INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY
advertisement

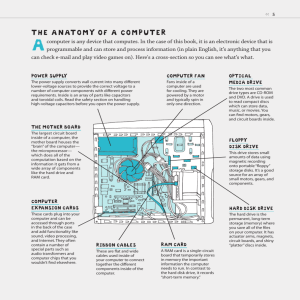
COMPUTER HARDWARE TECHNOLOGIES (Week 2, Thursday 1/18/2007) © Abdou Illia, Spring 2007 1 LEARNING GOALS Identify the major components of modern PCs Explain how the components of a computer work together; Explain input devices and how they operate. Describe output devices and how they operate. Describe I/O (secondary storage) devices and how they operate. Explain the role of the CPU and the RAM. Describe various types of computers. 2 The Core Computer Components Three subsystems in a computer system: 1. Input subsystem 2. Processing subsystem 3. Output subsystem 3 Input subsystem Main functions: Allowing the user to enter data Transmitting data to the Processing subsystem Includes keyboard, mouse, and other input devices Question: Name five other input devices ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 4 Input Devices Human input devices Allow a person to send data to the computer Examples: Keyboard, Mouse Machine-readable input devices Send data directly to computer without human involvement No human involvement means no human error Usually faster than human input Examples: Bar codes reader, Optical Characters Recognition (OCR) system 5 Machine-readable Input Devices Bar code scanners Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Uses light to read series of coded stripes Universal Product Code (UPC) – Adams.com Includes OCR Software and scanner Translates scanned digital image to character that user can recognize and manipulate Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) Character recognition technology used by banks to allow rapid routing of checks between banks 6 Output subsystem Main function: Show processing results Includes monitor, printer, and other output devices Q: Name two other output devices ____________________________ ____________________________ 7 Output Devices Monitors Cathode ray tube (CRTs) Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) Quality of display Resolution in pixels (e.g. 640 x 480) Dot pitch in millimeters (.26 to .28) Active-Matrix vs. Passive-Matrix display Touch screens Input and output via display device Monitor size Common resolution 15 inches 640 x 480 17 inches 800 x 600 or 1024 x 768 19 inches 1024 x 768 or 1280 x 1024 8 9 Printers Speed and resolution Pages per minute (PPM) Dots per inch (DPI) Impact printers Number of ink dots to fill a square inch Higher DPI = greater page clarity Create image by striking paper and ribbon Dot-matrix printers = most common impact printers Non-impact printers Create image by spraying or rolling ink on the page 10 Non-impact Printers Ink-jet technology printers Spray ink on the paper Quiet Color is readily and cheaply available Laser printers Laser heats drum which rolls ink (toner) on paper Can be faster than ink-jet More expensive than ink-jet 11 I/O devices or Secondary Storage Nonvolatile storage of digital data Magnetic or optical Magnetic storage (Floppy disk, Magnetic tape, Zip disk, Hard disk) Sequential access (tape) or direct access (HDD) Hard disk drives Two main standards: IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) aka ATA (AT Attachment) SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) SCSI allows disk fault-tolerance through RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks Disk speed: Transfer rate in MBps (Megabytes per second) Average Read Time (in milliseconds or ms) Platter rotation speed in RPM (5400/7200/10,000/15,000) 12 Optical Secondary Storage Compact disks (CDs) 600 MB capacity CD-ROM CD-R CD-RW Digital versatile disks (DVDs) 2 – 17 GB capacity DVD DVD+/-R DVD+/-RW 13 14 Processing subsystem Two major components CPU (Central Processing Unit) or Processor(s) Primary Storage: Random Access Memory (RAM) Read Only Memory (ROM) CPU Busses that transfer data Primary Storage 15 Central Processing Unit Processor Clock: generate time that synchronize other components ICU: Fetches instructions from RAM ALU: Execute instructions (arithmetic & logic operations) Registers: Store control information, data, intermediate results Clock Instruction Control Unit Arithmetic Logic Unit Registers 16 CPU speed Speed measured in hertz Hertz = # of instructions executed per second Megahertz = 1 million of instructions per second Gigahertz = 1 billion of instructions per second Major Processor manufacturers Intel - Celeron - Pentium 3, Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Xeon, Dual Core Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) - K6 series processors (which compete with Intel Pentium 3) - Athlon series (which compete with Intel Pentium 4) IBM - PowerPC 740, 750, 750FX, 750GL, 750GX 17 Primary Storage Computer’s memory stored on semiconductor chips Two categories: RAM (Random Access Memory) which is volatile Synchronous Dynamic RAM (SDRAM) Double Data Rate SDRAM or DDR SDRAM ROM (Read-Only Memory) which is non-volatile Capacity in Megabytes (MB) or Gigabytes (GB) Primary Storage RAM Program RAM holds running programs and the data they use ROM contains critical programs such as those that boot the computer Data ROM 18 Moore’s Law on Processor Speed RAM capacity tends to double every 18-24 months Processor speed tends to double every 18-24 months 19 Types of Computers Supercomputers Mainframes Minicomputers Servers Workstations Desktop computers Notebook computers (laptops) Handheld computers (PDAs) 20 Bead Bar : Exercise 2 Visit Dell website at www.dell.com in order to choose a computer system for Bead Bar. You must select the components based on the assessment of needs prepared by Stan after interviewing the Bead Bar employees (See the Assignment section’s of the course website for a copy of Stan’s memo to you) . Your job consist in filling out the Computer Hardware specification form found in the Assignment section of the course website with the characteristics of the computer system you have selected. Your assignment must include the printout of the description of the computer system from Dell website. 21 Summary Questions Malaga Notes 1) Name five (3) computer input devices 2) Name three (3) computer output devices 3) What computer devices can be used for both input and output? 4) What is the difference between: (a) a Kilobyte and a Gigabyte? (b) a Megabyte and a Terabyte? 5) Name the two main types of monitors used in today’s computer systems. 6) (a) Name main components of the Processing subsystem. (b) What is the function of the ALU? 7) Explain the difference between RAM and ROM. 8) Describe the various types of computers. 9) What is meant by Moore’s law? 22 File RAID RAID 0 Strips data across multiple disk No redundancy Advantage: Fast data access through multiple reads Disadvantage: Loosing one disk results in loosing data on all disks File RAID 1 Doesn’t strip data across many disk Mirrors data between two disks Data kept synchronized between two disks Advantage: Fault-tolerance, i.e. If one disk fails, the other continue working until failed disk can be replaced Disadvantage: Only half of available storage space is used. 23 RAID Data spread across these disks Last disk contains ECC* data for disks 1-4 RAID 3 Spreads data across multiple disks and uses ECC bits for recovery purpose in case of problem ECC bits determined based on data stored on data disks If one data disk fails, disk controller automatically regenerates missing data * Error Checking and Correcting 24 Dell XPS 700 Desktop computer Intel D955XBKLKR motherboard Pentium® 4 Processor with Dual Core Technology (3.00GHz, 800FSB) Windows® XP Professional Edition with re-installation CD 1GB Dual Channel SDRAM at 667MHz (2 DIMMs) 250GB Serial ATA 3Gb/s Hard Drive (7200RPM and 10 ms ART) 3.5 in Floppy Drive 17 inch UltraSharp LCD Active Matrix screen, 1280x1024 Resolution, 0.26 dot pitch. 16x CD-ROM Drive 16x DVD+/-RW Drive $1,640.00 nVidia GeForce 7900 GS Video card Sound Blaster® X-Fi™ XtremeMusic (D) Sound Card w/Dolby Dell A525 30 Watt 2.1 Stereo Speakers with Subwoofer Dell USB Enhanced Multimedia Keyboard Logitec Optical USB Mouse 56K PCI Telephony Modem 10/100/1000 NIC PCI Dell Inkjet Printer 924, Up to 17 PPM Black/White, 600 x 600 dpi 1Yr Ltd Warranty, 1Yr At-Home Service 25 PowerEdge SC1420 server computer Intel D955XBKLKR motherboard Dual Pentium® Xeon Processor with Dual Core Technology (3.00GHz, 800FSB) Windows® XP Professional Edition with re-installation CD 2.0GB DDR2 400MHz, 4X512MB SDRAM Two 73 GB 10K RPM SCSI Hard Drives Ultra 320 PERC Ultra 320 2-Channel SCSI RAID Controller Card 3.5 in Floppy Drive 48X IDE Internal CD-RW/DVD ROM Drive nVidia GeForce 7900 GS Video card $3,040.00 Sound Blaster® X-Fi™ XtremeMusic (D) Sound Card w/Dolby Dell A525 30 Watt 2.1 Stereo Speakers with Subwoofer Dell USB Enhanced Multimedia Keyboard Logitec Optical USB Mouse 10/100/1000 NIC PCI Dell Inkjet Printer 924, Up to 17 PPM Black/White, 600 x 600 dpi 1Yr Ltd Warranty, 1Yr At-Home Service 26