Chapter 1 Project Management Concepts
advertisement

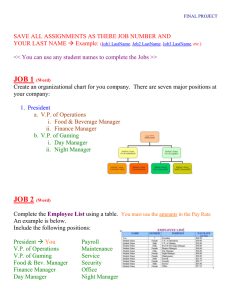
BUS 4017 PROJECT MANAGEMENT • • • • • Week 11 Agenda: MS Project. Resource allocation Types of Project Organizations Project Close out (Termination) phase Review - Final Group Work Learning Objectives • The characteristics of the three types of organization structures: - functional - project - matrix • The advantages and disadvantages of each 2 Real World Example • Vignette: A Survey by Technical Pathways • Results suggest the following project-oriented corporate policies: – – – – – – – – Establish meaningful organizational objectives Include project responsibilities in job descriptions Use team-based performance reviews Establish career paths Organize programs into projects and subprojects Prioritize using project inventories Optimize personnel resources Coordinate inter-group transitions Real World Example • Vignette: Office Politics • Organizational politics often play a major role in determining the outcome of a project. • People from different departments within an organization often work, think, and react very differently. • Unfortunately in many corporate systems there is often a focus on finding someone or some department to blame. • Putting personal or departmental interests ahead of corporate goals doesn’t work. • Projects go smoothly when everyone knows the goal and their part in attaining it. Organizational Structures authority ? Project PM TM PM PM TM TM Functional Matrix PM MGR MGR PM MGR. MGR TM TM TM TM Functional-Type Organization • Used in businesses that sell and produce standard products. • Groups consist of individuals performing the same function. • Periodically undertake in-house projects. • Team members can be assigned to the project. • Team members continue regular functional jobs. • Project manager does not have complete authority over team. 3 Project-Type Organization • Used in companies in the project business, not selling products. • Work on multiple projects at a time. • Project team is dedicated to one project. • Project manager has complete authority over team. • Each project team tends to be isolated. 4 Matrix-Type Organization • A mix of functional and project organization structures. • Used in companies that work on multiple projects at a time. • Provides project and customer focus. • Retains functional expertise. • Individuals can be assigned to various types of projects. 5 Matrix-Type Organization (Cont.) • Both project managers and functional managers have responsibilities. • The Project Manager is the intermediary between customer and company. • The Functional Manager decides how tasks will be accomplished. 6 Functional Organization Advantages-disadvantages • Reduces duplication and overlap of activities. • Provides specialization and functional excellence. • • • • Can be insular. Teamwork is not emphasized. Decisions may be parochial. Structure can slow communication, problem solving and decision making. • Lack of customer focus. • Stronger allegiance to function than project 7 Project Organization AdvantagesDisadvantages • Team has full control over resources. • Organization is highly responsive to customer. • Can be cost inefficient. • Tendency to stretch out work during slow periods. • Potential for duplication on concurrent projects. • Low level of knowledge transfer. • No functional “home”. • People may be laid off at the end of the project. 9 Matrix Organization Advantages Disadvantages • Allows efficient utilization of resources. • Individuals can be moved among projects. • Provides a core of functional expertise. • Facilitates information flow. • Team members can communicate with project and functional managers. • Customer focused. • • • Team members have a dual reporting relationship. A proper balance of power must be established between project and functional managers. Conflicts regarding priorities can arise between managers 11 Pros and cons of different Org. structures Type Proj. Matrix Functional Pros Delegation easy Shared resources Economical Cons. Expensive- Team Member 2 bosses Confusion for team members Problem solving –Team Members • Explain the deliverables • Be clear about level of effort needed • Help define obstacles and ways around them. • Discuss with the Team as a whole • Arrange one on one discussion time as needed. Conflict Resolution methods – Team P. 339 Gido • • • • • Conflict can be useful to help identify problem areas. Competing or forcing are not solutions Smoothing accommodates the differences but doesn’t resolve Compromise resolves but only with a degree of satisfaction Collaborating, confronting and problem solve is best . Start with a win-win attitude. Turning on the Teams 1. Show them the S.O.W. and how they fit in. 2. Let the Team Member develop their WBS. 3. Let them see the relationship of what they do on the Schedule relative to others 4. Bring in the Sponsor to reiterate purpose 5. Have Project Status Meetings – use open Task Reports 6. Update your Communication Plan Problem solving-staying on track • 5 step solution for variances • You might use last week’s 9 point problem solving plan to develop the solution 1. Monitor - find symptoms 2. Identify the source 3. Develop a solution 4. Implement it 5. Update the project plan. Know the above 1-5 Meeting tough deadlines. • Statement of Work • Project Plan • Risk management • Status Reports • Be very clear about objectives • Best use of resources – crash the times • Find the hi level and detailed risks -mitigate • Get info. Raise the alarm and repeat until everyone is motivated. Project Close Out (Termination) Action within your company. Gido and Clements p. P. 84-91 • Project review meetings. Communication effectiveness review • Technical (quality), cost and schedule performance review • Relationships teams/customer • Lessons learned from project. • Archiving documents • Cash accountability, audits • Future contracts and Networking • Human Resources department Project Close Out customer related • • • • • • • Problem solving methods as per today's P.Point's Outstanding issues on Issues Logs Outstanding changes on Change Logs Customer Evaluations completed Customer feedback-meetings and reports Sign off procedures re; deliverables/legal Future work enquiry process Presentation content • Final Project Group Work • Select presentation order for Group for • Wk. 12 and 13. • Final Presentations: • Would we buy your services? • Talk about your experiences in developing the project. Tell of of the challenges and remedies for gathering and compiling information. Linkages between hi-level plans and the WBS and Responsibility Matrix? • How the project was controlled? Presentations • Enthusiasm, energy, informative, interesting motivating and entertaining? • Enunciation, articulation, projection Smooth transitions to next speaker. Deliverables match the customer requirements - identify how? Common mark deductions (X) and earned (good) during presentations Don’t bunch Don’t .X lounge. X Hands in pockets X Passing notes X Introduce self- name. Good Eye contact with audience Good Don’t talk to team. X Disintere st. X No Q & A Don’t read at end X P. Point. X Speaker steps fwd Good Use cue cards. Good Vary voice – good Project voice. Good Smile. Good Home Assignment • Complete the Final Group Project written portion and hand in to Instructor at beginning of class in Week 12. • If handed in late the maximum mark for each Group Member 50%. • No late individual contributions will be accepted • If you miss your presentation-advanced Email notice or phone call to Instructor required plus medical or documented support SAP.