Mason Carpenter, Talya Bauer, and Berrin Erdogan
advertisement

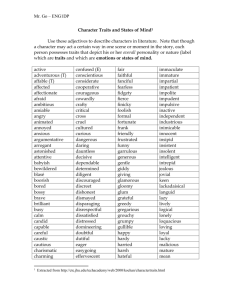
Principles of Management 2.0 Mason Carpenter, Talya Bauer, Berrin Erdogan, and Jeremy Short ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 1 Chapter 9 Leading People and Organizations Define what leadership is and identify traits of effective leaders Describe behaviors that effective leaders demonstrate Specify the contexts in which various leadership styles are effective Explain the concepts of transformational, transactional, charismatic, servant, and authentic leadership Develop your own leadership skills ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 2 Leadership and the P-O-L-C Framework ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 3 Leadership • Leadership in an organization develops the vision, creates the environment, and inspires individuals and the team to pursue goals and consistently achieve results substantially greater than they would on their own. • This is achieved within the framework of the organization’s values and aimed at the realization of the organization’s vision. Leadership Knowledge & Skills Wisdom About Human Nature Fundamental Traits • • • • Characters Learning Self-esteem Courage to lead • Transformational • Positive attitude • Energy Leadership Attributes • Strong personal convictions • Visionary • Emotional bonds • Inspirational • Team oriented • Risk takers • Drive to excel Fundamental Traits • Personal character: Beliefs and values that guide actions and reflect positively on yourself and your company. • Willingness to learn: The ability and desire of an individual to learn continuously, as influenced by intense curiosity, intellectual capability, and humility. • Self-esteem: Truly knowing yourself, being confident, and feeling comfortable with who you are. • Desire and courage to lead: I want to lead, I will lead, and I accept the “reality” of the responsibility and accountability that accompanies leadership. • Transformational: The desire, courage, and capacity to initiate and implement innovative change. • Positive attitude: An uplifting and encouraging mindset that influences how we perceive & respond to ourselves, others, & the world. • Energy: The physical, emotional, spiritual, & intellectual power that fuels & is fueled by inner desires & propels the pursuit of leadership. Leadership Attributes • • • • • • • Strong personal convictions Visionary Emotional bonds Inspirational Team oriented Risk takers Drive to excel Knowledge and Skills • Wisdom about human nature: Insight into what makes people tick, comprehending the diversity, & the ability to act accordingly. • Communication: The skill to listen effectively to acquire and disseminate knowledge and ideas, speak persuasively, write clearly, and read rapidly with high comprehension. • Business orientation: Understanding external factors and aligning resources to attain a balanced scorecard. • Building trust: The ability to create a mutual sense of reliability and assurance in relationships based on competence and personal character. • Empowerment: Creating and maintaining an environment where people want to, are enabled, and feel compelled to take action—with personal accountability for results. Knowledge and Skills • Team building: Creating a group of individuals who have a shared mission, common approach, and mutual accountability. • Nurturing: An attitude of caring and promoting development of individuals and teams to ensure their success. • Creating a vision: The ability to consider multiple, seemingly unrelated data points then developing and articulating a motivational view of the future that is not limited by today’s reality. • Dealing with ambiguity: Ability to balance things that are seemingly at odds, through exploration and discovery, without a given set of rules. • Decisiveness: The ability to decide, in a timely manner, and imperfect data. • Change management: The skill to cultivate successful change. Leadership is the act of influencing others to work toward a goal Formal leaders hold a position of authority and may utilize the power that comes from their position, as well as their personal power to influence others Informal leaders are without a formal position of authority within the organization but demonstrate leadership by influencing others through personal forms of power ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 10 Who Is a Leader? Traits Associated with Leadership ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 11 Big 5 Personality Traits ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 12 Discussion • What traits are evident in leaders you admire? Are they consistent with the traits discussed in this chapter? If not, why is this person effective despite the presence of different traits? • Can the findings of trait approaches be used to train potential leaders? Which traits seem easier to teach? Which are more stable? • How can organizations identify future leaders with a given set of traits? Which methods would be useful for this purpose? • What other traits can you think of that would be relevant to leadership? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 13 What Do Leaders Do? Behavioral Approaches to Leadership Task-oriented leader behaviors involve structuring the roles of subordinates, providing them with instructions, and behaving in ways that will increase the performance of the group *Task oriented behaviors are directives given to employees to get things done and to ensure that organizational goals are met People-oriented leader behaviors include showing concern for employee feelings and treating employees with respect *People oriented leaders genuinely care about the well being of their employees and they demonstrate their concern in their actions and decisions ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 14 It is better to lead from behind and to put others in front, especially when you celebrate victory when nice things occur. You take the front line when there is danger. Then people will appreciate your leadership. Nelson Mandela ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 15 Taoism on Leadership When the Master governs, the people are hardly aware that he exists . ... Next best is a leader who is loved. Next, one who is feared. The worst is one who is despised. If you don't trust the people, you make them untrustworthy. The Master doesn't talk, he acts. When his work is done, the people say, “Amazing: we did it, all by ourselves.” -- Tao Te Ching Chapter 17 – Translated by Stephen Mitchell 16 Leader Decision Making Autocratic decision making • Leaders make the decision alone without necessarily involving employees in the decision-making process Democratic decision making • Employees participate in the making of the decision Laissez-faire decision making • Leaders leave employees alone to make the decision; the leader provides minimum guidance and involvement in the decision ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 17 Styles of Leadership and Influence Styles of Leadership Authoritarian Leadership High Democratic Leadership Moderate Laissez-Faire Leadership Low Leader influence Peter G. Northouse, Introduction to Leadership Concepts and Practice, Sage Publications, Inc., 2009. Core Leadership Skills • Conceptual skills – Creating visions – Strategic planning – Problem solving • Interpersonal skills – Being socially perceptive – Showing emotional intelligence – Managing interpersonal conflict • Administrative skills – Showing technical competence – Managing resources – Managing people Peter G. Northouse, Introduction to Leadership Concepts and Practice, Sage Publications, Inc., 2009. Democratic Decision-Making Style Google co-founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, are known for their democratic decision-making styles Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Schmidt-Brin-Page-20080520.jpg ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 20 Discussion • Give an example of a leader you admire whose behavior is primarily task-oriented, and one whose behavior is primarily people-oriented. • What are the limitations of autocratic decision making? Under which conditions do you think autcratic style would be more effective? • What are the limitations of democratic decision making? Under which conditions do you think democratic style would be more effective? • What are the limitations of laissez-faire decision making? Under which conditions do you think laissez-faire style would be more effective? • Examine your own leadership style. Which behaviors are you more likely to demonstrate? Which decision making style are you more likely to use? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 21 Contingency Approaches to Leadership The Role of Context Fiedler’s Contingency Theory Situational Leadership Path-Goal Theory of Leadership ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Vroom and Yetton’s Normative Decision Model 22 Fiedler’s Contingency Theory ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 23 Situational Leadership • Leaders choose from four basic situational leadership styles as defined by Kenneth Blanchard and Paul Hersey. The style that a leader chooses is determined by situational factors such as employee readiness. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 24 Situational Leadership Styles Situational Leadership II Model Development of the Individual Follower Readiness Competence Level (Low) Competence (Low) Competence (Moderate to High) Competence (High) Commitment (High) Commitment (Low) Commitment (Variable) Commitment (High) Directing Behavior Coaching Behavior Supporting Behavior Delegating Behavior Recommended Leader Style Situational Leadership Theory helps leaders match their style to follower readiness levels. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 27 Path-Goal Theory of Leadership Influenced by Expectancy Theory of Motivation Their effort will lead to high performance Their high performance will be rewarded The rewards they will receive are valuable to them Employees are motivated if confident… ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 28 Four Leadership Styles Directive Supportive Participative Achievement Oriented ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 29 Predictions of Path-Goal Theory ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 30 Vroom and Yetton’s Normative Decision Model The decision tree approach is a guide leaders can use to decide how participative they should be given decision environment characteristics ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 31 The Decision Tree Leadership Styles based on participation of group members in decision making: 1. Decide 2. Consult Individual 3. Consult Group 4. Facilitate 5. Delegate ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 32 Discussion • Do you believe that the least preferred coworker technique is a valid method of measuring someone’s leadership style? Why or why not? • Do you believe that leaders can vary their style to demonstrate directive, supportive, achievement-oriented and participative styles with respect to different employees? Or does each leader tend to have a personal style that he or she regularly uses toward all employees? • What do you see as the limitations of the Vroom-Yetton leadership decision-making approach? • Which of the leadership theories covered in this section do you think are most useful, and least useful, to practicing managers? Why? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 33 GM CEO, Mary T. Barra (link) Sheryl Sandberg: Why we have too few women ... - TED.com Facebook COO ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 34 Transformational Leadership *Employees focus on company’s well-being rather than individual pursuits Transactional Leadership *Employees demonstrate the right behaviors because the leader provides resources in exchange. ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 35 Transformational leaders lead employees by aligning employee goals with the leader’s goals Inspirational motivation Intellectual stimulation Individualized consideration Charisma Transformational Leaders ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 36 Transformational leaders rely on their charisma, persuasiveness, and personal appeal Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, the founder and first president of the Turkish Republic Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ataturk_and_flag_of_Turkey.jpg ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 37 Methods Used By Transactional Leaders ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 38 Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory High quality LMX relationships have mutual respect between the leader and the followers Low quality LMX relationships portray lower levels of trust and respect between leaders and followers ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 39 According to the Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) approach, the unique, trust-based relationships leaders develop with employees is the key to leadership effectiveness ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 40 Servant Leadership Defines the leader’s role as serving the needs of others The primary mission of the leader is to develop employees and help them reach their goals Servant leaders put their employees first, understand their personal needs and desires, empower them, and help them develop in their careers ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 41 Servant Leadership has some overlap with other leadership approaches but there are some differences… Ethics Self-Sacrifice Community Development ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 42 Authentic Leadership Leaders are self aware Not afraid to act the way they are Possess high levels of personal integrity Leaders are introspective Understand where they are coming from Retain a thorough understanding of their own values and priorities ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 43 Howard Schultz, the founder of Starbucks coffee houses Witnessing his father’s losing jobs due to medical problems, he became passionate about a company’s need to care for its employees. Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/archive/a/ae/200 81006001508!Howard-Schultz-Starbucks.jpg ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 44 Discussion • What are the characteristics of transformational leaders? Are transformational leaders more effective than transactional leaders? • What is charisma? What are the advantages and disadvantages of charismatic leadership? Should organizations look for charismatic leaders when selecting managers? • What are the differences (if any) between a leader having a high quality exchange with employees and being friends with employees? • What does it mean to be a servant leader? Do you know any leaders whose style resembles servant leaders? What are the advantages of adopting such a leadership style? • What does it mean to be an authentic leader? How would such a style be developed? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 45 Developing Your Leadership Skills Steps to Develop Your Charismatic Leadership Skills Have a vision Tie the vision to history Watch your body language Make sure that employees have confidence in themselves Challenge the status quo ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 46 Develop Your Servant Leadership Skills Ask what you can do for your employees Help employees reach their goals Be humble Be open with your employees Find ways of helping the external community ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 47 Develop Your Authentic Leadership Skills Understand Your History Take Stock of Who You Are Now Reflect on Your Successes and Challenges Make Integrity a Priority Understand the Power of Words ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 48 Discussion • What is the connection between leadership and ethics? • Do you believe that ethical leaders are more successful in organizations? • Have you ever had an authentic leader? What did this person do that made you consider him or her to be authentic? How effective was his or her leadership? ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 49 http://faculty.washington.edu/janegf/level5leadership.htm Source: Good to Great: Why Some Companies Make the Leap...And Others Don't by Jim Collins Level 5 Leadership The great irony is that the animus and personal ambition that often drives people to become a Level 4 leader stands at odds with the humility required to rise to Level 5. Jim Collins , "Level 5 Leadership: The Triumph of Humility and Fierce Resolve (HBR Classic)", Harvard Business Review, Jul 01, 2005 ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 51 5 Attributes for The Level 5 Leader • They are self-confident enough to set up their successors for success. • They are humble and modest. • They have "unwavering resolve." • They display a "workmanlike diligence - more plow horse than show horse." • They give credit to others for their success and take full responsibility for poor results. They "attribute much of their success to 'good luck' rather than personal greatness." Not by Level 5 Alone • First Who, Then What: Get the right people on the bus, then figure out where to go. Finding the right people and trying them out in different positions. • Confront the Brutal Facts: The Stockdale paradox - Confront the brutal truth of the situation, yet at the same time, never give up hope. • Hedgehog Concept: Three overlapping circles: What lights your fire ("passion")? What could you be best in the world at ("best at") What makes you money ("driving resource")? • Culture of Discipline: Rinsing the cottage cheese. • Technology Accelerators: Using technology to accelerate growth, within the three circles of the hedgehog concept. • The Flywheel: The additive effect of many small initiatives; they act on each other like compound interest. Hearing the Truth • “Honesty is very expensive gift do not expect it from cheap people” - Warren Buffett • Creating a climate where truth is heard involves four basic practices: – – – – Lead with questions, not answers. Engage in dialogues and debate, not coercion. Conduct autopsies, without blame. Build red flag mechanisms that turn information into information that cannot be ignored. • Additional skills: – – – – Hide your preferences at the beginning of an initiative Let one individual/group be a sounding board or even play devil advocate. Don’t kill the messenger Flattering is poisonous Jim Collins , "Level 5 Leadership: The Triumph of Humility and Fierce Resolve", Harvard Business Review, Jul 01, 2005 55 Hedgehog What weConcept want to do Learn to do this better Learn to monetize Learn to say “No!” What we do well What we can be paid to do Self-Analysis: Individual (Company) Calling (Passion) What were you born to do? What you good at? Career (Niche, Strength) (What do you want to do?) What will people pay you to do? Source: Creative Confidence & Job (Revenue) http://nowpossible.com/2010/09/29/revisiting-good-to-great/ 58 Good to Great (Hedgehog) http://www.turnaround.org/Publications/Articles.aspx?objectID=1623 60 Strength-Based Leadership http://businessjournal.gallup.com/content/113956/strengths-leadership.aspx#2 • • • • • • • • • • Leader vs. Manager The manager administers, the leader innovates. The manager copies, the leader is an original. The manager maintains, the leader develops. The manager focuses on systems and structure, the leader focuses on people. The manager relies on control, the leader inspires trust. The manager has a short range view, the leader has a long range perspective. The manager asks how and when, the leader asks what and why. The manager has eyes always on the bottom line; the leader's eyes are on the horizon. The manager accepts the status quo, the leader challenges it. The manager does things right, the leader does the right thing. Warren Bennis, On Becoming A Leader, Basic Books, Fourth edition, March 2, 2009. The Truth About Managing People 2nd Edition Stephen Robbins • • • • • • • • PART I THE TRUTH ABOUT HIRING Truth 1 Forget Traits; It’s Behavior That Counts Truth 2 Realistic Job Previews: What You See Is What You Get Truth 3 Tips for Improving Employee Interviews Truth 4 Brains Matter; or When in Doubt, Hire Smart People Truth 5 Don’t Count Too Much on Reference Checks Truth 6 When in Doubt, Hire Conscientious People! Truth 7 Hire People Who Fit Your Culture: My “Good Employee” Is Your Stinker! • Truth 8 Manage the Socialization of New Employees http://www.pearsoned.co.uk/bookshop/detail.asp?item=100000000263509&tab=Table%20of%20Contents 63 • • • • • • • • • • • PART II THE TRUTH ABOUT MOTIVATION Truth 9 Why Many Workers Aren’t Motivated at Work Today Truth 10 Happy Workers Aren’t Necessarily Productive Workers! Truth 11 Telling Employees to “Do Your Best” Isn’t Likely to Achieve Their Best Truth 12 Not Everyone Wants to Participate in Setting Their Goals Truth 13 Professional Workers Go for the Flow Truth 14 When Giving Feedback: Criticize Behaviors, Not People Truth 15 You Get What You Reward Truth 16 It’s All Relative! Truth 17 Ways to Motivate Low-Skill, Low-Pay Employees Truth 18 There’s More to High Employee Performance Than Just Motivation ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 64 • • • • • • • • • • PART III THE TRUTH ABOUT LEADERSHIP Truth 19 The Essence of Leadership is Trust Truth 20 Experience Counts! Wrong! Truth 21 Most People THINK They Know What Good Leaders Look Like Truth 22 Effective Leaders Know How to Frame Issues Truth 23 You Get What You Expect Truth 24 Charisma Can Be Learned Truth 25 Make Others Dependent on You Truth 26 Adjust Your Leadership Style for Cultural Differences or When in Rome. . . Truth 27 When Leadership ISN’T Important ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 65 • • • • • • • • • • • • PART IV THE TRUTH ABOUT COMMUNICATION Truth 28 Hearing Isn’t Listening Truth 29 Choose the Right Communication Channel Truth 30 Listen to the Grapevine Truth 31 Men and Women DO Communicate Differently Truth 32 What You Do Overpowers What You Say PART V THE TRUTH ABOUT BUILDING TEAMS Truth 33 What We Know That Makes Teams Work Truth 34 2 + 2 Doesn’t Necessarily Equal 4 Truth 35 One Bad Apple Spoils the Barrel Truth 36 We’re Not All Equal: Status Matters! Truth 37 Not Everyone Is Team Material ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 66 • • • • • • • • • • • • PART VI THE TRUTH ABOUT MANAGING CONFLICTS Truth 38 The Case FOR Conflict Truth 39 Beware of Groupthink Truth 40 How to Reduce Work-Life Conflicts Truth 41 Negotiating Isn’t About Winning and Losing PART VII THE TRUTH ABOUT DESIGNING JOBS Truth 42 Not Everyone Wants a Challenging Job Truth 43 Four Job-Design Actions That Will Make Employees More Productive PART VIII THE TRUTH ABOUT PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Truth 44 Annual Reviews: The Best Surprise is NO Surprise! Truth 45 Don’t Blame Me! The Role of Self-Serving Bias Truth 46 The Case for 360-Degree Feedback Appraisals: More IS Better! ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 67 • PART IX THE TRUTH ABOUT COPING WITH CHANGE • Truth 47 Most People Resist Any Change That Doesn’t Jingle in Their Pockets! • Truth 48 & Truth 49 Use Participation to Reduce Resistance to Change • PART X SOME FINAL THOUGHTS ABOUT MANAGING BEHAVIOR • Truth 50 First Impressions DO Count! • Truth 51 People Aren’t Completely Rational: Don’t Ignore Emotions! • Truth 52 Employee Turnover Can Be a Good Thing • Truth 53 Beware of the Quick Fix ©2013 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. 68