Bloom's taxonomy of learning objectives
advertisement

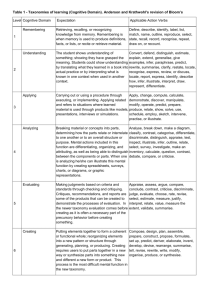
Bloom’s taxonomy of learning objectives Bloom’s taxonomy (or classification) (1956) identified categories of learning objectives in the form of nouns. This is often used in planning lessons. A review by Anderson and Krathwohl (2001) encouraged a change from nouns to verbs in order to facilitate visualisation of outcomes as well as specify what the pupils should be able to do by meeting the ILO (see Table 1 below). Table 1 Taxonomy of Learning Objectives. Bloom’s Taxonomy (1956) Anderson and Krathwohl (2001) Adapted Taxonomy Knowledge Remember Comprehension Understand Application Apply Analysis Analyse Synthesis Evaluate Evaluation Create (problem solve) Examples of measurable action words you want pupils to achieve are shown in Table 2 below. Table 2 Examples of measurable action words (verbs) reflecting appropriate levels and domain. Level Domain Knowledge Application Problem solving Psychomotor Observe Perform Create Point out Operate Design List Apply Analyse Describe Interpret Evaluate Respond Value Consider Receive Respect Resolve Cognitive Affective Learning to Teach Physical Education in the Secondary School, 4th Edition © 2015 Susan Capel and Margaret Whitehead (eds) 1 Table 3 Examples of measurable action words to aid planning of intended learning outcomes for lessons. Abstract Activate Acquire Adjust Analyse Appraise Arrange Articulate Assemble Assess Assist Associate Breakdown Build Calculate Carry out Catalogue Categorise Change Check Cite Classify Collect Combine Compare Complete Compose Compute Conduct Construct Contrast Convert Coordinate Count Criticise Critique Debate Decrease Define Demonstrate Describe Design Detect Develop Differentiate Direct Discover Discuss Distinguish Dramatise Draw Employ Establish Estimate Evaluate Examine Explain Explore Express Extrapolate Formulate Generalise Identify Illustrate Implement Improve Increase Infer Integrate Interpret Introduce Investigate Judge Limit List Locate Maintain Manage Modify Name Observe Operate Order Organise Perform Plan Point Predict Prepare Prescribe Produce Propose Question Rank Rate Read Recall Recognise Recommend Reconstruct Record Schedule Score Select Separate Sequence Simplify Sing Sketch Tabulate Test Theorise Trace Track Train Transfer Translate Update Use Utilise Verbalise Verify Visualise Write Learning to Teach Physical Education in the Secondary School, 4th Edition © 2015 Susan Capel and Margaret Whitehead (eds) 2 Recruit Reduce Reflect Relate Remove Reorganise Repair Repeat Replace Report Reproduce Research Restate Restructure Revise Rewrite Skim Solve Specify State Structure Summarise Supervise Survey Systematise Table 4 Some words for knowledge. analyse arrange calculate circle cite classify compare contrast define describe diagram differentiate evaluate give examples group identify interpret itemise label list match name outline plan recognise record revise select solve state tabulate Table 5 Some words for skills. adjust assemble chart collect demonstrate draw employ establish fit illustrate imitate interact locate maintain manipulate master measure modify operate organise perform practice rearrange return set up use Learning to Teach Physical Education in the Secondary School, 4th Edition © 2015 Susan Capel and Margaret Whitehead (eds) 3 Table 6 Some words for attitudes. accept adopt advocate approve assess challenge characterise choose criticise defend empathise evaluate formulate judge justify manage model persuade reassure recommend resolve select specify value Table 7 Words that may be used for each of Bloom’s six levels of learning objectives and hence assessment. Knowledge Comprehension Application (Knowledge and understanding) Analysis be aware of; calculate; circle; cite; classify; count; define; describe; diagram; differentiate; draw; This is the recall of enumerate; evaluate; examine; extract; give information and facts. examples of; group; identify; interpret; itemise; know; label; list; match; measure; name; organise; Common terms, facts, outline; plan; point out; present; quote; read; principles, procedures, asks recall; recite; recognise; record; recount; relate; these types of questions: repeat; reproduce; revise; select; show; solve; state; tabulate; underline; write. associate; clarify; classify; compare; comprehend; This is the grasping of compute; contrast; convert; defend; describe; meaning. differentiate; discuss; distinguish; estimate; exemplify; explain; express; extend; extrapolate; Understanding of facts and find; formulate; generalise; give examples of; principles, interpretation of identify; illustrate; indicate; infer; interpret; judge; material, asks these types of justify; name; paraphrase; perform; predict; questions: present; report; represent; restate; rewrite; select; summarise; translate; understand. add; apply; assess; calculate; change; choose; This is being able to use classify; compute; construct; control; information in new situations. demonstrate; determine; develop; discover; divide; draw up; establish; examine; exemplify; Solving problems, applying explain how; find; give examples; graph; illustrate; concepts and principles to interpolate; manipulate; modify; operate; new situations, asks these practice; predict; prepare; produce; relate; select; types of questions: show; solve; subtract; translate; use; verify. This is being able to break analyse; arrange; break down; categorise; classify; down information and combine; compare; conclude; connect; contrast; knowledge into parts to criticise; design; detect; develop; devote; understand the structure and diagnose; differentiate; discriminate; distinguish then make inferences and between; divide; elucidate; evaluate; examine; conclusions. explain; identify; illustrate how; infer; justify; order; outline; point out; question; recognise; Learning to Teach Physical Education in the Secondary School, 4th Edition © 2015 Susan Capel and Margaret Whitehead (eds) 4 Synthesis Evaluation Recognition of unstated relate; resolve; select; separate; subdivide; utilise. assumptions or logical fallacies, ability to distinguish between facts and inferences, asks these kinds of questions: account for; adapt; alter; anticipate; argue; build This is more than analysis: it is up; categorise; combine; compare; compile; being able to create and compose; conclude; contrast; create; derive; combine enabling deductions design; develop; devise; drive; engender; enlarge; to be made. explain; formulate; generalise; generate; group; integrate; manage; model; modify; order; Integrate learning from organise; plan; prescribe; present; précis; different areas or solve propose; put together; rearrange; reconstruct; problems by creative thinking, relate; reorganise; report; restate; revise; rewrite; asks these kinds of questions: select; specify; structure; suggest; summarise; synthesise; teach; tell; transform; validate; write. This is being able to judge the value of theory, make choices appraise; assess; choose; compare; conclude; on reasoned argument. Being contrast; criticise; critique; decide; defend; able to discriminate between describe how; determine; discriminate; evaluate; ideas. explain; grade; interpret; judge; justify; measure; question; rank; rate; recommend; reframe; select; Judging and assessing, asks summarise; support; test; value. these kinds of questions: The intended learning outcomes (ILO’s) you design should reflect the appropriate level and domain of learning (psychomotor; cognitive; affective). Meillie and Pinchin (2008) highlight the A, B, C, D approach to writing effective ILOs, where: A recognises the Audience expected to perform the desired behaviour B recognises the Behaviour the learner can now engage in C recognises the Condition(s) under which the ILOs should be attained and D recognises the Degree of competency expected upon completion of the ILO. Learning to Teach Physical Education in the Secondary School, 4th Edition © 2015 Susan Capel and Margaret Whitehead (eds) 5