ad0407
advertisement

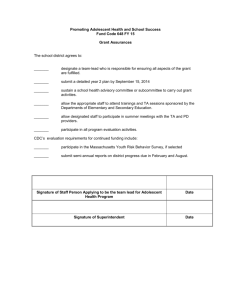
Adolescent Substance Abuse Lori Holleran, Ph.D., CISW, ACSW The University of Texas at Austin School of Social Work Experimentation “The majority of adolescents who use substances do/ do not develop a substance use disorder.” (circle one) (Newcomb, 1995) BIO-PSYCHO-SOCIALSPIRITUAL MODEL • Bio: genetics, tolerance, cravings, brain chemistry, blackouts • Psycho: low esteem & grandiosity, profound aloneness • Social: Disconnected, better or worse than, family disruption • Spiritual: “Hole inside,” lack of meaning, lack of belief in good Developmental Issues Puberty Individuation Peers as primary reference group Emergence of sexual awareness and identity Increased cognitive powers, formal operational thought (e.g., logic, future orientation, reasoning) Imaginary audience (self-centered and self-critical) Risk Factors Temperament Cognitive functioning Genetics Peer influence Parental use Divorce Discord Nondirectiveness; inconsistency Lack of closeness; bonding Life events Socio-economic Status Resiliency and Protective Factors • Mediators of risk: – – – – – – – (Glantz & Sloboda, 1999) Intelligence; Problem solving Social Skills Positive self esteem Supportive family/community Affect regulation Commitment/bonds at school Religious affiliation/activity Warning Signs: family substance abuse truancy or sudden grade drop change in peer group; quitting important activities legal difficulties drug-related paraphernalia unknown source of income physical changes "hanging out" in strange places Assessment/ Screening Tools (1) CAGE: Have you tried to Cut down? Are you Annoyed by others’ complaints about your use? Do you feel Guilty about use? Do you have an Eye-opener? (Ewing, 1984) A fast, easy initial screening method. More Assessment/ Screening Tools (2) MAST Michigan Alcohol Screening Test (Miller, 1976; Selzer, Vinokur, & Van Rooijen, 1974) (3) SASSI (Miller, 1990) (4) ASI (McLellan et al., 1980; McLellan et al., 1985) (5) TWEAK (Russell, 1994) Interviewing Informants Gather information on questions the adolescent was unable to answer or created confusion in your mind. Try to determine how the informant has interacted with the problems. How well equipped is the informant to help with the adolescent’s problems? Provide the parent with a review of your recommendations. What are the Stages of Change? Pre-contemplation “What problem?” Contemplation “Okay, so maybe I might have a problem. But then again…” Determination “I need to do something about this.” Action “This is what I plan to do…” Maintenance “I’d like to keep this up.” Relapse “I’ll have to get back on track.” Source: Miller, W. & Rollnick, S. (1991) Motivational Interviewing. Prochaska, J.O. and DiClemente,C.C. (1982), Transtheoretical Therapy in Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice, 19, 276-288. Adolescent • Confront & expect power struggle. • Educate on the disease model & emphasize here and now • Referral to young peoples groups • Goal: progress Adult • Confront denial • Educate on the disease model • Counseling based on 12Step model • Referral to AA, NA, CA, etc. • Goal: Lifetime abstinence Effective Work with Adolescent Substance Abusers Form honest, trustworthy connection Power struggles are normative Set boundaries, rules, structure Stay aware of developmental stages Expect limit testing- be firm and loving Diffuse/avoid lesser issues Be human, have fun & laugh at self (Johnson, 1999) How do you facilitate an adolescent’s needs for: POWER NON-CONFORMITY FREEDOM STRUCTURE PEER ACCEPTANCE (Caviola & Caviola, 1989) Families and Substance Abuse Boundaries: Rules & Roles Communication styles Homeostasis Family Disease “Don’t feel, Don’t think, Don’t talk” (Claudia Black) Roles: Hero, Scapegoat, Mascot, Lost Child, Chief Enabler. (Wegsheider-Cruse model) Family Roles Sharon Wegscheider (1981) HERO SCAPEGOAT MASCOT LOST/FORGOTTEN Summary… Build relationships! Remember the Bio-psycho-social model. View adolescents in CONTEXT. Don’t reinvent the wheel. Use a positive, strengths focus rather than pathology and scare tactics. Where to Get More Information lorikay@mail.utexas.edu http://www.niaaa.hih.gov/publications/ http://www.nida.nih.gov http://www.health.org http://www.alcoholics-anonymous.org/ http:///www.nacoa.net/ http://www.samhsa.gov/ PRS Confidential Employee Assistance Program (EAP): 1(800) 343-3822 or through INTRANET: Click on ‘Human Resources’ then click on ‘Other Resources’