5s-1
Decision Theory
Decision Theory
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Eighth Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright © 2005 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
5s-2
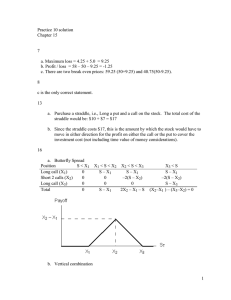
Decision Theory
Decision Theory
Decision Theory represents a general
approach to decision making which is suitable for a
wide range of operations management decisions,
including:
Capacity
planning
product and
service design
location
planning
equipment
selection
5s-3
Decision Theory
Decision Theory Elements
A set of possible future conditions exists that
will have a bearing on the results of the
decision
A list of alternatives for the manager to
choose from
A known payoff for each alternative under
each possible future condition
5s-4
Decision Theory
Decision Theory Process
Identify possible future conditions called
states of nature
Develop a list of possible alternatives, one of
which may be to do nothing
Determine the payoff associated with each
alternative for every future condition
5s-5
Decision Theory
Decision Theory Process (Cont’d)
If possible, determine the likelihood of each
possible future condition
Evaluate alternatives according to some
decision criterion and select the best
alternative
5s-6
Decision Theory
Causes of Poor Decisions
Bounded Rationality
The limitations on decision
making caused by costs,
human abilities, time, technology,
and availability of information
5s-7
Decision Theory
Causes of Poor Decisions (Cont’d)
Suboptimization
The result of different
departments each
attempting to reach a
solution that is
optimum for that
department
5s-8
Decision Theory
Decision Environments
Certainty - Environment in which
relevant parameters have known
values
Risk - Environment in which certain
future events have probable
outcomes
Uncertainty - Environment in which
it is impossible to assess the
likelihood of various future events
5s-9
Decision Theory
Decision Making under Uncertainty
Maximin - Choose the alternative with
the best of the worst possible payoffs
Maximax - Choose the alternative with
the best possible payoff
Laplace - Choose the alternative with the
best average payoff of any of the
alternatives
Minimax Regret - Choose the alternative
that has the least of the worst regrets
5s-10 Decision Theory
Format of a Decision Tree
Figure 5S.1
Payoff 1
Decision Point
Chance Event
Payoff 2
2
Payoff 3
1
B
Payoff 4
2
Payoff 5
Payoff 6
5s-11 Decision Theory
Expected Value of Perfect Information
Expected value of perfect information: the
difference between the expected payoff under
certainty and the expected payoff under risk
Expected value of
Expected payoff
perfect information = under certainty
-
Expected payoff
under risk
5s-12 Decision Theory
Solved Problem 5