1 globulins
advertisement
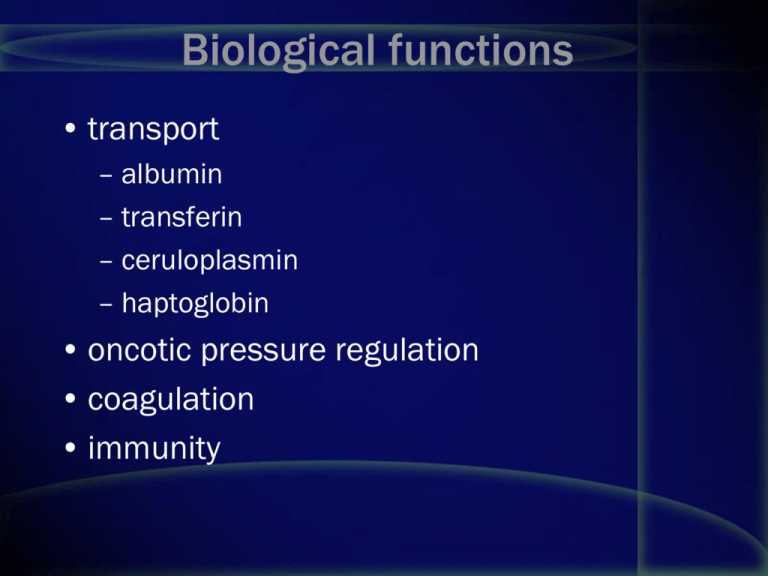
Biological functions • transport – albumin – transferin – ceruloplasmin – haptoglobin • oncotic pressure regulation • coagulation • immunity Hypoproteinemia • with hypoalbuminemia – impairment of liver function – protein loss – changes in ECF • without hypoalbuminemia – severe immunoglobulin deficiency Hyperproteinemia • hypergammaglobulinemia – polyclonal chronic inflammation chronic liver disease autoimmune diseases – monoclonal • multiple myeloma • Waldenstrom`s macroglobulinemia • heavy-chains disease • dehydration Methods of separation • SPE - serum protein electrophoresis • IEP – immunoelectrophoresis • IFE – immunofixation electophoresis Immunoelecctrophoresis (IEP) Immunofixation (IFE) Albumin (migrates to the anode) -1 globulins • -1 protease inhibitor (a-1 antitrypsin) • *-1 glycoprotein (* orosomucoid) • fetoprotein (if present) • high density lipoprotein (HDL) -2 globulins • -2 macroglobulin • antithrombin III • ceruloplasmin • haptoglobin (this is usually the predominant component) Beta globulins • beta and pre-beta lipoproteins (LDL and VLDL) • C3 • C-reactive protein • hemoglobin (free) • plasminogen • transferrin (*"principal component of the beta1 subdivision") Gamma globulins • Immunoglobulins Acute phase response (APR) • positive APR • negative APR beta - gamma (IgA) junction Multiple myeloma • B cell proliferation • monoclonal protein, Bence-Jones proteinuria • anemia, leukopenia, low platelet count • hypercalcemia • „myeloma kidney” • increased viscosity • TP, ESR • SPE, IEP, quantitating serum Ig Heavy chain disease • lymphocytic cell proliferation • only heavy chain production Benign monoclonal gammopathy • "monoclonal gammapathy of uncertain significance" • "MGUS” • paraprotein < 2.0 gm/dL, Bence-Jones protein (rarely present) < 60 mg/L Benign monoclonal gammopathy Case 1 • A 66-year-old man presented with sharp, constant, low back pain, dating from a fall from a ladder 6 weeks earlier. On direct questioning, he did admit to vague malaise for over 6 months. On examination, he was in considerable pain but otherwise seemed fairly fit. • He was mildly anaemic but had no lymphadenopathy and no fever. There were no signs of bruising, no finger clubbing, no hepatosplenomegaly and no abdominal masses Case 1 • On investigation, his haemoglobin was low (102g/l) due to fewer red cells but his white-cell count was normal (6.2 x 109/l). He had a normal differential white-cell count and a normal platelet count but his ESR was 98mm/h. • Total serum proteins were raised at 98g/l (NR 65-75g/l) Case 1 • His serum albumin, creatinine and urea were normal. • He had a raised serum calcium level (3.2mmol/l) but a normal alkaline phosphatase. • Serum protein electrophoresis revealed a monoclonal band in the gamma region, with considerable immunosuppression of the rest of this region. • The band was typed by immunoelectrophoresis and shown to be IgG of kappa type. • Quantitation of serum immunoglobulins showed a raised IgG of 67g/l (NR 7.2-19.0g/l), a low IgA of 0.3g/l (NR 0.8-5.0g/l), and a low IgM of 0.2g/l (NR 0.5-2.0g/l). • Electrophoretic examination of concentrated urine showed a monoclonal band in the beta region. On immunoelectrophoresis, this band was composed of free kappa light chains. • X-rays of his back showed a small, punched-out lesion in the second lumbar vertebra Case • Bone marrow examination showed an increased number of atypical plasma cells; these constituted 45% of the nucleated cells found on the film. This man showed the features required for a diagnosis of multiple myeloma Case • A 49-year-old woman presented with a 6month history of vague aches and pains in her chest. On examination, she was overweight but had no abnormal physical signs. Case 2 • Her haemoglobin was 136g/l with a white-cell count of 6.7 x 109/l and a normal differential. • Her ESR was 34mm/h. • Tests of thyroid function were normal. Case 2 • However, protein electrophoresis showed a small paraprotein band in the gamma region; this band was an IgG of lambda type. • Her serum IgG was raised at 20.1g/l (NR 7.2-19.0g/l), • with an IgA of 1.9g/l (NR 0.8-5.0g/l) and an IgM of 3.0g/l (NR 0.5-3.0g/l). • electrophoresis of concentrated urine showed no proteinuria. The paraprotein measured 10g/l by densitometry. • A bone marrow examination showed only 12% plasma cells. Case 2 • the absence of – osteolytic lesions, – monoclonal free light chains in the urine • normal serum IgA and IgM levels, • these findings supported a diagnosis of benign monoclonal gammopathy, also known as a monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) • This woman has been followed at 6-monthly intervals for 3 years with no change in the paraprotein level, and the urine remains free of monoclonal light chains. She will continue to be seen at yearly intervals.