PowerPoint Presentation - Aqueous Reactions & Solutions
advertisement

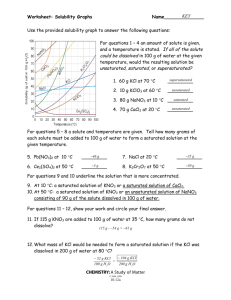
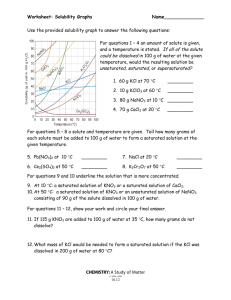
Aqueous Solutions Concentration / Calculations Dr. Ron Rusay Solutions 1 Homogeneous solutions are comprised of solute(s), the substance(s) dissolved, [The lesser amount of the component(s) in the mixture], and solvent, the substance present in the largest amount. Solutions with less solute dissolved than is physically possible are referred to as “unsaturated”. Those with a maximum amount of solute are “saturated”. Occasionally there are extraordinary solutions that are “supersaturated” with more solute than normal. Concentration and Temperature Relative Solution Concentrations: Saturated Unsaturated Supersaturated _____________ Dilute Concentrated A solution of 35g of potassium chloride in 100g H2O @ 25oC is Saturated & Concentrated; @ 75oC it is Unsaturated but Concentrated. Refer to: Lab Manual & Workshop QUESTION What describes a solution of 0.250g SO2 in 1.00L of H2O @ 10oC? A) Dilute B) Concentrated C) Saturated D) Unsaturated QUESTION What describes a solution of 0.250g SO2 in 1.00L of H2O @ 70oC? A) Dilute B) Concentrated C) Saturated D) Unsaturated What describes a solution of 25.0g ammonium chloride in 0.10kg of H2O @ 10oC? A) Dilute B) Concentrated C) Saturated D) Unsaturated What describes a solution of 25.0g ammonium chloride in 0.10kg of H2O @ 70oC? A) Dilute B) Concentrated C) Saturated D) Unsaturated DHMO, dihydromonoxide : “The Universal” Solvent http://www.dhmo.org Water : “The Universal” Solvent The oil (nonpolar) and water (polar) mixture don’t mix and are immiscible. If liquids form a homogeneous mixture, they are miscible. Generally, likes dissolve likes, i.e. polar-polar and nonpolar-nonpolar. If polar and nonpolar mix , eg. oil and water: QUESTION Aqueous Reactions & Solutions 1 Many reactions are done in a homogeneous liquid or gas phase which generally improves reaction rates. The prime medium for many inorganic reactions is water which serves as a solvent (the substance present in the larger amount), but does not react itself. The substance(s) dissolved in the solvent is (are) the solute(s). Together they comprise a solution. The reactants would be the solutes. Reaction solutions typically have less solute dissolved than is possible and are “unsaturated”. Salt dissolving in a glass of water Refer to Lab Manual & Workshop: Water dissolving an ionic solid Solution Concentrations Refer to Lab Manual 1 A solution’s concentration is the measure of the amount of solute dissolved. Concentration is expressed in several ways. One way is mass percent. Mass % = Mass solute / [Mass solute + Mass solvent ] x100 What is the mass % of 65.0 g of glucose dissolved in 135 g of water? Mass % = 65.0 g / [65.0 + 135]g x 100 = 32.5 % Solution Concentration 1Concentration is expressed more importantly as molarity (M). Molarity (M) = Moles solute / Liter (Solution) An important relationship is M x Vsolution= mol This relationship can be used directly in mass calculations of chemical reactions. What is the molarity of a solution of 1.00 g KCl in 75.0 mL of solution? M KCl = [1.00g KCl / 75.0mL ][1molKCl / 74.55 g KCl ][ 1000mL / L] = 0.18 molKCl / L QUESTION 20.0-g of HF [MM = 20.0 g/mol] was dissolved in water to give 2.0 x 102 mL of HF(aq), a weak acid solution. The concentration of the solution is: a) 1.0 M b) 3.0 M c) 0.10 M d) 5.0 M e) 10.0 M Solution Concentrations: Solute vs. Ion Concentrations HCl 1.0M 100% Ionized [H+] = [Cl-] = 1.0M Acetic Acid (HC2H3O2) < 100% Ionized [H+] = [C2H3O2-] < 1.0M Refer to Lab Manual QUESTION Solutions: molarity & volume mass Preparation of Solutions Preparing a Standard Solution QUESTION A 51.24-g sample of Ba(OH)2 [MM= 171.3 g/mol] is dissolved in enough water to make 1.20 liters of solution. What is the molarity of the solution? a) 0.300 M b) 3.33 M c) 0.278 M d) 2.49 x 10-1 mol/L e) 42.7 g/mL Solution Concentration 1 The following formula can be used in dilution calculations: M1V1 = M2V2 A concentrated stock solution is much easier to prepare and then dilute rather than preparing a dilute solution directly. Concentrated sulfuric acid is 18.0M. What volume would be needed to prepare 250.mL of a 1.50M solution? V1 = M2V2 / M1 V1 = 1.50 M x 250. mL / 18.0 M V1 = 20.8 mL QUESTION Solution Dilution Solution Applications 1 A solution of barium chloride was prepared by dissolving 26.0287 g in water to make 500.00 mL of solution. What is the concentration of the barium chloride solution? MBaCl2 = ? MBaCl2 = = [26.0287g BaCl2 / 500.00mL ][1mol BaCl2 / 208.23g BaCl2 ] [1000mL / L] = 0.25000 mol / L Solution Applications Scoville Units / Capsaicin Will all molecules with the same molecular formula taste hot? Capsaicin: C18H27NO3 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scoville_scale Molecular Applications Capsaicin / Prosidol Will all molecules with the same molecular formula taste hot? Capsaicin: C18H27NO3 Prosidol: C18H27NO3 (opiate analgesic) QUESTION What happens to the number of moles of C12H22O11 (sucrose) when a 0.20 M solution is diluted to a final concentration of 0.10 M? A) The number of moles of C12H22O11 decreases. B) The number of moles of C12H22O11 increases. C) The number of moles of C12H22O11 does not change. D) There is insufficient information to answer the question. Solution Applications 1 10.00 mL of this solution was diluted to make exactly 250.00 mL of solution which was then used to react with a solution of potassium sulfate. What is the concentration of the diluted solution. M2 = ? MBaCl2 = M1 M2 = M1V1 / V2 M2 = 0.25000 M x 10.00 mL / 250.00 mL M2 = 0.010000 M QUESTION QUESTION Solution Applications 1 20.00 mL of a M2 = 0.010000 M barium chloride solution required 15.50 mL of the potassium sulfate solution to react completely. MK2SO4 = ? BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) ? + ? BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4 (aq) 2 KCl(aq) + BaSO4 (s) ?MK2SO4 = [MBaCl2x VBaCl2 / VK2SO4 ] [? molK2SO4 / ? molBaCl2 ] ?MK2SO4 = ?MK2SO4 0.010000 molBaCl2 x 0.02000 LBaCl2 x 1 molK2SO4 LBaCl2 x 0.01550 LK2SO4 x 1 molBaCl2 = 0.01290 molK2SO4 / LK2SO4 = 0.01290 MK2SO4 Solution Applications How many grams of potassium chloride are produced? BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) ? + ? 1 BaCl 1 2(aq) + K2SO4 (aq) 2 KCl(aq) + BaSO4 (s) ?gKCl = 0.010000 molBaCl2 / LBaCl2 x 0.02000 LBaCl2 X 2 molKCl / 1 molBaCl2 X 74.55 gKCl /molKCl = 0.02982 gKCl Solution Applications If 20.00 mL of a 0.10 M solution of barium chloride was reacted with 15.00 mL of a 0.20 M solution of potassium sulfate, what would be the theoretical yield of barium sulfate? BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4 (aq) 2 KCl(aq) + BaSO4 (s) 1 Which is the Limiting Reagent? MolBaCl2 = MBaCl2x VBaCl2 MolK2SO4= MK2SO4x VK2SO4 = 0.10 molBaCl2 / LBaCl2 x 0.02000 LBaCl2 = 0.20 molK2SO4 / LK2SO4 x 0.01500 LK2SO4 1 molBaCl2 = 2.0 x 10-3 1 molK2SO4 = 3.0 x 10-3 2.0 x 10-3 < 3.0 x 10-3 2.0 x 10-3 mol is limiting Solution Applications If 20.00 mL of a 0.10 M solution of barium chloride was reacted with 15.00 mL of a 0.20 M solution of potassium sulfate, what would be the theoretical yield of barium sulfate? BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4 (aq) 2 KCl(aq) + BaSO4 (s) 1 Must use the limiting reagent: 0.10 molBaCl2 x 0.02000 LBaCl2 x 1 molBaSO4 x 233.39 g BaSO4 = LBaCl2 = 0.47 g 1 molBaCl2 molBaSO4 QUESTION