Lecture notes
advertisement

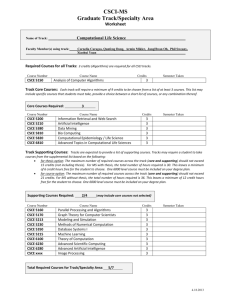
CSCE 548 SDLC Reading This lecture – The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), http://www.elucidata.com/refs/sdlc.pdf – Practical UML™: A Hands-On Introduction for Developers, http://dn.codegear.com/article/31863 Next lecture – McGraw: Chapter 3 CSCE 548 - Farkas 2 Software Engineering Building of SW systems of high quality Functional requirements Software Engineering Life Cycle Includes programming but not only programming Can a good programmer be a bad software engineer? CSCE 548 - Farkas 3 What is a “High Quality” System? Satisfies requirements Sophisticated Structured Supports abstraction Reusable Documented CSCE 548 - Farkas 4 SDLC Finite and definite period of time – Starts: when the SW product is conceived – Ends: when the SW is no longer used or available SDLC is composed of phases CSCE 548 - Farkas 5 SDLC Phases Initiation and planning: high-level view, goal of the project Requirement gathering and analysis: determine whether there are any problems Design: planning the system components and their interactions Implementation: implementing the project Testing: evaluate satisfaction of functional and nonfunctional requirements Maintenance: follow up on the project Retirement: remove system components CSCE 548 - Farkas 6 SDLC Models Waterfall (enhanced waterfall) V-model Evolutionary prototyping Rapid prototyping Spiral Reuse oriented Formal CSCE 548 - Farkas 7 Software development process Waterfall model Source: Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_development_process#Software_development_activities CSCE 548 - Farkas 8 Example SDLC CSCE 548 - Farkas 9 How the customer imagined it CSCE 548 - Farkas Copyright: This and the following slides on SDLC are modified from Project Cartoon http://www.projectcartoon.com/cartoon/1078 10 What the business analyst understood CSCE 548 - Farkas 11 How the architect designed it CSCE 548 - Farkas 12 What development believed the architect was describing CSCE 548 - Farkas 13 How the programmer implemented it CSCE 548 - Farkas 14 How the project manager explained it CSCE 548 - Farkas 15 How the project was documented CSCE 548 - Farkas 16 What operations installed CSCE 548 - Farkas 17 How the client was billed CSCE 548 - Farkas 18 Portion of original code that still can be used CSCE 548 - Farkas 19 What the client really needed CSCE 548 - Farkas 20 So if software engineering is hard already, why do we want to make it harder by adding security considerations? CSCE 548 - Farkas 21 Class Discussion on Projects Each class member presents: Area of interest Strengths and weaknesses Group status CSCE 548 - Farkas 22 Next Class Seven Touchpoints CSCE 548 - Farkas 23