Stockholders’ Equity
Presentations for Chapter 12 by Glenn Owen
Key Points
The three forms of financing and their relative importance to major
U.S. Corporations.
Distinctions between debt and equity.
Economic consequences associated with the methods used to
account for stockholders’ equity.
Rights associated with preferred and common stock and the
methods used to account for stock issuances.
Distinctions among the market value, book value, and par (stated)
value of a share of common stock.
Treasury stock.
Cash dividends and dividend strategies
followed by corporations.
Stock dividends and stock splits.
Liabilities as a Percentage
of Total Assets
Company (Industry)
General Electric (Manufacturing)
Chevron Oil (Oil drilling and refining)
Super Value (Grocery)
Tommy Hilfiger (Clothing)
Yahoo (Internet search engine)
Cisco (Internet systems)
SBC Communications (Telcom services)
Wendy’s (Restaurant services)
Bank of America (Banking services)
Merrill Lynch (Investment services)
Liabilities
/Total Assets
.88
.52
.73
.46
.16
.19
.69
.43
.93
.95
Contributed Capital as a Percentage
of Total Assets
Company (Industry)
General Electric (Manufacturing)
Chevron Oil (Oil drilling and refining)
Super Value (Grocery)
Tommy Hilfiger (Clothing)
Yahoo (Internet search engine)
Cisco (Internet systems)
SBC Communications (Telcom services)
Wendy’s (Restaurant services)
Bank of America (Banking services)
Merrill Lynch (Investment services)
Capital
/Total Assets
-.02
-.03
-.05
.25
.82
.55
.12
.04
.01
.01
Retained Earnings as a Percentage
of Total Assets
Company (Industry)
General Electric (Manufacturing)
Chevron Oil (Oil drilling and refining)
Super Value (Grocery)
Tommy Hilfiger (Clothing)
Yahoo (Internet search engine)
Cisco (Internet systems)
SBC Communications (Telcom services)
Wendy’s (Restaurant services)
Bank of America (Banking services)
Merrill Lynch (Investment services)
Retained Earnings
/Total Assets
.14
.51
.28
.29
.02
.25
.19
.62
.06
.04
Debt vs. Equity
Debt
Formal legal contract
Fixed maturity date
Fixed periodic payments
Security in case of default
No voice in management
Interest expense
Equity
No legal contract
No fixed maturity date
Discretionary dividends
Residual asset interest
Vote - board of directors
Dividends reduce RE
Distinctions Between
Debt and Equity
Interested Party
Debt
Equity
Investors /
Creditors
Lower investment risk Higher investment risk
Fixed cash receipts
Variable cash receipts
Management
Contractual future
cash payments
Dividends are
discretionary
Effects on credit
rating
Interest is tax
deductible
Effects of dilution/
takeover
Dividends are not
tax deductible
Liabilities section
of the balance sheet
Income statement
effects from debt
Stockholders’ equity
of the balance sheet
No income statement
effects from equity
Accountants/
Auditors
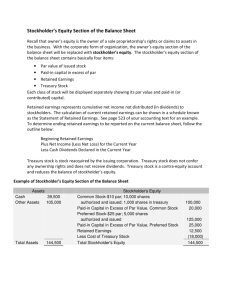
Accounting for
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock
Common stock
Treasury stock
Stock options
Dividends
Preferred Stock
Authorized, issued, and outstanding preferred
shares
Preferred dividend payments
Cumulative preferred stock
Participating preferred stock
Debt or equity?
Common Stock
Market value
Book value
Par value
Accounting for issuances
Treasury Stock
Why companies purchase treasury stock
Purchasing treasury stock
Reissuing treasury stock for more than acquisition
cost
Reissuing treasury stock for less than acquisition
cost
The magnitude of the treasury
stock account
Stock Options
Stock options as a means of compensation
Methods used to account for stock options
Are stock options compensation expense?
Dividends
Dividend strategy
Accounting for cash dividends
Stock splits
Stock dividends
Retained earnings appropriations
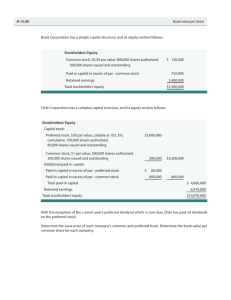
Review Problem - 2001
The company issued 1,000 shares of $1 par value
stock for $70 per share.
Cash (+A)
Common Stock (+SE)
Additional Paid-In Capital (+SE)
Issued common stock.
70,000
1,000
69,000
Review Problem - 2001
The company issued 500 shares of no par value,
$5, cumulative preferred stock for $50 per share.
Cash (+A)
Preferred Stock (+SE)
Issued preferred stock.
25,000
25,000
Review Problem - 2001
Net income during the year = $2,000
Dividends = $0
No entry
Review Problem - 2001
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2001
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh., no par value)
$25,000
Common stock (1,000 sh. @ $1 par value)
1,000
Additional paid-in capital (C/S)
69,000
Retained earnings
2,000
Total stockholders’ equity
$97,000
Note: Dividends in arrears on
cumulative preferred stock = $2,500
(500 sh. x $5/sh.)
Review Problem - 2002
The company purchased 200 treasury (common)
shares for $60 per share.
Treasury Stock (-SE)
Cash (-A)
Acquired treasury stock.
12,000
12,000
Review Problem - 2002
Net income for the year = $20,000.
Dividends = $6,600:
$5,000 for preferred shareholders [$2,500
dividends in arrears and $2,500 (500 sh. x
$5/sh.)], and $1,600 for the common
stockholders (800 outstanding sh. x $2/sh.).
The dividends were declared and paid.
Preferred Dividends (-SE)
Common Dividends (-SE)
Dividends Payable (+L)
Declared dividends.
5,000
1,600
Dividends Payable (-L)
Cash (-A)
Paid dividends.
6,600
6,600
6,600
Review Problem - 2002
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2002
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh, no par value)
$25,000
Common stock (1,000 sh. @ $1 par value)
1,000
Additional paid-in capital (C/S)
69,000
Retained earnings
15,400 *
Less: Treasury stock (200 sh. x $60/sh.) (12,000)
Total stockholders’ equity
* $2,000 + $20,000 - $6,600
$98,400
Review Problem - 2003
The company reissued 100 treasury shares for $65 each.
Cash (+A)
Treasury Stock (+SE)
Additional Paid-In Capital, T/S (+SE)
Reissued treasury stock.
6,500
6,000
500
Review Problem - 2003
The company reissued 50 treasury shares for $40 each.
Cash (+A)
Additional Paid-In Capital, T/S (-SE)
Retained Earnings (-SE)
Treasury Stock (+SE)
Reissued treasury stock.
2,000
500
500
3,000
Review Problem - 2003
The company declared a 10 percent stock dividend.
There were 950 common shares outstanding at the
time of the dividend, each with a fair value of $5.
Stock Dividend (-SE)
Common Stock (+SE)
Additional Paid-In Capital (+SE)
Declared stock dividend.
475
95
380
Review Problem - 2003
Net income for the year = $35,000
Dividends = $4,690: $2,500 to preferred shareholders
and $2,190 to common shareholders (1,095 sh.
outstanding x $2/sh.).
The dividends were declared but unpaid at year-end.
Preferred Dividends (-SE)
Common Dividends (-SE)
Dividends Payable(+L)
Declared dividends.
2,500
2,190
4,690
Review Problem - 2003
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2003
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh. no par value)
Common stock (1,095 sh. @ $1 par value)
* $1,000 + $95
$ 25,000
1,095 *
Review Problem - 2003
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2003
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh. no par value)
Common stock (1,095 sh. @ $1 par value)
Additional paid-in capital
* $69,000 + $500 - $500 + $380
$ 25,000
1,095
69,380 *
Review Problem - 2003
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2003
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh. no par value)
Common stock (1,095 sh. @ $1 par value)
Additional paid-in capital
Retained earnings:
Restricted
$30,000
Unrestricted
14,735
$ 25,000
1,095
69,380
44,735 *
$15,400 - $500 - $475 + $35,000 - $4,690
Review Problem - 2003
Pike Place Corporation
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2003
Stockholders’ Equity
Preferred stock (500 sh. no par value)
Common stock (1,095 sh. @ $1 par value)
Additional paid-in capital
Retained earnings:
Restricted
$30,000
Unrestricted
14,735
Less: Treasury stock
Total stockholders’ equity
$ 25,000
1,095
69,380
44,735
(3,000) *
$137,210
* 50 sh. x $60/sh. or $12,000 - $6,000 - $3,000
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2003, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in
Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the
express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
Request for further information should be addressed to the
Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser
may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for
distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility
for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these
programs or from the use of the information contained herein.