Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
advertisement
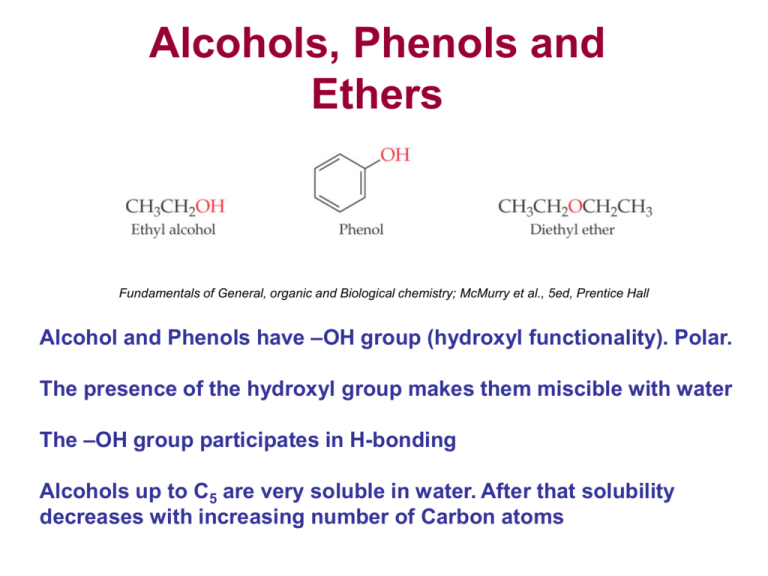
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Fundamentals of General, organic and Biological chemistry; McMurry et al., 5ed, Prentice Hall Alcohol and Phenols have –OH group (hydroxyl functionality). Polar. The presence of the hydroxyl group makes them miscible with water The –OH group participates in H-bonding Alcohols up to C5 are very soluble in water. After that solubility decreases with increasing number of Carbon atoms Alcohols Naming alcohols •Start with the parent chain and replace the hydrocarbon –e ending with –ol •Number the hydrocarbon chain. The carbon containing the –OH group should have the lowest number •Number the position of the –OH group •Number and name other side chains or functionalities using IUPAC rules 1-butanol 2-methyl-1-propanol Primary /secondary/tertiary 2-butanol A 2o alcohol (secondary) 2-methyl-2-propanol A 3o alcohol (tertiary) 1-propanol (1o alcohol) Distinguish the difference between 1o, 2o and 3o structures Nomenclature contd. In a cyclic alcohol, it is understood that the –OH group is on C-1 Alcohols What is the identitity of this molecule? 2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol Menthol Alcohols (diols, triols) •-diols or –triols mean two or three hydroxy groups in the molecule •Number the hydroxy group carbons with the lowest possible numbers •Prefix uses the full parent name, i.e butane , Ethane-1,2-diol (ethylene glycol) Propane-1,2,3-triol (glycerol) Properties of alcohols • Alcohols are polar compounds because the –OH group participates in H-bonding • Smaller straight chain alcohols are usually liquids • Alcohols such as 1-heptanol (C8) tends to act more like alkanes • Diols and triols have higher b.p’s and are more water soluble Reactions of alcohols • Dehydration: Loss of water to form an alkene. Occurs in presence of acid catalyst • Oxidation: In presence of oxidizing agents alcohols get oxidized to carbonyl compounds Dehydration reaction Fundamentals of General, organic and Biological chemistry; McMurry et al., 5ed, Prentice Hall Dehydration of alcohols Hint- More substituted alkene will be major product Dehydration of alcohols Predict the starting alcohol in the following: ? ? Write all possible structures then keep the most substituted ones! Oxidation *Note- Depending upon the alcohol and reaction conditions a different types and mixtures of carbonyl products may be formed Image Adapted from http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/Carey5th/Ch15/ch15-4-6.html Oxidation of alcohols Secondary alcohols get converted to ketones upon oxidation but no further Q: What is oxidation reaction for a tertiary alcohol Image Adapted from http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/Carey5th/Ch15/ch15-4-6.html Oxidation of alcohols ? ? Hydroxybenzene (a.k.a Phenol) • Have been used as an antiseptic •Many OTC sore throat medications contain substituted phenols •Most phenols are somewhat water soluble •BHA and BHT are often used as food preservatives BHA BHT Acidity of phenols Alcohols and Phenols are weakly acidic They dissociate in water to give the alkoxide or the phenoxide anion Phenols • Methanol and Ethanols are as acidic as water, i.e weak acids, Ka = 10-15 • Their anion (alkoxide ion) is a strong base, similar to the hydroxide ion • Phenols are more acidic than alcohols • Phenolic Ka is 1.0X 10-10





