Building an Understanding of the Classroom as a Group
advertisement

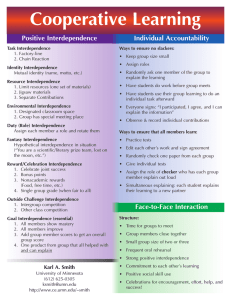
Cooperative Learning 109614027李佩瑜 109614032郭承宜 109614023古博宇 109614024黃嚴誼 109614028魏秀妤 109614029黃巧秀 Student-student interaction patterns HOW they feel HOW much they have Interact when Learning Three basic ways Compete Work individually Work cooperatively Cooperation Among Students Celebrate Encourage Work together regardless of any kind of background Basic Definition Student should be able to 1. be effective 2. select the appropriate interaction Individualistic learning vs. Cooperative learning Back to Basic 1800s Ability of student to work cooperatively Technical skills Certain conditions of CL Clearly perceived positive interdependence Considerable primitive interaction Clearly perceived individual accountability and personal responsibility to achieve the group’s goals Frequent use of the relevant interpersonal and small-group skills Frequent and regular group processing of current functioning to improve the group’s future effectiveness The Teacher’s Role 1) Select the groups' size most appropriate for the lesson. 2) Arrange the classroom. 3) Assign the students to groups. 4) Provide the appropriate materials. 5) Explain the task and cooperative goal structure to the students. 6) Monitor the groups as they work. Group Processing 1)Feedback 2)Reflection 3)Improvement Goal 4) Celebration Teaching material Johnny’s Alex’s teaching : teaching : Animal pictures Animal pictures Color cards Word cards A lot container Class activities which use cooperative learning Team Pair Solo (presented by Johnny’s teaching) Numbered Heads Together (presented by Alex’s teaching) Jigsaw Think-Pair-Share Three-Step Interview RoundRobin Brainstorming Three-minute review Circle the Sage Partners Grouping Heterogeneous Groups High Achievers never lose Usually better Male/Female pairs most off task Homogeneous Groups Low Achievers fastest to quit More interaction in all female groups than all male Building Better Groups Outcome Interdependence Means Interdependence Individual Accountability Task Complexity Introduction to Advantage of Cooperative Learning Benefits to the Learner Benefits to the Teacher 1. Improves academic performance 2. Made achievement consistently 3. Disadvantaged students get benefits 4. No stop to individual initiative 5. Positive effects on students' self-esteem 6. Students understand the material better 7. Transfer to interaction with peers Back 1. Use time effectively 2. New attitude toward the job 3. Manage easily 4. Validate students’ values and ideas 5. Interact in personal manner with students 6. Less paperwork 7. Less stress Introduction to disadvantage of cooperative learning Drawback to the Learner Drawback to the Teacher 1. Irritated by being asked to participate 2. Worry members of the group bring their grades down 3. Advanced students doing all the work 4. Frustration of the lower ability group 5. Group conflict 6. Noise level will escalate 7. Work time takes longer Back 1. Teachers must receive training 2. Resist using CL techniques 3. Initial lessons take longer 4. Unable to give students the freedom 5. Showing their expertise is important to teachers 6. Create additional materials 7. Difficult to have a paper and pencil test. Thank you for your listening.