fiscalvmonet
advertisement

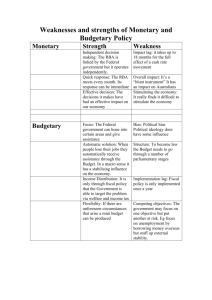
Fiscal vs. Monetary The real world Conventional Wisdom about Monetary and Fiscal Policy • Monetary and fiscal policy are not tools to finetune the economy, but they can be useful in guiding it toward the macroeconomic goals. • Monetary policy is more important in the short-run because it is more flexible and less influenced by politics. • Long-run consequences of expansionary policy include: – Inflation (monetary policy) – Higher interest rates and crowding out (fiscal policy) Conventional Wisdom about Monetary and Fiscal Policy • Monetary and fiscal policy are useful to achieve high growth, low inflation, and low unemployment. Conventional Wisdom about Monetary and Fiscal Policy • Of the two, monetary policy is the more important policy for short-run stabilization. • It is more flexible and less influenced by politics than fiscal policy. Conventional Wisdom about Monetary and Fiscal Policy Option Monetary Expansionary policy Contractionary Advantages Disadvantages 1. Interest rates may fall. 2. Economy may grow. 3. Decreases unemployment. 1. Inflation may worsen. 2. Capital outflow. 3. Trade deficit may increase. 1. Helps fight inflation. 2. Trade deficit may increase. 3. Capital inflow 1. Risks recession. 2. Increases unemployment. 3. Slows growth. 4. May help cause short-run problems. 5. Interest rates may rise. Conventional Wisdom about Monetary and Fiscal Policy Option Fiscal policy Expansionary Contractionary Advantages Disadvantages 1. May increase output growth in the short run. 2. May help solve short-run political problems. 3. Decreases unemployment. 1. Budget deficit worsens. 2. Hurts country’s ability to borrow in the future. 3. Trade deficit may increase. 4. Upward pressure on interest rate, discouraging growth. 1. May help fight inflation. 2. May allow a better monetary/fiscal mix. 3. Trade deficit may decrease. 4. Interest rates may fall, stimulating investment and growth in the long run. 1. Risks recession. 2. Increases unemployment. 3. Slows output growth in the short run. 4. May help cause short-run political problems. Alternatives and Supplements to Monetary and Fiscal Policy • Monetary and fiscal policy aren’t the only policies that affect aggregate demand. • Any policy that affects autonomous spending without having offsetting effects on other expenditures can achieve the same results. Directed Investment Policies: Policy Affecting Expectations • Poor investor expectations can become self-fulfilling. • If they expect a recession, they might not invest, driving the economy into a Depression. Rosy Scenario: Talking the Economy into Fiscal Health • Gloomy government pronouncements may affect expectations and decrease investment and consumption spending. • Rosy scenario – government policy of making optimistic predictions and never making gloomy predictions. Financial Guarantees • Government guarantees or promises of guarantees can bolster business confidence. Autonomous Consumption Policy • Making credit more available to consumers can expand aggregate demand. • Economists watch indexes of consumer credit and consumer confidence to gauge the direction of the economy. Trade Policy and Export-Led Growth • Export-led growth policies – policies designed to stimulate U.S. exports and increase aggregate expenditures on U.S. goods. • Any policy that restricts imports will have the same effect on the economy. Interdependencies in the Global Economy • Any time a nation attempts to restrict imports, it is equivalent to getting another country to follow an import-led decline of its economy. Interdependencies in the Global Economy • There is a risk of retaliation whenever a nation applies trade restrictions against another nation. Exchange Rate Policies • Exchange rate policy – a policy of deliberately affecting a country’s exchange rate in order to affect its trade balance. • A low value of a country’s currency relative to other currencies encourages exports and discourages imports, and vice versa. Credibility in Aggregate Demand Policy • Effective policy must be credible policy. Rational Expectations • People generally act rationally in the sense that they are forward looking. • Rational expectations – forward-looking expectations that use available information. Rational Expectations • For example, if the public is convinced that the Fed is deadly serious about its goal of cooling down the economy, the policy will work. Uncertainty About the Effects of Policy • The central role of expectations means that there is a great deal of uncertainty in the economy. • There are a multiplicity of expectational strategies which can shift rapidly. Uncertainty About the Effects of Policy • This undermines the ability to develop deterministic models of the economy which gives the economy an unpredictability that precludes fine tuning. Uncertainty About the Effects of Policy • Depending on the beliefs that individuals have, monetary and fiscal policy will work in different ways. Policy Regimes and Expectations • A policy regime is a rule. • It is a predetermined statement of the policy that will be followed in various circumstances. Policy Regimes and Expectations • A policy is a one-time reaction to a problem. • It is chosen without a predetermined framework. Policy Regimes and Expectations • Policy regimes can help generate the expectations that make the government’s tools work. Rules versus Discretion and Credibility • The focus on credibility has led to a call for rules to guide policy rather than giving policymakers wide policy discretion. Summary • Fiscal policy is affected by the following problems: – Interest rate crowding out. – The government may not know what the situation is. – The government may not know the economy’s potential income. – Government can not respond quickly. – The size of the government debt does matter. – Economic goals may conflict. • Activist policy is now built into U.S. institutions through automatic stabilizers. • Economists’ challenge is to find the appropriate mix of policy to balance the trade-off between low unemployment, high growth, and low inflation. Summary • Three alternatives to monetary and fiscal policy are: – Directed investment policies – Autonomous consumption policy – Trade policy • Policy is a process, not a one-time event, and policy regimes are often more important than any particular policy. • Credibility can be built by establishing policy rules, but the trade-off is that policymakers will be unable to respond to an unforeseen event. Review Question 14-1 Identify three automatic stabilizers and explain how they would lessen the severity of a recession. Welfare payments, unemployment insurance, and income tax are automatic stabilizers. In the case of a recession, unemployment increases, so welfare payments and unemployment insurance increase, offsetting some of the decrease in income. With lower incomes, people pay less tax. An increase in government spending and a decrease in taxes is an expansionary policy that will increase AD. Review Question 14-2 What are the six assumptions of the AS/AD model that lead to problems with fiscal policy? 1. Financing the deficit has no effect. (It can cause crowding out). 2. The government knows what the situation is. (The government uses estimates of the mpe and other exogenous variables. 3. The government knows potential income. (There is a wide range of estimates). 4. The government has flexibility in changing spending and taxes. 5. Size of the debt doesn’t matter. 6. Fiscal policy doesn’t affect other economic goals.