as deep as 1000m Anthozoa (division in gastrovascular cavities) Help build coral reefs Only polyp stage Sea anemones o thought to live for centuries o live in all oceans (tropical, temperate, artic) Corals o Warm ocean water o Secrete cuplike calcium carbonate, protection o When polyp dies leaves limestone skeleton o Adds to the reef, 2mm per year