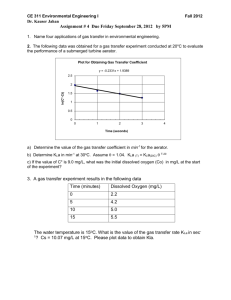
i. Content knowledge
advertisement

Student Seminar for HK Institute of Education From Understanding to Practice Curriculum Reform and Teachers 2 Oct 2002 Dr. KK Chan, Chief Executive Curriculum Development Institute Education Department Components of presentation A. What is the current curriculum reform about? B. Why are professional development (PD) & teachers important to the reform? C. How to prepare ourselves for a future career in teaching? Understanding and reflecting on what we need Understanding and reflecting on how we learn, unlearn and relearn D. Curriculum Development in Hong Kong : Building on strengths A. What is the current reform about? Why changes? • • • • • • • • Knowledge-based society and economy Rising need for moral considerations Fast social, environment, cultural, political and technological changes and their impact on moral values Impermanent knowledge Globalization Interdependent but competitive world Impact of information technology Increasing civic participation in government Policy recommendations: Education Commission report (2000) Learning to Learn Report (CDC, 2001) Basic Education Curriculum Guide (CDC, 2002) replacing 1993 version 8 KLA & GS Curriculum Guides (CDC, 2002) – learning targets & contents, core, extension, pedagogy, exemplars Seven learning goals for 10 year strategic plan (2001-2011) (CDC, 2001) Short-term targets 2001-2006 (1) (interim review in 2006) 1. Four key tasks Reading to Learn Moral & Civic Education IT for Interactive Learning Project Learning Short-term targets 2001-2006 (2) (interim review in 2006) 2. Critical thinking, creativity, and communication in 8 Key Learning Areas 3. Connect “central curriculum” in 8 KLA Guides with school-based curriculum development at different levels (flexibilities and balance) References: Key Learning Area Curriculum Guides (CDC, 2002) http://www.cdc.org.hk; http://cd.ed.gov.hk) Medium-term targets 2006-2011 i. Continue to improve learning & teaching based on results of review in 2006 ii. Adopt latest curriculum framework with more school-based curriculum development iii. Smooth interface with new senior secondary education Diagrammatic Representation of English Language Education KLA Curriculum Framework English Language Education Curriculum 9 Generic Skills Interpersonal Knowledge Experience Flexible and diversified modes of curriculum planning + Effective learning, teaching and assessment Overall Aims and Learning Targets of English Language Education Values and Attitudes Strands Diagrammatic Representation of Mathematics Education KLA Curriculum Framework Mathematics Curriculum Generic Skills Learning Dimensions effective linkage of learning, teaching and assessment Overall Aims and Learning Targets of Mathematics Values & Attitudes Diagrammatic Representation of PSHE KLA Curriculum Framework Sanctity of life, truth, aesthetics ... Equality, kindness, benevolence… optimistic, participatory, critical ... Personal & Social Development Time, Continuity & Change Culture & Heritage Place & Environment Resources & Econ. Activities Social Systems & Citizenship critical thinking skills, self management skills, problem solving skills, numeracy skills, collaboration skills, communication skills, creativity, study skills, IT skills Diagrammatic Representation of Science Education KLA Curriculum Framework Strands Learning in science should centre on scientific investigation that develops understanding of scientific concepts and principles, and the interconnections between science, technology and society. Existing 15 TE Subjects Framework used by Technology Education TE Learning Diagrammatic Representation of Arts Education KLA Curriculum Framework Overall Aims of Arts Curriculum Learning Targets Developing Creativity & Imagination Developing Skills & Processes Cultivating Critical Responses Understanding Arts in Context Learning Objectives Generic Skills *KS1 *KS2 *KS3 *KS4 Visual Arts Media Arts Students develop skills, knowledge and positive attitudes in the arts through Learning Activities by means of Effective Learning & Teaching and Assessment Dance Drama Music Values and Attitudes Other Emerging Art Forms Diagrammatic Representation of Physical Education KLA Curriculum Framework B. Why are professional development (PD) & teachers important to the reform? (1) Classroom practice most effective amongst factors affecting effective schools (Hattie, 1992) For every $500 spent, increasing teacher education more effective than lowering pupilteacher ratio, increasing teacher salaries, teacher experience (Greenwald, et al 1996) · B. Why are professional development (PD) & teachers important to the reform? (2) The “content” and “research-based knowledge on how students learn” (deep understanding) in PD have more long-lasting effect in teacher practice than promoting specific pedagogical practice first and different PD format (Ingvarson, 2002) Role-modelling of teachers & students’ time Professional responsibility Other reform contexts in HK • • • • • • Workload of teachers Physical setting of schools On-going educational reviews, e.g. medium of instruction School-based management Diversification of school funding systems Political, economic & social environment C. How to prepare ourselves for a future career in teaching? 1. Understanding & reflecting on what we need 2. Understanding how we learn, unlearn and relearn 1. Understanding & reflecting on what we need i. ii. Content knowledge Pedagogical & content-pedagogical knowledge and skills iii. Assessment including feedback iv. Central curriculum & flexibilities for schoolbased curriculum development v. Educational values, principles, theoretical perspectives i. Content knowledge (e.g. Eng, Chin, Maths, Arts, General Studies, PE, Moral & civic education) • Is the content knowledge of the KLA relevant, update for teaching & learning of the latest curriculum framework? • How much should I know? • How to keep abreast of it? • How could I broaden my horizon in general? ii. Pedagogical & content-pedagogical knowledge & skills (1) • What are the learning & teaching strategies of achieving the learning targets/objectives in KLA/subjects I am going to teach? • How to develop critical thinking, creativity and communication skills of students? • How could project learning, reading to learn, etc. help achieve student learning? ii. Pedagogical & content-pedagogical knowledge & skills (2) • What are the learning problems of achieving the learning targets/objectives? • Are theories and principles I’ve learned working in HK contexts, e.g. our students, our classroom? • What works with me? • How could my work be improved? iii. Assessment (including feedback) • • • • How could assessment help learning? Do I give meaningful feedback to help students improve learning? What is the purpose of assessment change? What assessment change would take place at school level and system level in the next five years? How they different from my experiences in the past? Why the change, & how to cope? iv. Central curriculum & flexibilities for school-based curriculum development • • • • What is the purpose for flexibilities & professional judgement? What are the purpose and different modes of curriculum planning, learning & teaching strategies? How to cater for student diversity? Am I competent and confident? v. Educational values, principles, theoretical perspectives • • • Do I share them? How do I know? Would I regard moral & civic education as a responsibility of every teacher? When & how do I use them for improving practice & reflection? v. Educational values, principles, theoretical perspectives • What perspectives are affecting curriculum, learning & teaching, assessment and other educational policies above? Philosophy (aims of education, views of knowledge) Psychology (of learning, moral development) Sociology Curriculum Studies, School management & organisational theories Policy studies and administration Teachers’ professional development & life-long learning 2. Understanding & reflecting on how we learn, unlearn, and relearn Theoretical knowledge, principles in literature, research, lectures, from taught courses, reading Learning through practice & practical knowledge – – Changing theory into practice which works Practices which work A teacher: 反思過往自己在校內只重實 務,忽略理念的情況,期望 將來教得更有效。 Personal construction of knowledge from theory, practice, collaboration, sharing & talking, reflections, practice which inform principles & theories A teacher: 我很希望學生能真正有機會實踐全方位學習 ,因為更具真實性、震撼性、影響性,讓學 生不只是學習到在學校環境內的知識,或只 是用模擬、假設性的情景,靠學生自己聯想 。我相信這樣學生會多留意自己身邊及社會 各樣事物,加強他們的觀察力和好奇心,讓 學生領悟到知識不只是在學校內,其實身邊 無時無刻都有東西可以學習及留意,是很切 身的。 Connecting individual learning with organisational learning 透過與其他老師(包括同科和不同科 目的老師)的交談和討論,我所學習 到的也不少。(當然與他們所建立的 友誼更是一項重大的收獲!) D. Curriculum Development in Hong Kong: Building on our strengths Eleven Essential Themes (Basic Education Curriculum Guide, CDC 2002) 1. Overview of the Curriculum Reform – Reflecting on strengths and getting ready for action 2. Whole-school curriculum planning – Achieving learning goals and short-term targets of school curriculum development 3. Four key tasks – Achieving learning to learn 4. Effective learning and teaching – Acting to achieve 5. School policy on assessment – Changing assessment practices Eleven Essential Themes (Basic Education Curriculum Guide, CDC 2002) 6. Life-wide learning – Enriching learning through authentic experiences 7. Quality learning and teaching resources and school library development – Bringing about effective learning 8. Meaningful homework – Consolidating learning , deepening understanding and constructing knowledge 9. Interfaces at various levels of schooling – Supporting transition What are our strengths and achievements? Strengths & Achievements 1. Maintaining strengths recognised in BECG e.g. value for effort 2. Changing discourse from focus on “teaching” to “learner” & “learning” 3. Curriculum is not only document, acceptance of flexibility 4. More effective practices in schools, obvious in confidence to speak, reading & writing 5. Have “moved” schools, 30% vs 10% 6. Enhance evidence-based & reflective culture 7. Over-subscription PD programmes & projects 8. CDC/HKEA “one document” & “one committee” approach, teacher/SB assessment What is my mission of joining the teaching profession? A teacher: 可能是中國人的文化 吧! 好的東西不好意思說出來, 免得被人覺得自己自大囂張。而 不好的東西又怕與人分享,免得 被人覺得自己無能。 在演講的最末,有學生問楊振寧, 他認為一生人最大的成就是甚麼? 楊振寧回答:是幫助改變了中國 人覺得不如人的思想